Chmod Octal
U G W rwx rwx rwx chmod 777 filename rwx rwx r-x chmod 775 filename rwx r-x r-x chmod 755 filename rw- rw- r-- chmod 664 filename rw- r-- r-- chmod 644 filename U = User G = Group W = World r = Read w = write x = execute - = no.
Chmod octal. Omitted digits are assumed to be leading zeros. Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers. So if you take the octal digit that expresses the permissions in each category, and you line them up in order, you get a three-digit octal number.
Chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits. The second digit contains the permissions for group members, 0 is the octal code that is set is to no permissions amongst the members. Actually, in early Unix days, permissions were called mode of access.
View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 644 (chmod a+rwx,u-x,g-wx,o-wx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily. The chmod system call cannot change their permissions. Before doing that, make sure you understand what does chmod -R 777 do, and why you should never set permissions to 777.
Chmod changes the file mode of each specified FILE according to MODE, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits. This notation assigns a unique number to each permission type. U is for user, g is for group, and o is for others.
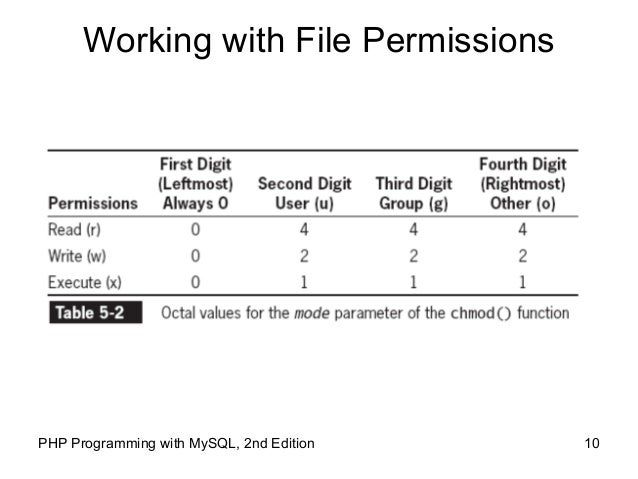
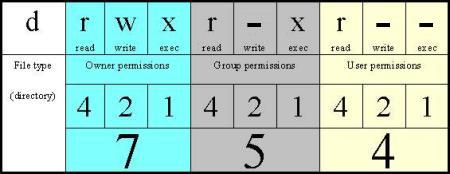
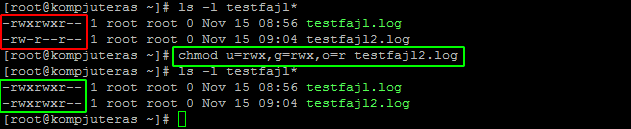
The third digit contains the. The mode parameter consists of three octal number components specifying access restrictions for the owner, the user group in which the owner is in, and to everybody else in this order. Chmod stands for change mode.
One component can be computed by adding up the needed permissions for that target user base. Unix or any *nix uses octal for permissions – it’s pretty simple once you get the chart into your brain 😉. Chmod syntax using octal mode.
Chmod options You can extend chmod permissions with options. The chmod command can be used with either a text-based argument or 3 octal digits (see note 1) to change the permissions on a file. The syntax for changing the file permission recursively is:.
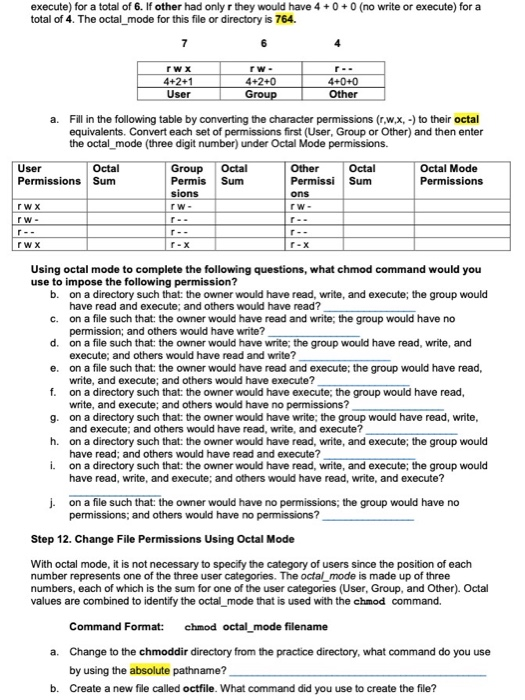
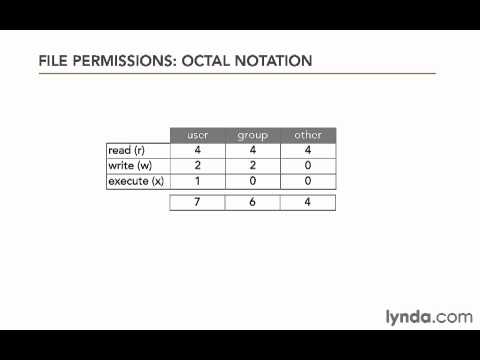
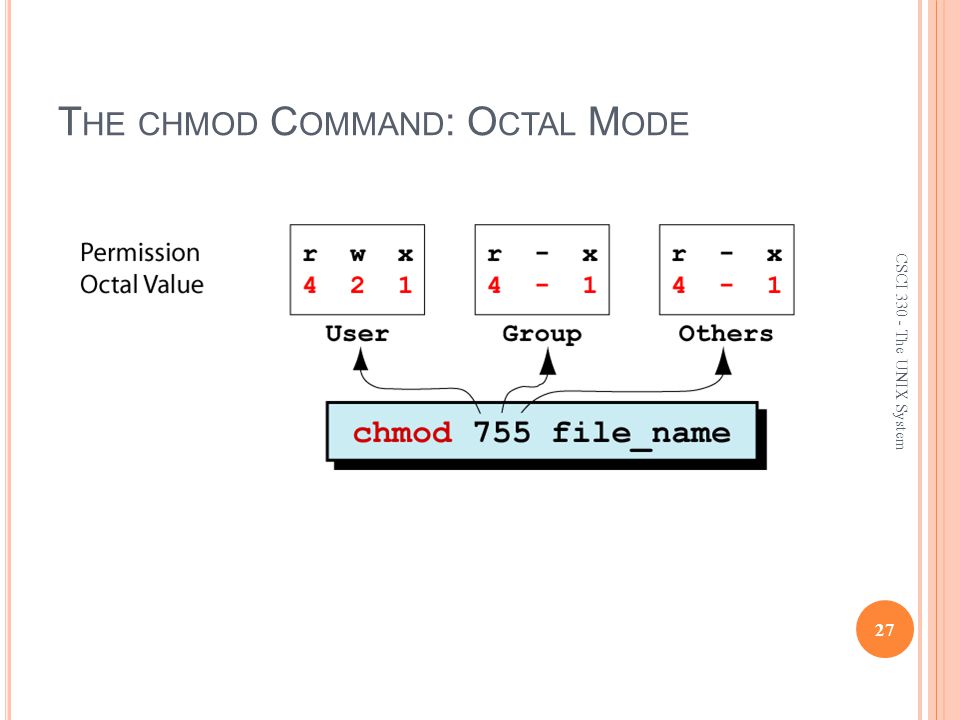
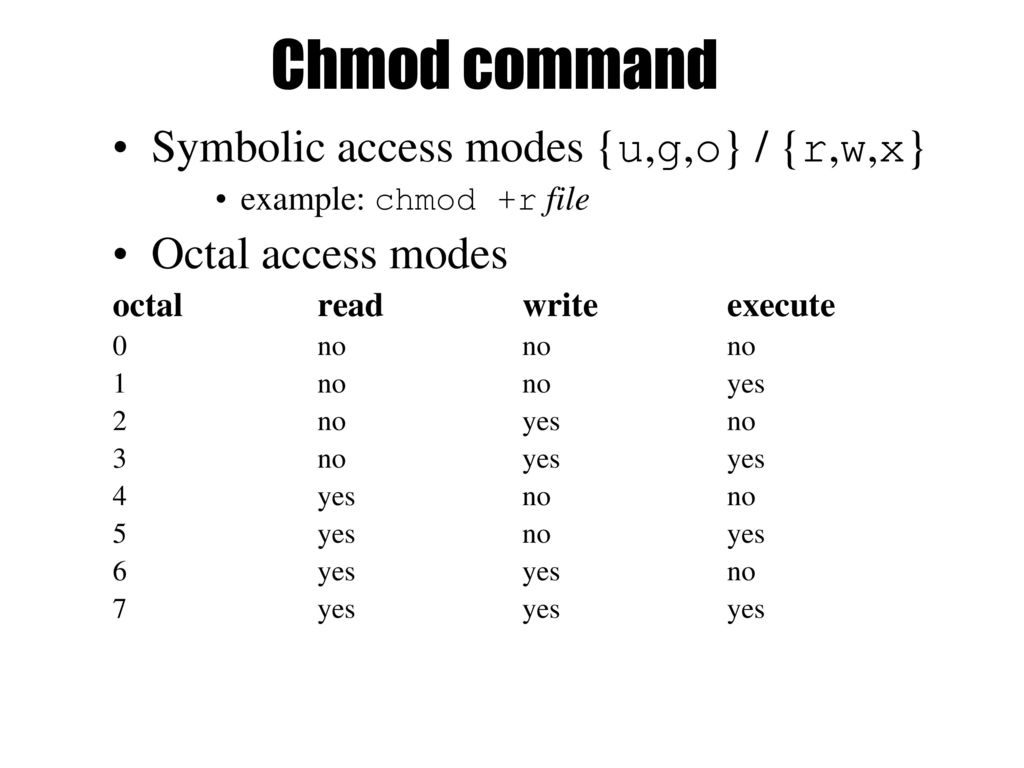
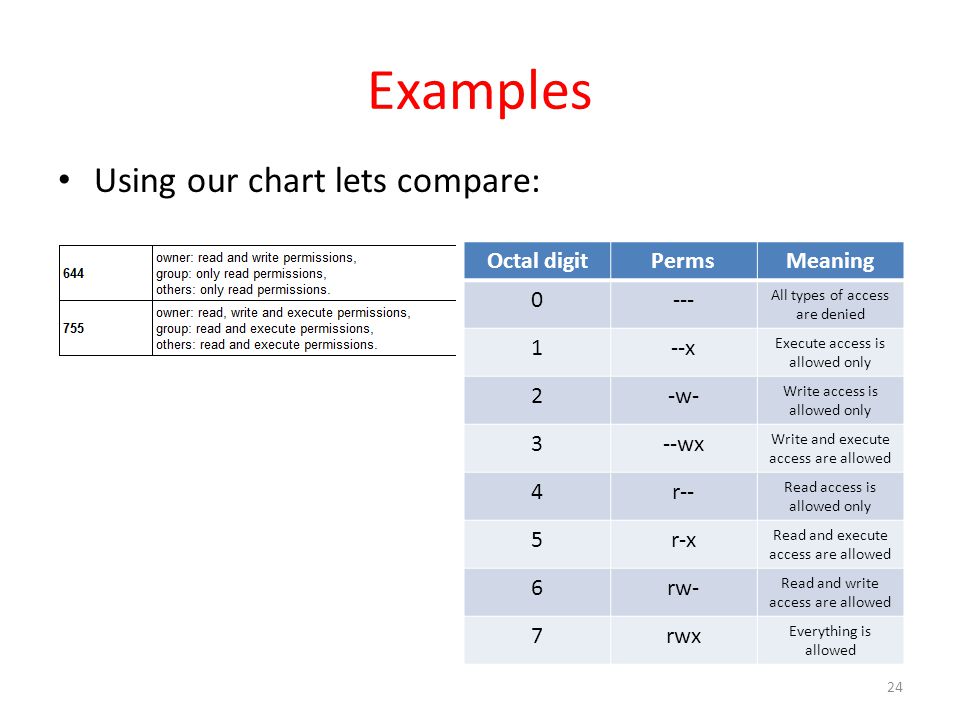
$ chmod OPTIONS MODE filename. This article explains the basic Linux permissions model and what the numbers corresponding to the permissions. The octal (0-7) value is calculated by adding up the values for each digit User (rwx) = 4+2+1 = 7 Group(rx) = 4+1 = 5 World (rx) = 4+1 = 5 chmode mode = 0755.
In such cases, the chmod recursive option (-R or --recursive) sets the permission for a directory (and the files it contains). When we use the chmod command later on, you’ll see that you can change the permissions using either symbols or octal numbers. The first digit contains the permissions for file owner, 7 is the octal code in which the permissions are set for the owner:.
This manual page documents the GNU version of chmod. Chmod +x new_script.sh Setting Permissions for Multiple Files. Chmod command has the following syntax:.
Add read permission to the user, remove write permission from the user, and set the group permissions to be the same as the other permissions:. All of them are listed in man chmod, but I will type them out here as well. Is it not meant for changing the permission?.
Binary executables with the setgid bit (chmod g+s path) can be executed with the privileges of the file's group. File access, meaning permissions, can be represented alphanumerically (using symbols like r for read, w for write and x for execute) or using octal numeric values (755 for example). Chmod changes the permissions of each given file according to mode, where mode describes the permissions to modify.
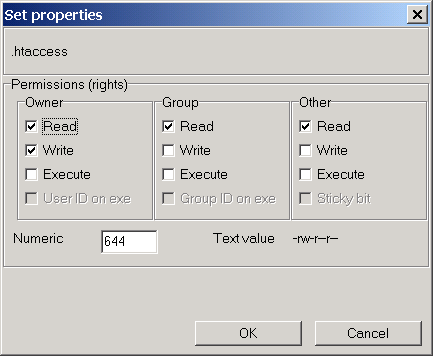
How to set permissions with chmod in octal mode. Man chmod man ls A variable called `umask' is used as a permission mask for all newly created files and directories. For example, to set the permissions of filename to -rw-r--r--you could run the command:.
This command is used for changing the mode of access. Use chmod to set additional file system modes for files and directories. If you need a more in-depth guide on how to use Chmod In Linux to change file permissions recursively, read our Chmod Recursive guide.
Now if we can just get support for 0sNNN (for sexagesimal) and put base-64 numbers into our code. The permission in octal form is useful for many commands such as chmod command and other sysadmin tasks. Using octal value & position:.
Example of octal modes:. The chmod command uses a three-digit code as an argument. The chmod command also permits you to use octal notation for the mode.
Instead of “u=rwx,go=rx”, you would have “755”. For example, to set the sticky bit, prefix a 1 to the number sequence:. Umask is a 3 digit octal number.
It’s usually used when installing and configuring various services and features in a Linux system. With a sticky bit, only the file owner, the directory owner, or the root superuser can delete the file, regardless of the file's read-and-write group permissions. In octal, the setgid bit is represented by 00 e.g:.
The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file. Any omitted digits are assumed to be leading zeros. Chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits.
Command line users are likely familiar with using chmod to set file permissions in numerical or octal format, for example running a command like ‘chmod 755 filename’, but have you ever wondered how you can get file permissions in octal format?. Chmod u+r,u-w,g=o myfile Octal Modes. I am assuming you don't want the binary codes, though I quite like them, so here are the text codes:.
– Lawrence Dol Dec 3 '09 at 7:15. Only the root user or a regular user with sudo privileges can change file or directory permissions. Sets group ID on execution.
Sets user ID on execution. Mode can be specified with octal numbers or with letters. An example of the text-based command to add "read" permission for group members and others to a file named foo is:.
Earlier we discussed about how to use octal permission bits with chmod. How stupid was using a lead 0. Chmod a+x,og-r myfile file2 zzz.
Chmod command octal notation In octal notation we use numbers instead of symbols for permission types. It can be invoked with either octal values representing the permission flags, or with symbolic representations of the flags. Chmod option mode file.
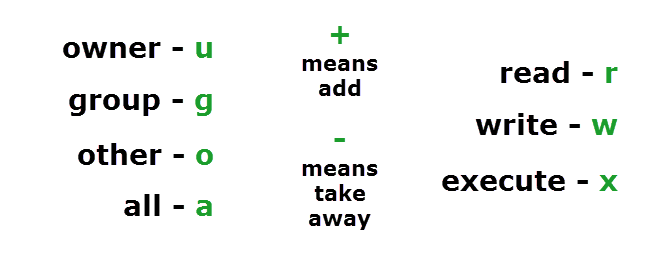
Unlike symbolic notation where three fields are available in each level, in octal notation there is only one field available in each level. Ugoa +-= perms. The following table shows how the setgid and setuid file modes are represented in octal:.
Chmod is a well known command line utility, that's used to manage file permissions on MacOS, Linux and other Unix like operating systems. Chmod 754 myfile Setgid and setuid. We can apply permissions to multiple files all at once.
The string rwxr-xr-x represents the permissions of this file. Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;. Octal Number Representation So that’s how permissions are displayed in Linux using symbols.
A useful property is to set the setgid bit on a directory so that all files and directories newly created within it inherit the group from that directory. Select the permissions you require below. Read, write, execute 0:.
The command can accept one or more files and/or directories separated by space as arguments. The octal values have the following meaning:. The tool will provide you with an octal code that corresponds to these permissions which can then be applied to relevant directories and files with chmod.
Examples chmod 400 file - Read by owner chmod 040 file - Read by group chmod 004 file - Read by world chmod 0 file - Write by owner chmod 0 file - Write by group chmod 002 file. It is common to use the basic chmod command to change the permission of a single file. Let’s say we want to remove the write permissions for the “other” users from files that have a “.page” extension.
This is why this particular command was named chmod. We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article. The three digits of the chmod code set permissions for these groups in this order:.
And there you have it:. In octal mode, permissions are specified with a three-digit octal number. It takes the following syntax:.
The numeric mode is the sum of one or more of the following values:. The optional leading digit, when 4 digits are given, specifies the special setuid, setgid, and sticky flags. How to get octal file permissions on Linux/Unix command line.
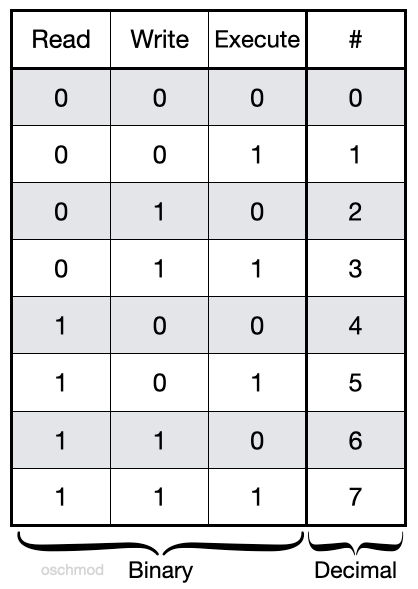
U = user g = group o = other (not user or group) a = all + = add permissions - = remove permissions r = read w = write x = execute t = sticky bit. Chmod command is used to change permissions of a given file according to a certain mode which might be a set of octal characters or a set of alphabetical characters. A numeric mode is from one to four octal digits (0-7), derived by adding up the bits with values 4, 2, and 1.
Chmod u+s filename This works fine. Where OCTAL-MODE is the octal form of the permissions. You are trying to fix a permission issue with your web server and found information on the Internet, saying that you need to recursively chmod 777 the web directory.
Chmod 707 myfile chmod – is the command to change permissions 7:. For more information, including octal specification of permissions, refer to the Unix User's Manual pages for chmod(1) and ls(1). Sets the permission for owner, group and others with octal values , 4 for read , 2 for write , 1 for execute and any sum of these number to get cumulative permissions.
We can do this with the following command:. Following are the symbolic representation of three different permissions:. I understand (to some good extent) file permissions, the concept of umask, setuid and using octal numbers with chmod.
The chmod numerical format accepts up to four octal digits. To view these online, enter. But the octal number 4000 is always associated with setuid (in books etc).
In this article, let us review how to use symbolic representation with chmod. Chmod¶ The chmod ("change mode") command is used to change the permission flags on existing files. The format of a symbolic mode is:.
I wish every language required this for octal numbers;. A numeric mode is from one to four octal digits (0-7), derived by adding up the bits with values 4, 2, and 1. The three rightmost digits define permissions for the file user, the group, and others.
Following are the symbolic representation of three different roles:. Owner (you) Group (a group of other users that you set up) World (anyone else browsing around on the file system) Each digit of this code sets permissions for one of these groups as follows. The output of this command will look something like this:.
It can further. However, you may need to modify the permission recursively for all files within a directory. The second way to represent the same permissions is by using octal numbers.
The first digit selects the set user ID (4) and set group ID (2) and restricted deletion or sticky (1) attributes. Linux chmod command is one of the most commonly used commands especially by system administrators when assigning modifying file and folder permissions. These are the files in the current directory:.
Or to change permissions to -rwxrwxrwx you could use the command:. While there are multiple ways to use chmod, on this site, we have chosen to focus exclusively on using chmod with Octal Notation. The command chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits.
The chmod command in Linux is used to change file and directory permissions using either text (symbolic) or numeric (octal) notation. The same permission settings can be defined using the octal format with the command:. This quick tutorial shows how to use the stat command to view octal file permissions.
Define File Permission in Octal/Numeric Mode. But I still cannot figure out the relationship between the octal number 4000 and setuid. It can be applied recursively using the "-R" option.

Linux Chmod Command Clearly Explained Codedodle

Understanding File Permissions 2buntu

14 Permission And Modification Times
Chmod Octal のギャラリー

Chmod Helper Is A Simple Online Tool For Calculating File Permissions Adafruit Industries Makers Hackers Artists Designers And Engineers

Is There A Web Based Converter Between Rwx And The Octal Version Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Explain Absolute And Relative Permission Using Chmod Linuxteach
Chmod Help
Class File Tree Structure Home Csc156 Yourusername Chegg Com

Chmod File Permission And The Octal Notation Netseed
Chmod Ultimate Octal Helper On The App Store
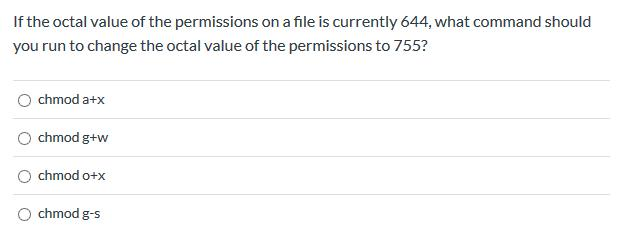
Solved If The Octal Value Of The Permissions On A File Is Chegg Com
Linux File Permissions Octal Mode

Everything About Chmod Command In Linux Hackerearth

Solved B To Remove Myfile Ordinary File From The Paren Chegg Com

Understanding Linux File Permissions With Chmod Umask Chown And Chgrp Liquidon Net

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
Why Would Using Chmod 777 Recursively From The Root Cause A Linux Box To Not Boot I Could Understand This If I Were Limiting Permissions But Why Would Adding Permissions Cause This

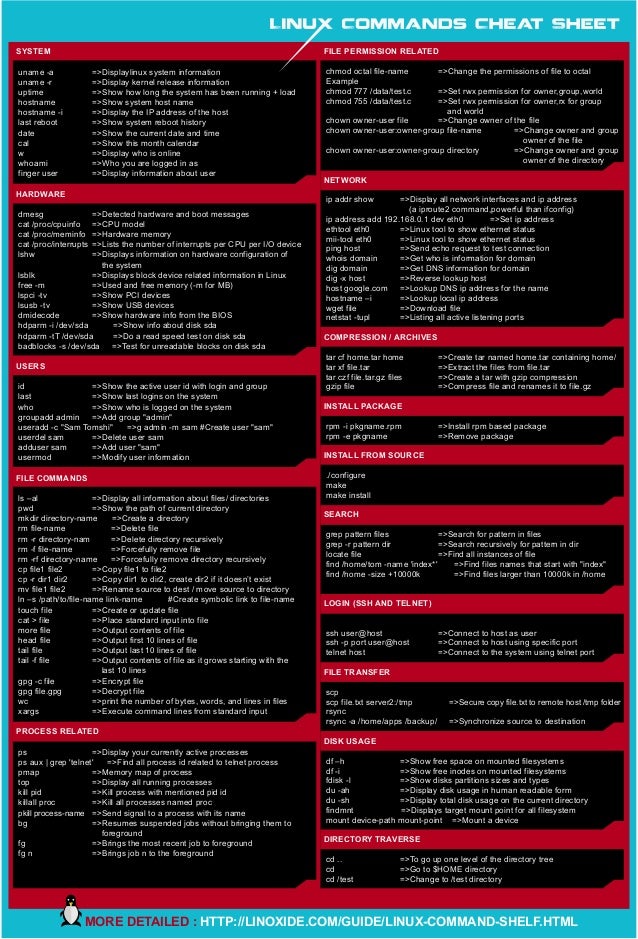
Common Bash Commands

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Unix Permissions

How To Get Octal File Permissions On Linux Unix Command Line Nixcraft
0406 Setting Permissions Using Octal Notation Youtube

File Security

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage
Linux Chmod Tips

Read Write Access Chmod 775

Linux Users And Groups Linode

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

The Language To Be Used Is Javascript And The Pag Chegg Com
9g2kbl3fl68hem
06 Users Groups And Permissions

Setting Permissions Using Octal Notation

Solved Part 3 Permissions For Files Follow The Instructi Chegg Com
Csci The Unix System The File System Ppt Video Online Download

File Security Viewing Permissions Ls L Permission Values Ppt Download

Bif703 File Permissions Ppt Download
Q Tbn 3aand9gct7wt7gzhduflbfyn8phh8frjezj69hwxbeqqg4p T9 V8epo92 Usqp Cau
Securing Files On Windows Macos And Linux By Dirk Avery Faun Medium
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr2lfpzbutqythmvbwafnxvyggqfj7hnw6fhh Kcozkk8m5 V7o Usqp Cau

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

How To Change Permissions In Linux

Explain Unix File Permissions

M03t3 2 Intro To Linux Chmod Octal Permissions Youtube

Linux Users And Groups Linode
Chmod Ultimate Octal Helper By Thierry Lubrez

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

I Made This Chmod Cheat Sheet And Thought It Might Be Useful Linux4noobs

How To Get Octal File Permissions From Command Line In Mac Os Osxdaily
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsqtj7hmhwhqltb Dg3vru7pifk7qn5xlkqq4c3n1r24dp3rp4d Usqp Cau

Unix File Permissions Computer Science

Carswell Ch 06 Directory Commands Flashcards Quizlet
Github Jhuesser Chmod Calculator A Small Chmod Calculator For Windows

Permissions In The Finder And Command Line The Eclectic Light Company
Media Management Permissions Error Must Contain A Valid Unix Permissions Octal Issue 3869 Sonarr Sonarr Github

Chmod Wikipedia

What Is Ftp Chmod Chmod Change Mode Impress Org

Linux Permissions Pluralsight
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqhfr U2abgulny1unrbvdd1u2an6tuvn0tfanoivzco5yi2qb3 Usqp Cau

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Ppt Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Powerpoint Presentation Id

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

Instructions

Please Help Me Out This All I Will Give You Helpf Chegg Com
Chmod 0400 Means

Os Mkdir And Os Mkdirall Permission Value Stack Overflow
Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Unix Chmod Cheat Sheet Computer Science Programming Learn Javascript Linux Operating System

A Quick Introduction To Unix Permissions Wikibooks Open Books For An Open World

Tech It Easy Chmod Calculator Built With Angularjs And Material Design
2
Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
How To Display File Permissions In Octal Format In Linux Kompjuteras

Chmod Chown Not Working Solved V3 Testing Sonarr Forums

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

Pysnippet Chmod Fu For Ios

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Solved Chmod Can Be Used To Change The Mode Of The File Chegg Com
Linux Cheat Sheet

Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command

Cmpsc 122 Lecture Notes Fall 17 Lecture 2 Chmod Octal Superuser

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World
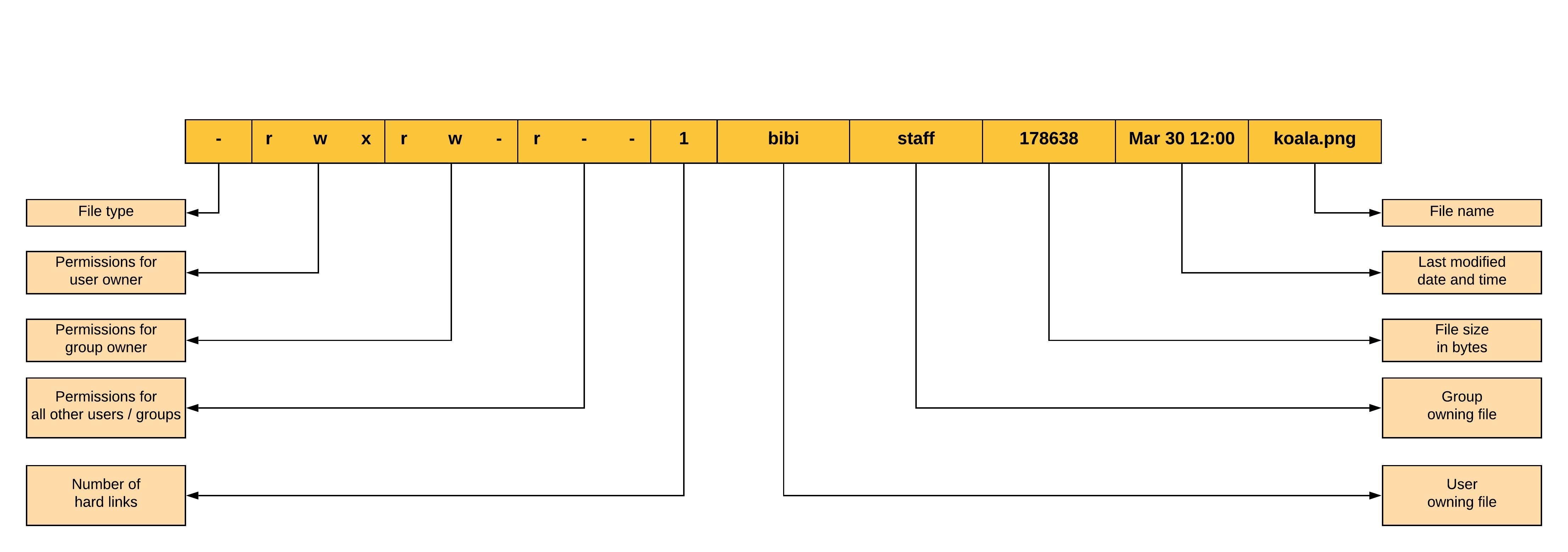
Linux File Permissions And Ownership By Udara Bibile Level Up Coding

Solved File Permissions In Linux Can Be Set Using A 3 Dig Chegg Com

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

Chmod Options Permissions Files Linux Pocket Guide Book

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod
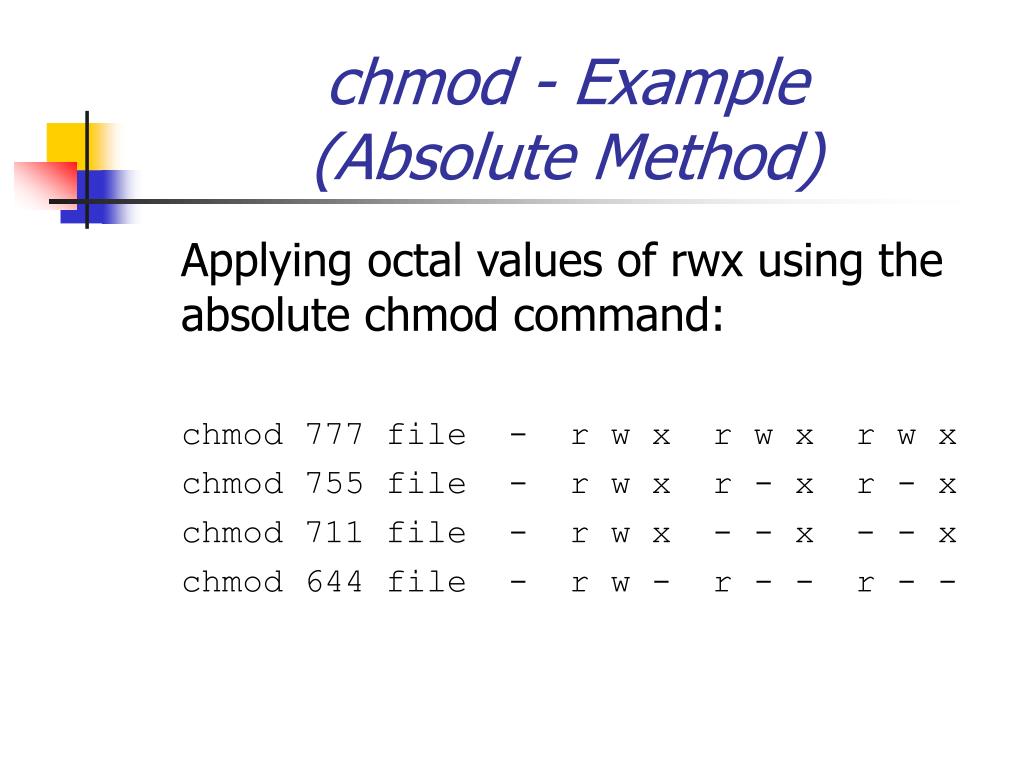
Ppt Agenda Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode
Why Does Doing Chmod 777 Not Make A File Executable But Chmod 755 Does Isn T 777 Greater Than 755 Quora
Solved Question 3 The Rm R Command Can Be Used To Delete Chegg Com

A Unix And Linux Permissions Primer Daniel Miessler

Please Help Me Out This All I Will Give You Helpf Chegg Com

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage
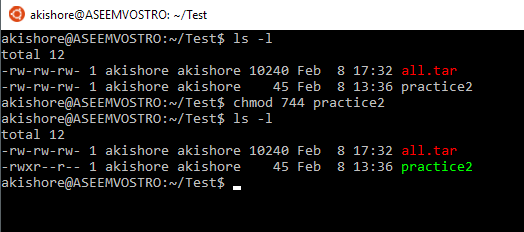
Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage
Media Management Permissions Error Must Contain A Valid Unix Permissions Octal Issue 3869 Sonarr Sonarr Github



