Chmod Give All Permissions To Everyone
The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode.

Chmod give all permissions to everyone. To set all permission bits on (anyone can read/write/execute):. Or give all permissions on this file?. The second way to modify permissions with the chmod command is to use a number to specify each set of permissions for the file.
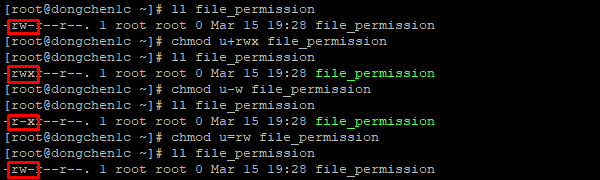
To remove write permission from orgcht:. To give owner, group and everyone else read and write permission on file. To give the owner all permissions and world execute you would type chmod 701 filename.
The resulting permissions would be like this:-rwxrwx--x 1 abhi itsfoss 457 Aug 10 11:55 agatha.txt. And actually, in the interest of full disclosure, if you fail to specify to whom you want the permissions to apply, chmod will automatically apply them to all users. Users can simply modify file permissions using the chmod (change mode) command.
Here are some common examples of settings that can be used with chmod:. G+w — adds write access for the group. To change the permissions of a file, one uses the chmod command, with the following syntax:.
So the following chmod command line would also result in. $ chmod -R 0755 directoryNameHere However, if you need to apply conditional file permissions recursively, you need to use combination of the find and chmod command. Chmod command is followed by which level user i.e.
Chmod og+rx prog* - Adds read and execute permissions for group and others to all files which contain "prog" as the first four characters of their name. We can combine references to set permissions all at once. Characters 8-10 for all others.
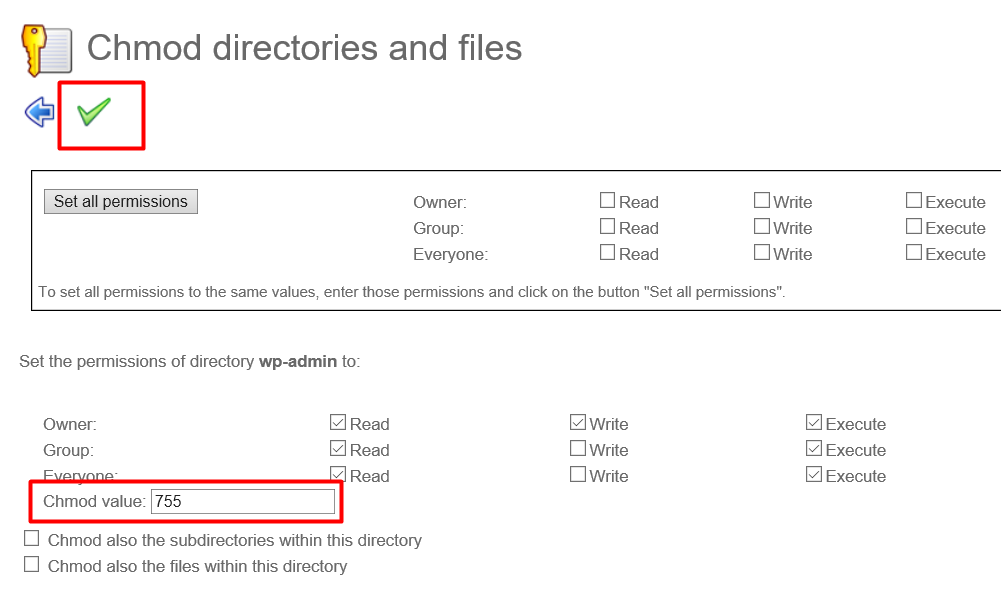
Everyone can read, only owner can write. To give write permissions to everyone, execute:. Assume you want to find a folder’s current permissions and then change them to 755.
The name speaks for itself. Chmod is a command to change permission of a file. The second way is through terminal.
Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty Images. Chmod a+r sample.f - Adds read permission for all users to the file sample.f. + for adding and – for removing.
For example, we can make our document read-only for every user and group with:. If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command. Changing permissions with chmod.
Chmod -R a+rwX directory/ as root. It can be used for individual files or it can be run recursively with the -R option to change permissions for all of the subdirectories and files within a directory. % chmod u+rw who.out.
Using letters is easier to understand for most people. To change directory permissions for everyone, use “u” for users, “g” for group, “o” for others, and “ugo” or “a” (for all). To turn on read, write, and execute permissions, and turn off the set-user-ID bit, set-group-ID bit, and sticky bit attributes.
If you want to set permissions on all files to a+r, and all directories to a+x, and do that recursively through the complete subdirectory tree, use:. Sudo chmod 777 pathtofile/folder Eg :sudo chmod -R 777 /var/www/smarttips/ sudo chmod -R 777 /var/www/smarttips/index.php. The highly productive Linux system offers various levels of permission to ensure that the user has enough ways to interact with files and directories.
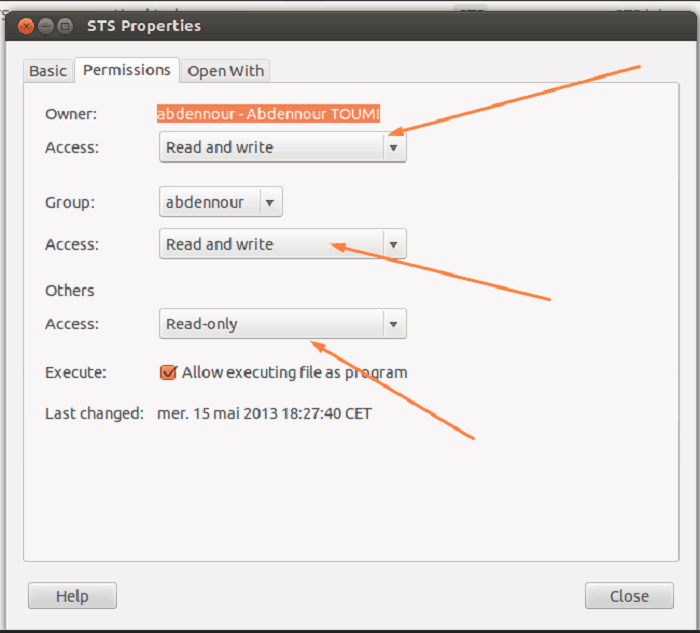
Chmod a=r foldername to give only read permission for everyone. This would give you as the owner read, write and execute permissions, and everyone else read and execute permissions. To make file readable, writable and executable by everyone.
To remove the write permission for all other users, we run:. That looks like. Chmod permission directory name To change the permissions of a directory with its files and sub-directories recursively, we run:.
The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file. Chmod command understanding how-to grant file permissions why i said title like that, because chmod command used for changing file mode bits. The command that executes such tasks is the chmod command.
The first digit contains the permissions for file owner, 7 is the octal code in which the permissions are set for the owner:. For file myfile, to grant read, write, and execute permissions to yourself (4+2+1=7), read and execute permissions to users in your group (4+0+1=5), and only execute permission to others (0+0+1=1), you would use:. We can add the execute permission for everyone with the following command:.
The absolute mode functions like the exclusive permission of the symbolic mode in that it exclusively sets the permission specified removing all other. Which way of using chmod is better depends on what you. Use the command cat foo.txt to verify that you, the file owner, can read the file again.
We use 'rwx' to remove read, write and execute permissions. I also want to transfer this file to my windows machine and to other friends etc, so I want to take away all permissions from this file. Group and others will have no permissions, not even read.
The second string shows the number of links that exist to the file. One ways is to right click on on file/folder and edit permissions. This can be achieved by changing file permissions.
Chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits. Chmod permission file_name There are two ways to define permission:. Add the numbers of the permissions you want to give;.
To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the -R, (--recursive) option. This command will give read, write and execute permission to the owner. $ find /home/user/demo -type f -print.
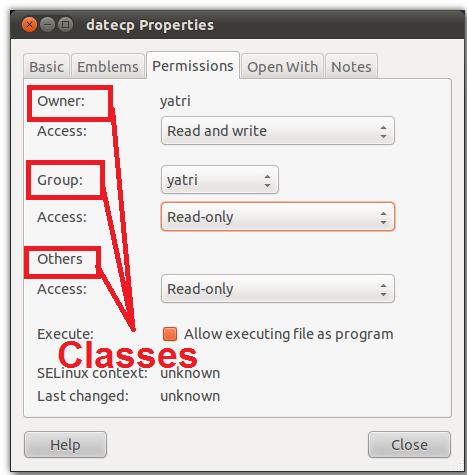
Permissions defines the permissions for the owner of the file (the "user"), members of the group who owns the file (the "group"), and anyone else ("others"). To assign reasonably secure permissions to files and folders/directories, it's common to give files a permission of 644, and directories a 755 permission, since chmod -R assigns to both. Chmod is command which changes permission of a file or folder for particular user or group as per instructions provided.
Using the command, we can set permissions (read, write, execute) on a file/directory for the owner, group and the world. The other way is terminal , where you can change the permission via Chmod. Chmod ugo+rwx foldername to give read, write, and execute to everyone.
Using chmod with Absolute Permissions. To give the owner all permissions and world read and execute you would type chmod 705 filename. Running chmod would change the permissions to all the files in your home directory:.
Right now, the owner and group can read and write to the file. In this example, you are setting permission to 0755:. Special permissions can be added which allow you the special ability to automatically change users or group, or to specify a directory as a "temporary" directory.
U+x — allows the file owner to execute the file. Type “sudo chmod a+rwx /path/to/file” into the terminal, replacing “/path/to/file” with the file you want to give permissions to everyone for, and press “Enter.” You can also use the command “sudo chmod -R a+rwx /path/to/folder” to give permissions to a folder and every file and folder inside it. Here are some examples of how to use the chmod command in numeric mode:.
This will remove the execute. It stands for change mode. Each permission is assigned a value, as the following table shows, and the total of each set of permissions provides a number for that set.
With this next one, owner will have read and write while group and everyone else have read permission. You should be admin to do this. After user level we have provide what needs to be done i.e.
Chmod -R a+rX * The X (that is capital X, not small x !) is ignored for files (unless they are executable for someone already) but is used for directories. To make the document read-only for group and others, we can use:. Chmod a+x new_script.sh If we take a look at the permissions, we’ll see that the execute permission is now granted to everyone, and the existing permissions are still in place.
For example, to give all users read and write access to myfile.txt, run chmod as follows:. You can give yourself permission. To change the mode of a file, use the chmod command.
Characters 5-7 similarly show the permissions for the group;. This indicates the setuid/setgid permission. Read, write, execute 0:.
For total control over permissions, you can use two Unix commands - ls and chmod - to display permissions and modify them. Chmod changes the permissions of each given fileaccording to mode, where modedescribes the permissions to modify. User, group or all.
If you are the owner of the file or are logged into the root account you can change any permissions for the owner, group, and others. How to Change Groups of Files and Directories in Linux. If you truly want any user to have full permissions on all files under directory/ (which may be OK if this is your personal computer, but is definitely not recommended for multi-user environments), you can issue this:.
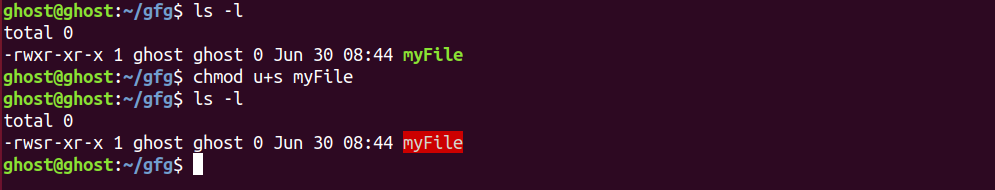
$$$ chmod a=rw myfile.txt. An s can be added to the owner or group 'read' permission. To modify the permission flags on existing files and directories, use the chmod command ("change mode").
This is equivalent to chmod 0777 aprsal:. A(all (everyone)), u(user),g(group) and o(other). Using symbols (alphanumerical characters) using the octal notation method.
By - Linux tutorial - team. The second digit contains the permissions for group members, 0 is the octal code that is set is to no permissions amongst the members. If set on the group read permission, it sets the setgid bit.
Two ways give permissions in Ubuntu. How To Change File Permissions In Linux Using ‘chmod’ Command. If you want to change the permissions for all three kinds of users at the same time, you can use it in the following manner:.
$ chmod u=rw,g. The operator determines whether to add (+), remove (-) or explicitly set (=) the particular permissions. Give the file’s owner read, write and execute permissions, read and execute permissions to group members.
The third string identifies the owner of the file and the fourth string tells what group the owner of the file is in. Chmod 775 /path/to/file chmod command uses & Explanation. To change the permissions of a directory, we run:.
$ chmod a+r file.pl Delete execute permission for all everyone (a):. This command gives the owner read/write permissions for the file called who.out. The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders.
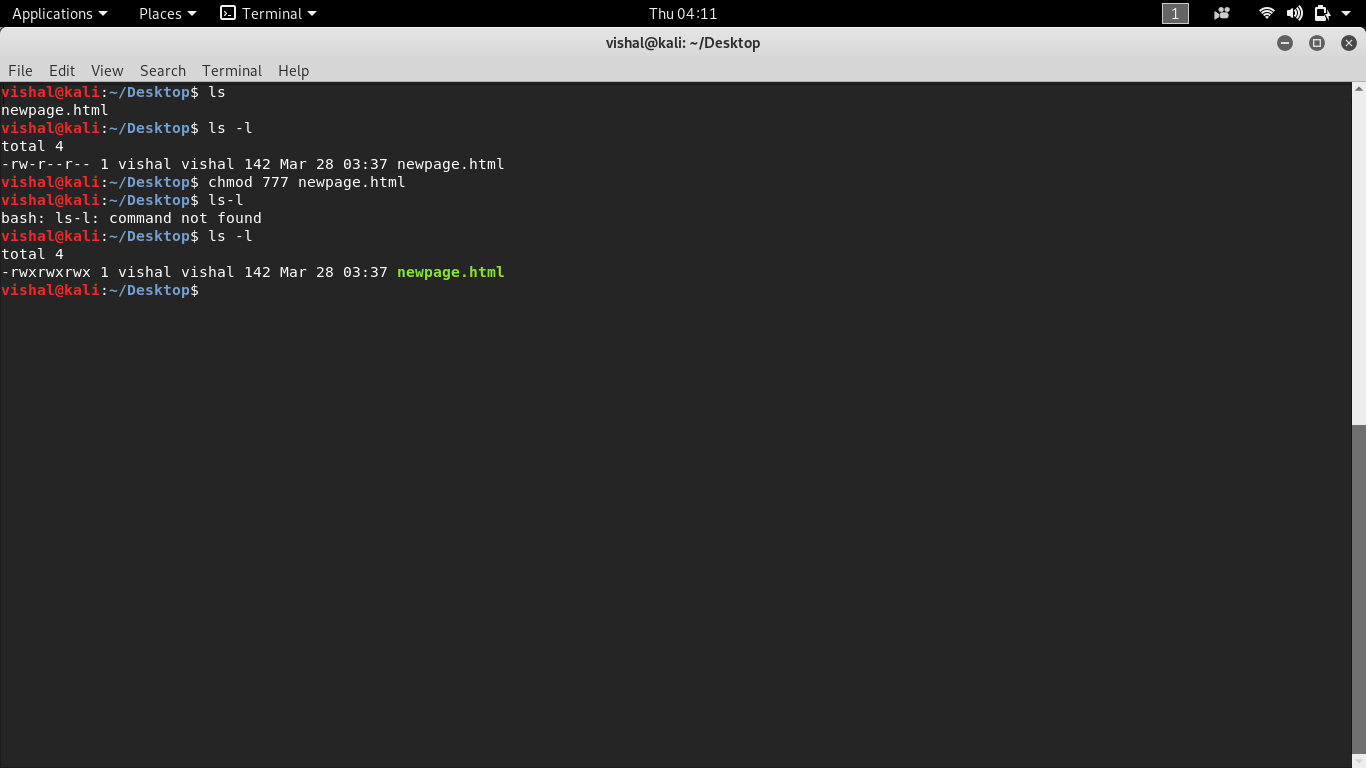
This example shows how to change the permissions on file1.txt with the chmod command. Chmod references operator modes filename The references are shorthand (u, g, or o) for each class. There even is a shorthand notation – a – to set permissions for all references.
As all Linux users, you will at some point need to modify the permission settings of a file/directory. To find all files in /home/user/demo directory, enter:. O-rwx — removes all permissions for others.
The letter u represents the owner. I actually give group write permissions as well, for users which need to modify content, such as users used to deploy code. Chmod -R a+rX * click below button to copy the code.
You can do all of it one single command:. Give the file’s owner read and write permissions and only read permissions to group members and all other users:. If you want to set permissions on all files to a+r, and all directories to a+x, and do that recursively through the complete subdirectory tree, use:.
You can usechmod letterwhere the letters are:. Anyway the permissions for "Other" is read only, and when I try to install the font using the font viewer I am denied based on permissions. Use a + or - (plus or minus sign) to add or remove permissions for a file respectively.
Chmod o-r sample.f - Removes read permission for others to the file sample.f. Here’s a fairly complex example where we’re giving all permissions to the file owner and removing write permission for everyone else. Next, allow users of the same group (and 'other') to enter the /var/www.
To change permission of only files under a specified directory. Chmod -R MODE DIRECTORY. So all types operations need root permissions.
Chmod +x filename.shto make filename.sh executable. Modecan be specified with octal numbers or with letters. Use sudo, the find command, and a pipemill to chmod as in the following examples.
$ chmod a+rx pager.pl Next, sets read and write permission for user, sets read for group, and remove all access for others:. $ chmod go-rwx /var/www. If you use chmod 777 that means you assigned all the permissions i.e.
To grant read, write, and execute permissions on the current directory to yourself only, you would use:. The general syntax to recursively change the file’s permissions is as follows:. If no options are specified, chmod modifies the permissions of the file specified by file name to the permissions specified by permissions.
The third digit contains the. The chmod command specifies which class or classes (user, group, other) have access to the. Say you do not want your colleague to see your personal images.
Chmod 700 /path/to/file chmod 666:. The owner of a file can also add or subtract permissions for himor herself. Chmod -c 666 /path/to/file chmod 644:.
Use the chmod command to change permissions. In other words, give read permission to user, group and others:. $ chmod a-x myscript.sh Adds read and execute permissions for everyone (a):.
We can use the ' chmod' command which stands for 'change mode'. Controlling file permissions with umask. Chmod 707 myfile chmod – is the command to change permissions 7:.
A+rw — allows everyone to read and write to the file. Controlling file permissions with umask;. Use an equals sign =, to specify new permissions and remove the old ones for the particular type of user(s).
We use '-', which means remove permissions.

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
Chmod Give All Permissions To Everyone のギャラリー

How Do Linux File Permissions Work
44 File Permissions Chown Chgrp Chmod Umask Dong A Place To Track My Time Log

Using Terminal To Set File Permissions Amsys
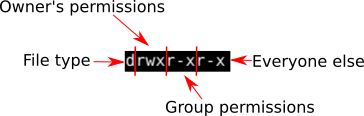
Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin

How To Set Access Rights For Files And Folders With Chmod
What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Permissions Why Use Chmod Instead Of Chmod U Rw Go R Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Chmod Why It Matters User Permissions In Os X Droppedframe Com

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions

Csc128 Permissions And Links Chmod And Ls

Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube
.jpg)
Give Write Access Chmod 666

Ownership And Permissions

Chmod Wikipedia

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Linux Permissions Pluralsight

Linux Permissions Pluralsight

Change Ownership And Rights To Files And Folders In Linux Smashing Lab
What Is Chmod 777
Chmod 0400 Means

8luq0n6gud9v3m

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux
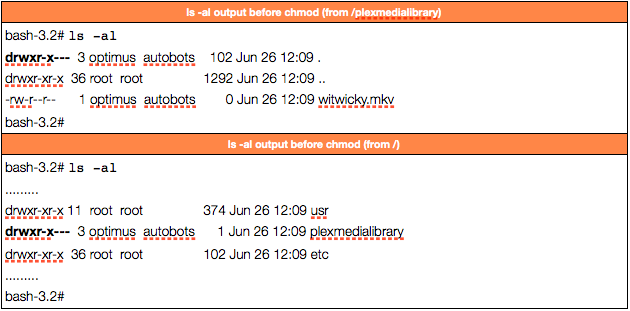
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support
Advance File Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Command Line How To Make A File Executable Ask Ubuntu

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier
Unix Commands Basic To Advanced Unix Commands With Example

Software Carpentry
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs J72hjomdluhqe6xjivy M6yrjmkqx9x3z3ps Rpnb8by3w7z Usqp Cau

Chmod 0400 Means

Chmod Give Everyone Write Access

Chmod Wiki Ask Ubuntu

Ppt Just Enough Unix Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples

From Command Line On Macos How To Add A User Group To The Sharing And Permissions List For A Directory Ask Different

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

Understanding File Permissions

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux
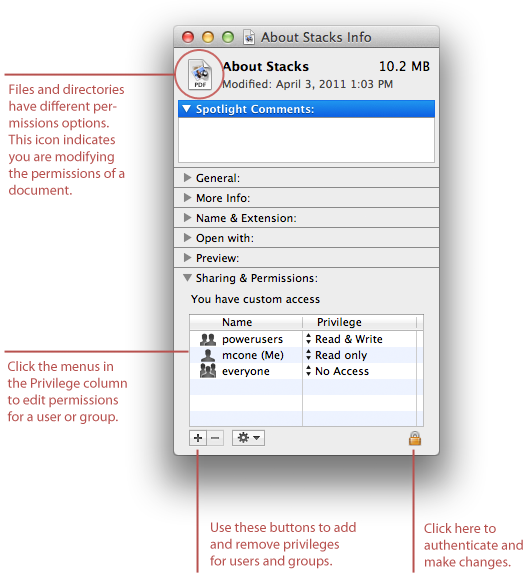
How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Permissions In The Finder And Command Line The Eclectic Light Company

Setting File And Directory Permissions Computational And Information Systems Laboratory

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Understanding Unix Permissions And File Types Unix Linux Stack Exchange

How To Give Read Write Permissions To A Folder In Ubuntu Code Example
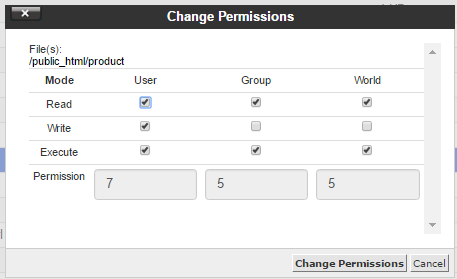
What Is Chmod 777

Chmod Why It Matters User Permissions In Os X Droppedframe Com

Unix File Permissions Computer Science

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft
Q Tbn 3aand9gcslbhvh5emm 4 Trrp3thfcmqosdrfzef Gvyldtqf1wtkgi37f Usqp Cau

File And Folder Properties

Unix Tutorial Five

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Give Permissions In Ubuntu Itechzo Give Permissions In Ubuntu

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

Chmod Why It Matters User Permissions In Os X Droppedframe Com

Give Write Access Chmod 775

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners

How To Change File Permissions Using The Terminal Chriswrites Com
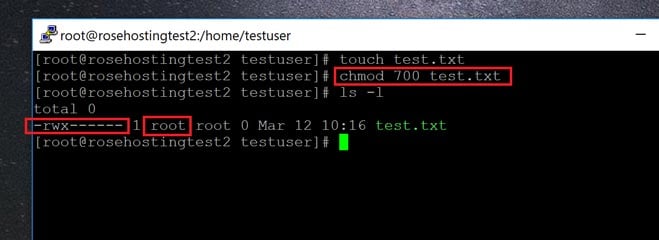
How To Deny File Permissions To Everyone Except Yourself In Linux Linuxhostsupport
Www Dellemc Com Resources En Us Asset White Papers Products Storage H Wp Access Control Lists On Dell Emc Isilon Onefs Pdf
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq2oq90gyu7qjtwwppsiodhgqotjbz3awrstnhczkm6hwgdiahx Usqp Cau

File Permission In Linux Chmod Command Armantutorial

Ownership And Permissions

Permissions Assignment Owner Can Change Others Can Only Read Automated Hands On Cloudxlab
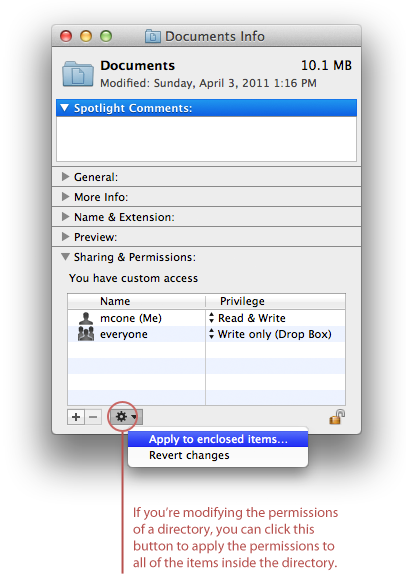
How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Solved File Permissions In Linux Can Be Set Using A 3 Dig Chegg Com
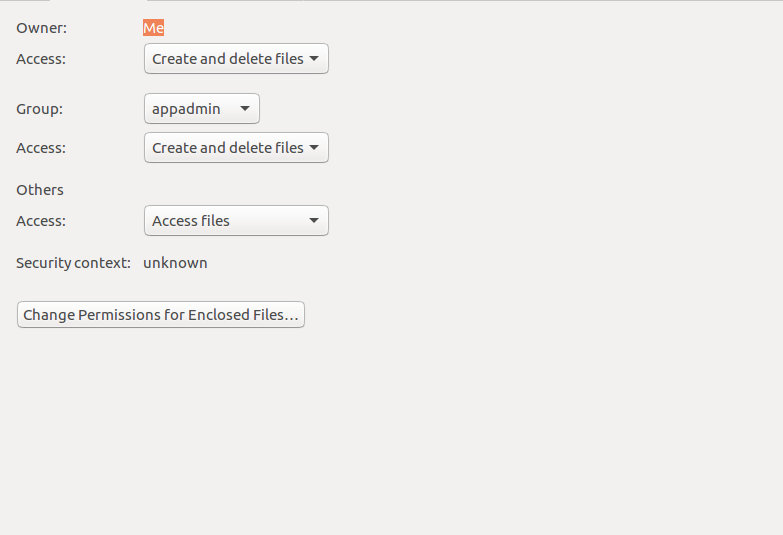
Chmod 777 What Does This Mean Learn Linux Permissions Easy Way

Solved 8 Which Of These Commands Could You Use To Show O Chegg Com

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Ownership And Permissions

How Can I Recursively Change The Permissions Of Files And Directories Ask Ubuntu

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

Protect Your Data With Super Easy File Security Tricks

Everything About Chmod Command In Linux Hackerearth

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft
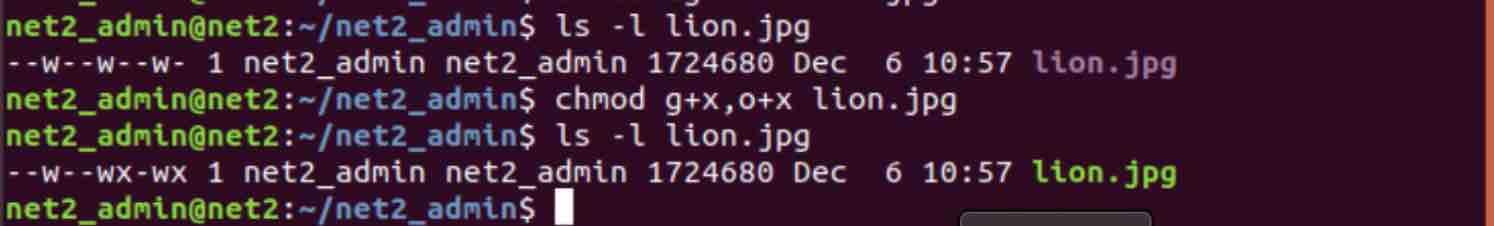
How To Manage Permissions In Linux Guide For Beginners

Ownership And Permissions

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight
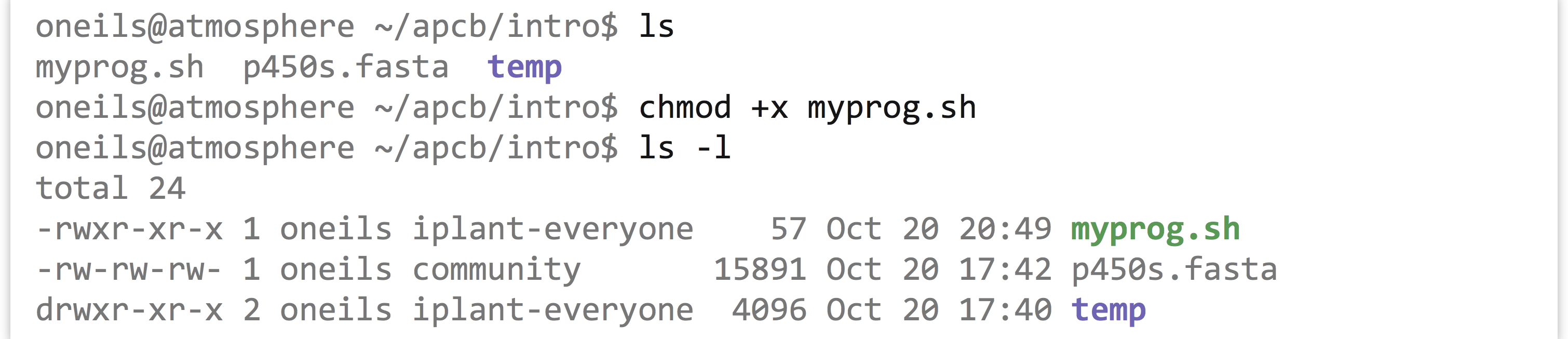
Permissions And Executables A Primer For Computational Biology

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

How To Use The Chmod Command 2 Minute Linux Tips Network World

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux
%20access%20permission%20%EC%98%88)%20chmod%20644%20test.jpg)
Permissions Why Use Chmod Instead Of Chmod U Rw Go R Unix Linux Stack Exchange
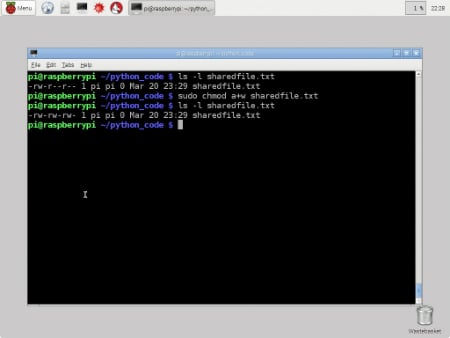
Working With File Permissions On Your Raspberry Pi Dummies

Whatever You Knew About Chmod Is Wrong Alien Coders
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr9rnnth31jdnr94db Zmbdt5bh907clokeeor9me5yqbuufaiw Usqp Cau
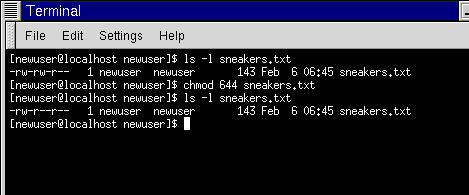
Fun With Numbers In Chmod

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage



