Chmod File Permissions Example
One can use file permissions to control access to their files.

Chmod file permissions example. Permission denied abhinav. The general syntax to recursively change the file’s permissions is as follows:. To remove permission from any file/directory you have to use “–” Symbol.
In the previous example, the output showed that test.txt is a regular file with read and write permission assigned to the owner, but gives read-only access to the group and others. We can set these same permissions with the symbolic notation:. All files have three types:.
For example, to set the permissions of filename to -rw-r--r--you could run the command:. The -R (or --recursive) options make it recursive. Search permission for directories.
$ sudo chmod –reference=ref_file filename. The three rightmost digits define permissions for the file user, the group, and others. Sudo chmod u+w /my/directory/ Another example would be “g-w,” would remove write permissions for the group.
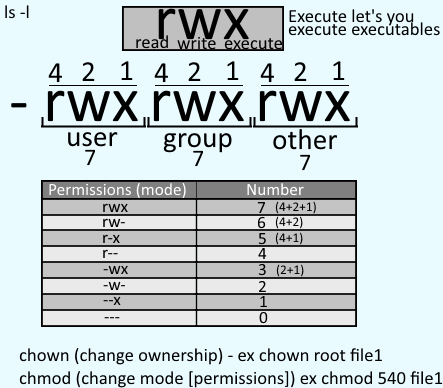
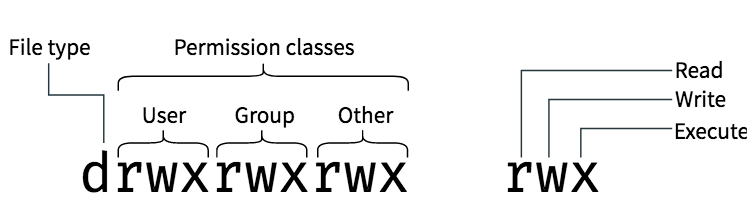
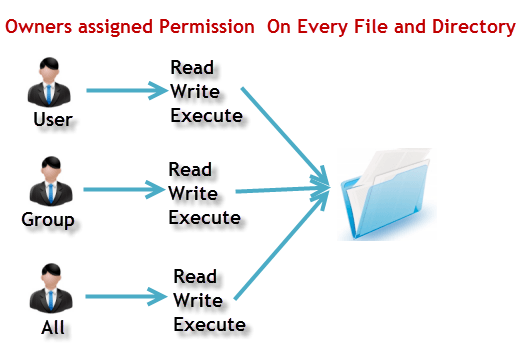
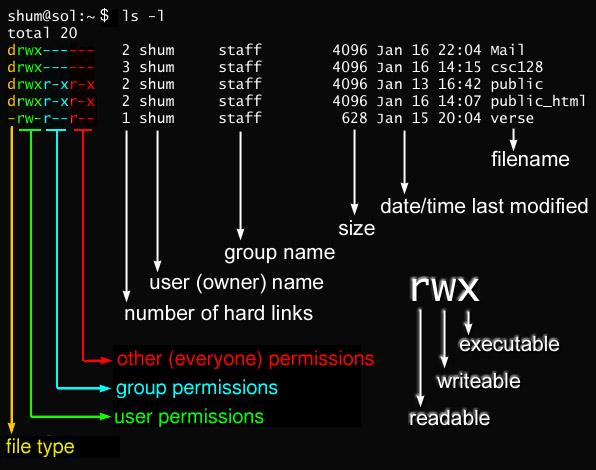
Let’s add write permission to group. Owner – Person or process who created the file. In this, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of users.
Add single permission to a file/directory. To Give permission to any file/directory you have to use “+” Symbol. Using Chmod Command to Change File Permissions.
Sysadmins can enforce a security policy based upon file permissions. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file. Chmod a=rwx file turns on read, write, and execute permissions, and turns off the hidden, archive, and system attributes.
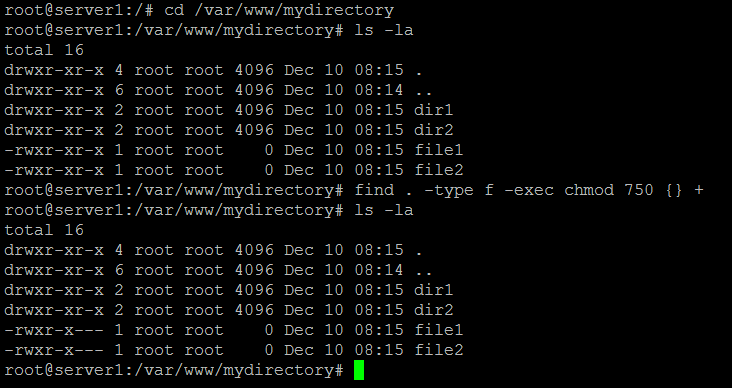
To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the -R, (--recursive) option. Execute permission for files;. Chmod +hrs sysfile sets the hidden, read-only, and system attributes for sysfile.
For example, to set the sticky bit, prefix a 1 to the number sequence:. Localhost@user1$ chmod 664 <file-name> Example 2:. Chmod ug+x file ;.
There are two basic ways of using chmod to change file permissions:. In our previous example, if you want to add execute permission for group owner, you can use chmod command like this:. This is a shortcut, but can save some time.
In this example we remove users execute permission from file ping.txt $ chmod u-x ping.txt Copy Permissions From Other File. 7 Chmod Command Examples for Beginners 1. Chmod is a very helpful command to change the file permissions of a file or a folder in any UNIX-like operating system.
This example uses symbolic permissions notation. The chmod numerical format accepts up to four octal digits. Chmod Command in Linux Linux File Permission Introduction to Linux File Permission.
You can also add permissions without specifying a full permission string. Using chmod command is very easy if you know what permissions you have to set on a file. Localhost@user1$ chmod 744 <file-name> Using symbolic representation.
Let’s give Read and Write permission to User/Owner using chmod command. An example of this would be “u+w,” which would add write permission to the user. Chmod a-x file Allow read permission to everyone:.
Chmod -R 777 /www/store. We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article. In assgn1_client.c, has owner’s permission as rw-, which means the owner mik can only read(r) and write(w) the file but cannot execute(x).
But the "x" permission value does still apply, even if it has little or no meaning. For example, to add the execute permission for the user to file1:. It stands for change mode.
Linux File Permission :. Changing file permissions is simple with the chmod command:. For example, if I wanted to give file permissions to a script called script.sh, I could do:.
You can combine multiple references and modes to set the desired access all at once. Let’s say we have a file where everyone has full permissions on it. Understanding file permissions for chmod and chown command.
This is equivalent to chmod 0777 file On 7/08R2/8/16/19, the command. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode. You can use the chmod command to set permissions in either of two modes:.
After you have assigned the executable permissions to the script, you can run the script without bash command as shown. To put it simply, use chmod command to change the file or directory permissions. Chmod 700 filename You can do the same in symbolic mode.
Execute permission for files if the current (unmodified) mode bits have at least one of the user, group, or other execute bits set. Say you do not want your colleague to see your personal images. For example, we can add write permissions for others:.
Using the command, we can set permissions (read, write, execute) on a file/directory for the owner, group and. View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 644 (chmod a+rwx,u-x,g-wx,o-wx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily. The default permissions for that file do not include execute.
The X flag is ignored if the File parameter is specified and none of the execute bits are set in the current mode bits. $ chmod u+x hello_script.sh Step 5:. The options are set in two file mode bits:.
777 ) or symbolic notation (e.g. Bhinav@ETHICALHACKX:~/dir1$ chmod g+w file2 abhinav@ETHICALHACKX:~/dir1$ ls -l file2 file1 -rwxr--r-- 1 abhinav abhinav 0 kax 28 19:08 file1-rw-rw-r-- 1 abhinav abhinav 0 kax 28 19:42 file2 Remove Read permission from user. Use comma to separate the multiple permission sets as shown below.
A superuser or the file owner can use a chmod command or chmod() function to change two options for an executable file. To set the permissions of a file or directory using numeric modes, simply use the format:. Linux file permission is a very important aspects in terms of security issues for the system administrator of Linux Operating System.
Now, let’s go over what permissions that gives. If we have already set some file permissions we can use this file as a reference point for permission. Setting And Modifying Permissions.
This is illustrated in the calculation below. The chmod command enables you to change the permissions on a file. In this example, users who are not the owner of the file and who are not members of the Group (and, thus, are in the Others class) have no permission to access the file.
Chmod 1755 participants With a sticky bit, only the file owner, the directory owner, or the root superuser can delete the file, regardless of the file's read-and-write group permissions. Symbol are used to assign the permissions :. Let’s say you are currently in the root directory of your Unix-like system and you want to change the file permissions of a folder and all of the other files and sub-directories present inside that folder.
Set-user-ID (S_ISUID) with the setuid option. Use the syntax below. For example, I created a file with Sticky Bit Special permission under /opt/dir.
Use chmod to set additional file system modes for files and directories. How to use Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (e.g. To change permission of only files under a specified directory.
+ symbol means adding permission. If you want to restrict write permissions to all others except the file’s owner, you can use:. As explained in the article Permissions in Linux, Linux uses a combination of bits to store the permissions of a file.We can change the permissions using the chmod command, which essentially changes the ‘r’, ‘w’ and ‘x’ characters associated with the file.
Following are some examples:. You must be superuser or the owner of a file or directory to change its permissions. Or if you want to make all the files in the current directory have all permissions type:.
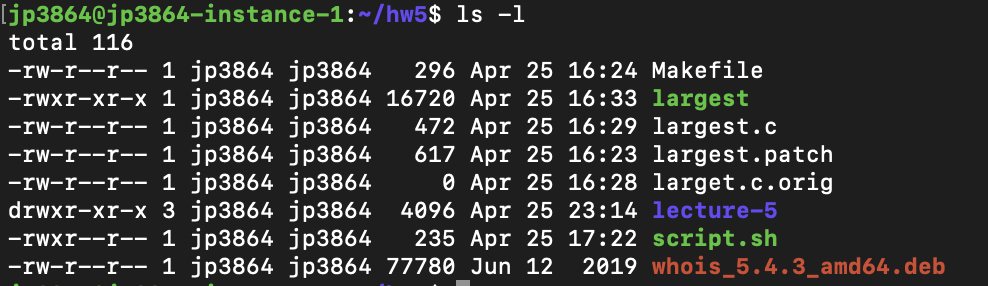
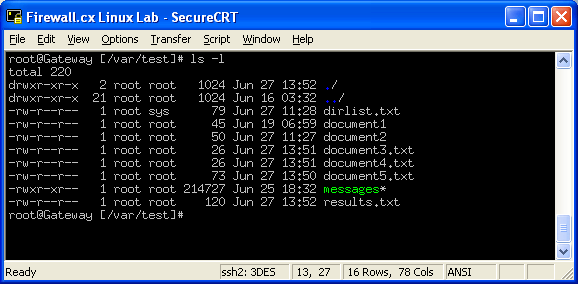
Following is a sample of ls -l command output. Chmod -R MODE DIRECTORY. Using Numeric Modes With Chmod.
Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers. Absolute Mode – Use numbers to represent file permissions (the method most commonly used to set permissions). The second way to execute a bash script is by setting up the executable permissions.
Changing file permissions with chmod command using octal notation. It’s also possible to add permissions incrementally. In this method, you make use of the –reference=ref_file option to set the permissions of a file to be the same as those of another reference file.
This would also remove any special permission if already assigned to any of the files or directories under /opt/dir. Rwxrwxrwx ) to see its value in other formats. To assign 755 permission of all files and directories under /opt/dir # chmod -c -R 755 /opt/dir.
Chmod g+x agatha.txt If you look at the permissions on this file now, you’ll see that execute permission has now been added:. We can do using the following command:. To make file readable, writable and executable by everyone.
The 3rd and 4th columns represents the name of the owner of the file and the group to which the owner belongs respectively. For example, to explicitly make file3 readable and executable to everyone:. So if I try this:.
View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 700 (chmod a+rwx,g-rwx,o-rwx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily. Actually, chmod Command in Linux plays a greater role to keep all the files and directories of the system safe and secure so that no unauthorized person. Changing permission to a single set.
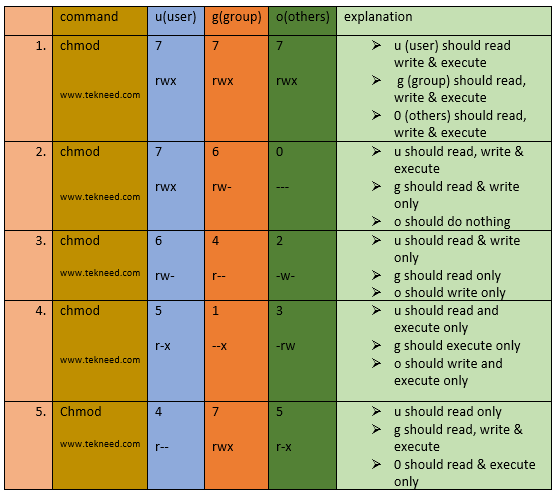
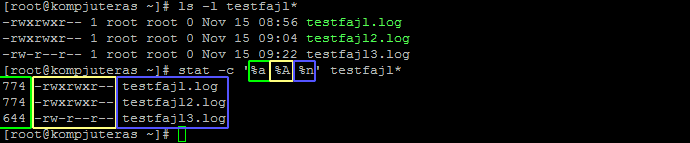
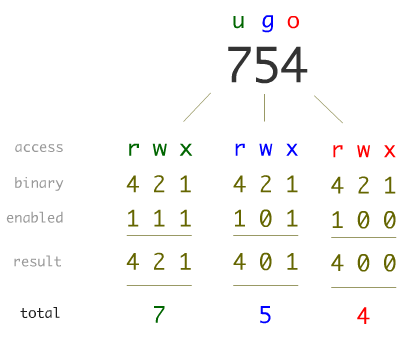
Permissions may also be displayed in numeric mode, numbering from 0 to 7. For example, to change file permissions of a file file1.txt, to say rw-r--r--execute:. Make a shell script executable by the user/owner $ chmod u+x myscript.sh.
If you use chmod 777 that means you assigned all the permissions i.e. You can also change permissions using symbolic representation rather than numeric. T he format of ‘chmod’ is 3 digits.
To change file permissions of a file use the syntax below. -rw-r--r-- 1 john john 272 Mar 17 08:22 test.txt. Chmod examples using symbolic mode :.
Root@localhost ~# chmod -v -R 777 example mode of ‘example’ retained as 0777 (rwxrwxrwx) mode of ‘example/hello.rs’ changed from 0644 (rw-r--r--) to 0777 (rwxrwxrwx) mode of ‘example/hello’ changed from 0755 (rwxr-xr-x) to 0777 (rwxrwxrwx). Set-group-ID (S_ISGID) with the setgid option. For example, if you want the owner to have all the permissions and no permissions for the group and public, you need to set the permission 700 in absolute mode:.
How to Change File Permissions and Ownership. To make a script executable use +x or u+x, for example :. Add multiple permission to a file/directory.
U – user , g – group, o – others , a – all + to add permission , – to remove permission , = to assign permission r w x is used for read , write,execute , s is used to set the sticky bit;. The number “775” is to provide permission to the file. Or similarly, we can take away write access for the group by calling:.
The letters u, g, and o stand for " user ", " group ", and " other ". For example, to set file permissions of file2.txt to be the same as those of file1.txt run the command:. We can use the 'chmod' command which stands for 'change mode'.
So if you want to recursively change the permission of all the files of example directory to 777 then you need to use chmod -R 777 example command as shown below. A command line / terminal window ( Ctrl + Alt + T or Ctrl + Alt+F2) A user account with sudo privileges (optional) A Linux system. Further, the ownership of files also depends on the uid (user ID) and the gid (group ID) of the creator, as discussed in this.
Chmod octal value file-name. The owner of a file can change the permissions for user (u), group (g), or others (o) by adding (+) or subtracting (-) the read, write, and execute permissions. Assign execute permission to user and group in file.
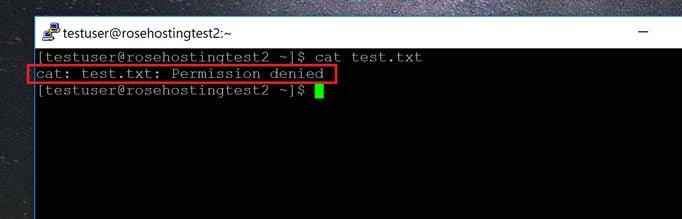
For example, I created a test.txt file and added some text. This can be achieved by changing file permissions. You can then execute it like this:.
The format of the digits are:. Changing file/directory permissions with 'chmod' command. For example, if you can’t open a script file, you can add permission for the owner to execute with:.
To change file and directory permissions, use the command chmod (change mode). The equals sign (" = ") means "set the permissions exactly like this," and the letters " r ", " w ", and " x " stand for "read", "write", and "execute", respectively. We can copy given file permissions to the specified file.
Ls -l new_ file.txt. We want the user dave to have read and write permissions and the group and other users to have read permissions only. Chmod 775 /path/to/file chmod command uses & Explanation.
To remove the write permission for others for file2:. We will use --reference option and the reference file name. EXAMPLES chmod -w nowrite makes file nowrite read-only.
The command can accept one or more files and/or directories separated by space as arguments. Sudo chmod g-w /my/directory/ The Numeric Mode. Abhinav@ETHICALHACKX:~/dir1$ chmod u-r file1 abhinav@ETHICALHACKX:~/dir1$ cat file1 cat:.
Chmod is a command to change permission of a file. Examples of Using chmod command Assign permission to a File. Chmod -R 777 ./ If you need more info about chmod command see:.
Examples Deny execute permission to everyone:. Chmod a+r file Make a file readable and writable by the group and others:. Here I have a file named file.txt.
To assign reasonably secure permissions to files and folders/directories, it's common to give files a permission of 644, and directories a 755 permission, since chmod -R assigns to both.

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux

Solved File Permissions In Linux Can Be Set Using A 3 Dig Chegg Com

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight
Chmod File Permissions Example のギャラリー

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Unix File Access Permissions Unix Chmod Chown And Chgrp

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples
Freekb Linux Commands Chmod Change A File Or Directory Standard Permissions
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Linux Users And Groups Linode

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct
Chmod Jessica Peng
Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Linux File Permissions And Chmod Doug Vitale Tech Blog
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)
How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux

Chmod Command In Unix Learn Unix Online Fresh2refresh Com

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint
How To Set And Manage File Permission In Linux Part 1

Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube

Chmod Wikipedia

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

Recommended File Permissions For Wordpress Asdqwe Dev

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples
/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

11 Popular Unix Linux Chmod Command Examples To Change File Permissions Cyberithub
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org
How To Chmod Files Only On Linux

Linux File Permissions Chmod Umask Tutonics

Chmod Recursive Change Permissions Recursively On Files Folders

Unix Permissions

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

Understanding File Permissions 2buntu

Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu

Ownership And Permissions
How To Deny File Permissions To Everyone Except Yourself In Linux Linuxhostsupport

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

Unix Command Line Basics 4 Permissions Lennoxfiles
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau

How To Change File Permissions Hostwinds Guides
How To Display File Permissions In Octal Format In Linux Kompjuteras

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Linux File Permission Javatpoint

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight

Chmod Ftp File Permissions Stadtaus Com

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Unix Commands Changing Permissions Dreamhost Knowledge Base

Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets
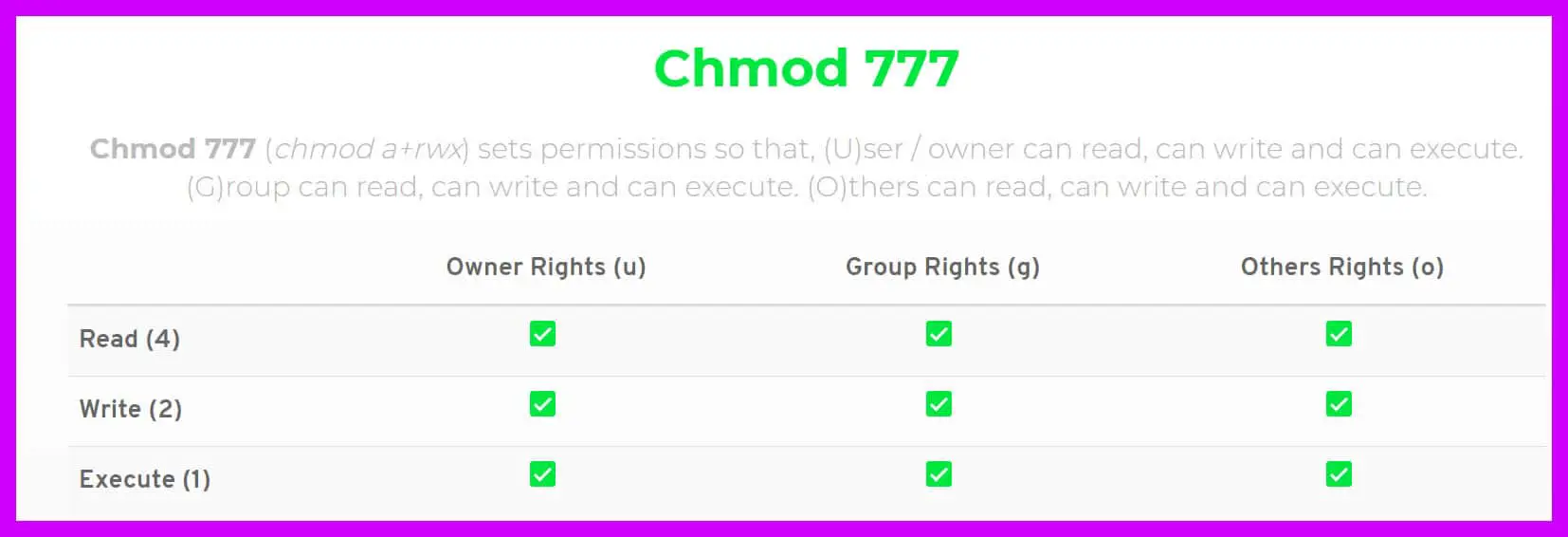
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions
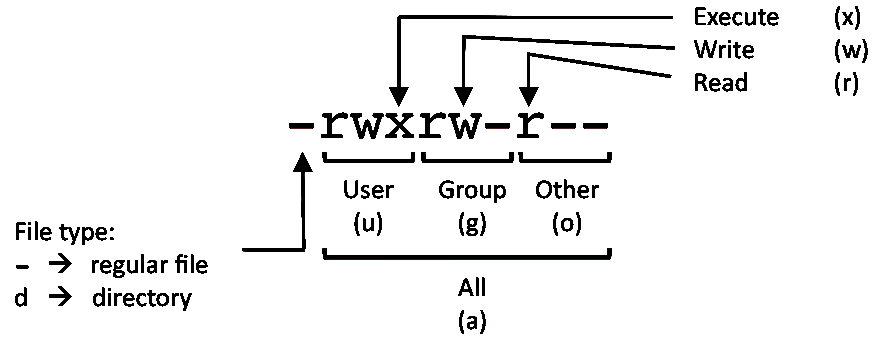
Linux Command Cheat Sheet

Understanding File Permissions

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

File Security

What Are User And Group Permissions 荷树栋 开发者的网上家园

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
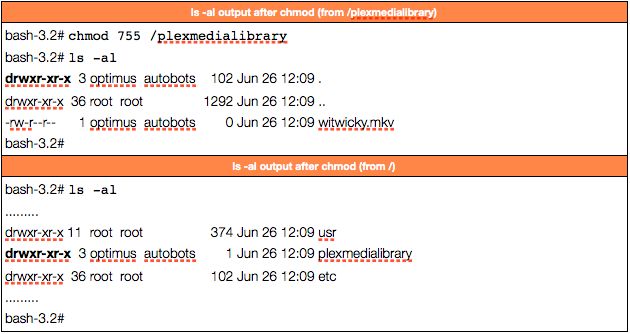
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support
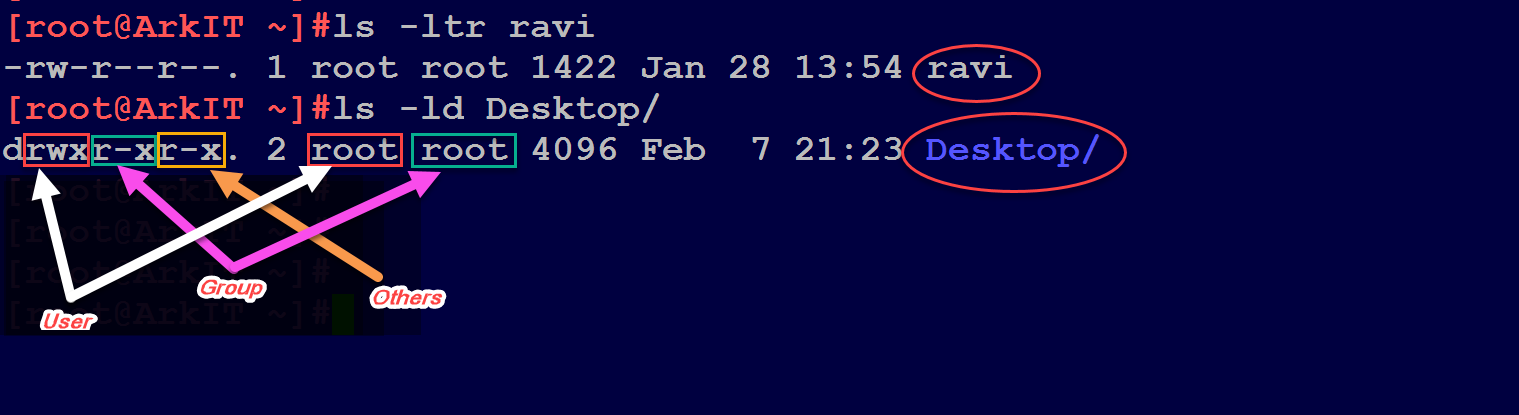
Chmod Command Understanding How To Grant File Permissions

Is There A Web Based Converter Between Rwx And The Octal Version Unix Linux Stack Exchange
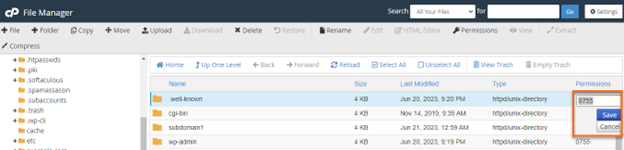
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

How To Modify The File S And Directories Permission In Linux Vasanth Blog

Unix File Permissions Computer Science

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin
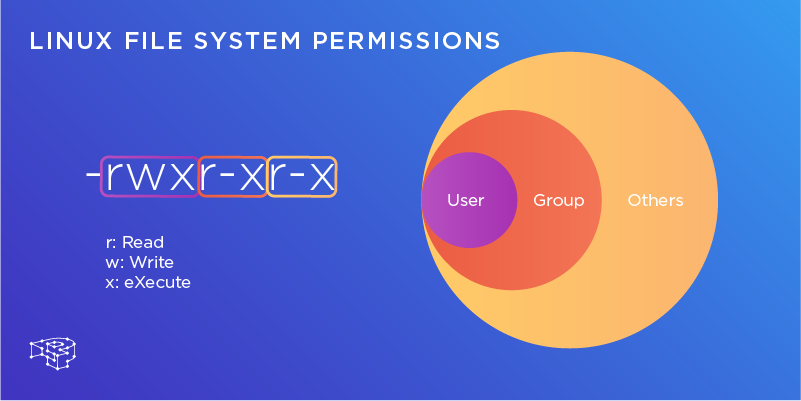
Deciphering Linux File System Permissions Pressidium Managed Wordpress Hosting

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions
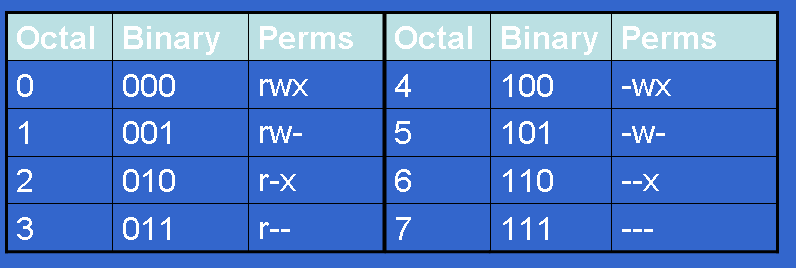
Controlling File Permissions With Umask
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr2lfpzbutqythmvbwafnxvyggqfj7hnw6fhh Kcozkk8m5 V7o Usqp Cau

Linux Chmod Command Help And Examples

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Laptrinhx
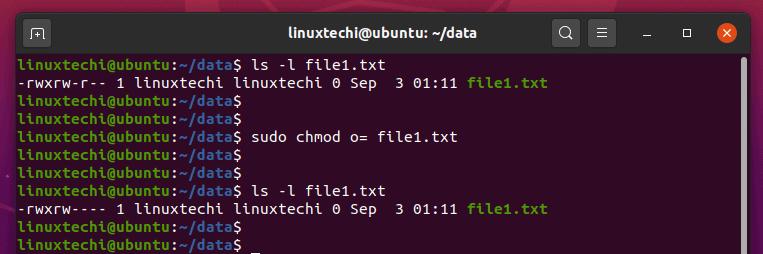
9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux
Github Fed Command Line Cheatsheet Unix Command Line Cheatsheet

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Understanding Linux File Permissions With Chmod Umask Chown And Chgrp Liquidon Net
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

How To Change File Permissions Recursively With Chmod In Linux

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau

Pin By Dr Stefan Gruenwald On Cheatsheets Computer Science Programming Learn Javascript Linux Operating System

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

Unix Linux Os X File Permissions

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners

Linux File Permissions For Beginners

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech
Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube
Chmod Command In Unix Unix File Permissions Chmod With Examples Chwn Command Chgrp Command Unmask

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Linux File Folder Permissions

Understand Linux File Permissions Using Chmod And Chown Commands Programming Tips For Versatile Coders



