Chmod File Permissions Ubuntu
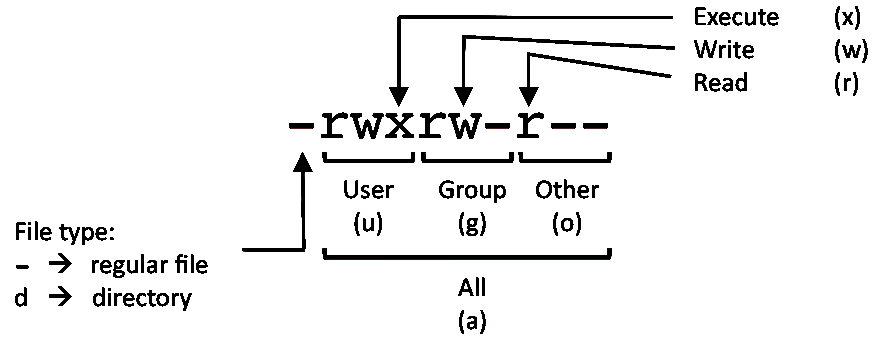
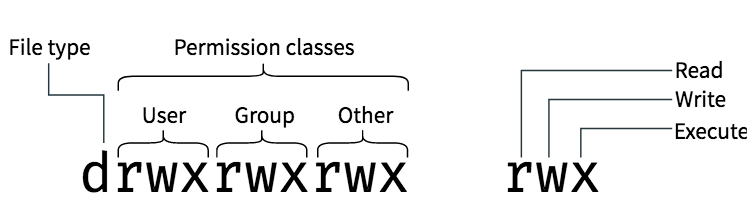
User - What the owner of the file can do Group - What users of the same group can do Other - What anyone else can do.
Chmod file permissions ubuntu. Chmod -R MODE DIRECTORY. Chmod 660 sentiment.pem After the update, the permissions were set to:. The chmod command stands for change mode … and it’s used to limit access to resources….
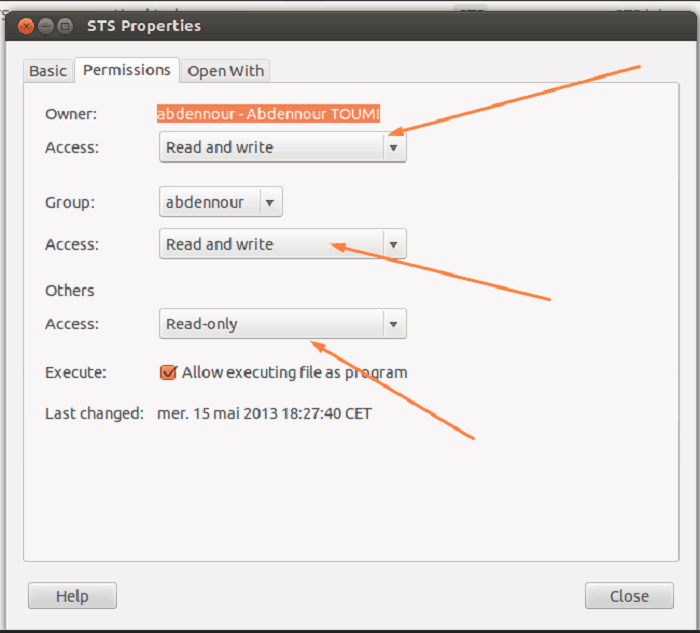
Owner – The Owner permissions apply only the owner of the file or directory, they will not impact the actions of other users.;. All files have three types:. There will be a Permission tab where you can change the file permissions.
Let’s see the chmod options for the permissions:. By - Linux tutorial - team. We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article.
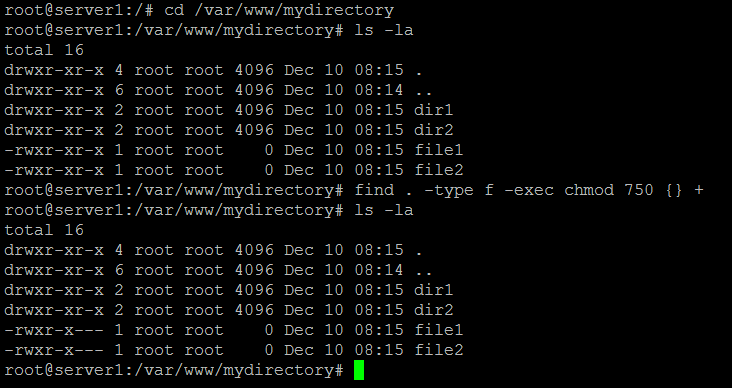
-type f -exec chmod 750 {} +. File permissions are identified through file mode bits. Show activity on this post.
Other people in the same group as the owner;. $ ls -l file* -rwxr-xr--. # mv /tmp/chmod /usr/bin Method 6 - Using Busybox.
Chmod +x filename to allow executable permissions. Chmod -R a+rX * The X (that is capital X, not small x !) is ignored for files (unless they are executable for someone already) but is used for directories. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions of files using symbolic or numeric mode.
In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of permissions. If no options are specified, chmod modifies the permissions of the file specified by file name to the permissions specified by permissions. Chmod command is used to set permission bit on file or directory.
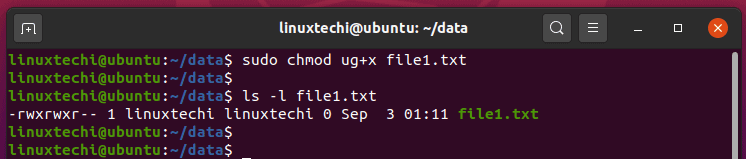
1 lrendek lrendek 0 Apr 7 14:40 file2 Both files have different permissions. $ chmod u+r,g+x filename 3. One can use file permissions to control access to their files.
You can change permissions using characters or number. Press Alt + F2 to access the "Run Applications" dialog and enter gksu nautilus Next, browse to and right click on the folder you would like to modify. Linux Command with Examples.
1 lrendek lrendek 0 Apr 7 14:39 file1 -rw-rw-r--. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file. In short, “chmod 777” means making the file readable, writable and executable.
Use comma to separate the multiple permission sets as shown below. Sample output:-r-xr-xr-x 1 root root May 27 10:01 /tmp/chmod. Linux file permission is a very important aspects in terms of security issues for the system administrator of Linux Operating System.
If the permissions are OK, simply overwrite the original file with /tmp/chmod file:. The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file. Simply enter this line:.
In the above command, source-file is the file whose permission bits you want to copy, and destination-file is the file whose permission bits you want to change. Navigate to the target file or folder. In Linux, you can easily change the file permissions by right-clicking the file or folder and select “Properties”.
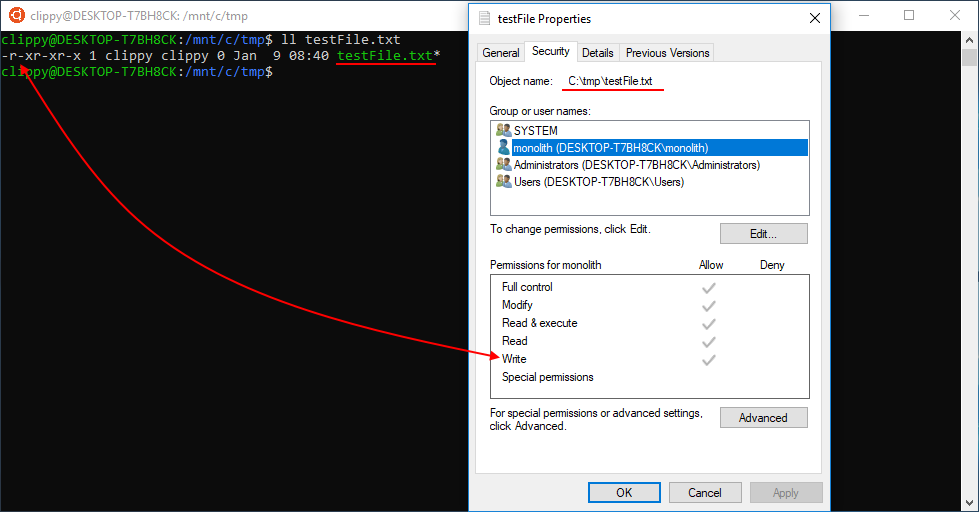
In this article you will learn how file permissions work and how you change file permissions using chmod command. We’ve added new file system features to WSL in Insider Build 1706 3.You can now set the owner and group of files using chmod/chown and modify read/write/execute permissions in WSL. Change permission for all roles on a file/directory.
How to Use chmod Command. A symbolic modehas the form. Let’s say you need to allow everyone to gain read/write permissions to the folder TEST.
If you need a more in-depth guide on how to use Chmod In Linux to change file permissions recursively, read our Chmod Recursive guide. For example, you could set the metadata to display that you have write permissions to a file using chmod 777, but if you tried to access that file you would still not be able to write to it. How to Copy Files and Directories in Ubuntu.
Change permissions If you want to change permissions you need to use chmod. The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders. It also allows to clone/copy permissions of one file to another.
Permissions defines the permissions for the owner of the file (the "user"), members of the group who owns the file (the "group"), and anyone else ("others"). Sudo chmod -R a+w /var/www But if you want to use the literal permissions of read/write, you may want to select files versus folders:. For example, if you want the owner to have all the permissions and no permissions for the group and public, you need to set the permission 700 in absolute mode:.
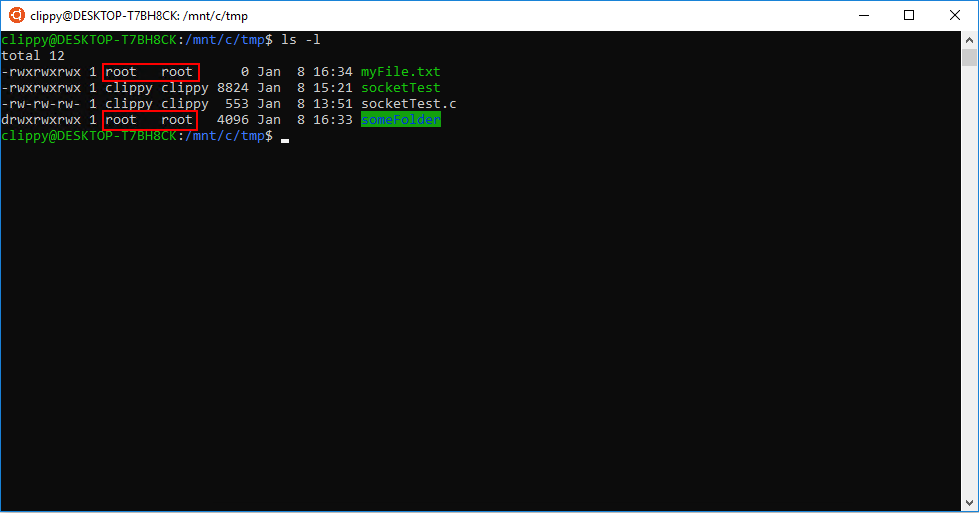
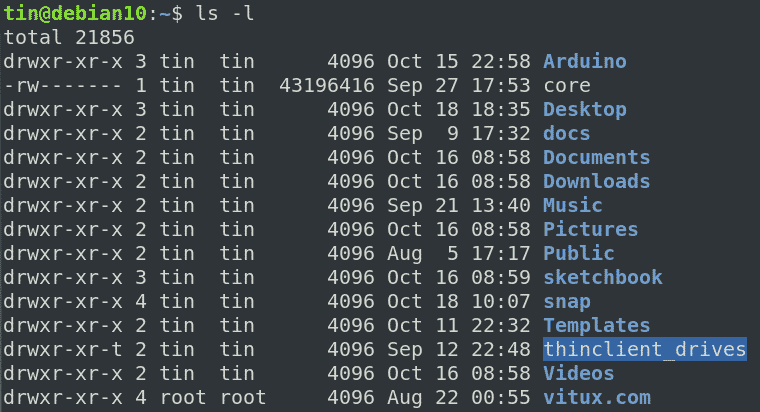
Cd /var/www/mydirectory find. If you want to set permissions on all files to a+r, and all directories to a+x, and do that recursively through the complete subdirectory tree, use:. In linux terminal, to see all the permissions to different files, type ls -l command which lists the files in the working directory in long format.
For example we have two files with following permissions:. How to Set File Permissions Using `chmod' Files and directories in Unix may have three types of permissions:. Owner – Person or process who created the file.
$ chmod u-rx filename 4. How to use Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (e.g. Each permission may be `on' or `off' for each of three categories of users:.
You can also create special files like fifos, unix sockets, and device files. Run this command to get the permissions of every file/directory on the system:. Hope most of the things work (not everything will work I believe).
And you can do the same thing for file ownership as well. Chmod -R a+rX * click below button to copy the code. To add permissions for a user, we can use following combinations – chmod u+r ABC.txt chmod u+w ABC.txt chmod u+x ABC.txt.
The syntax for changing the file permission recursively is:. Chmod +rwx filename to add permissions. Actually, chmod Command in Linux plays a greater role to keep all the files and directories of the system safe and secure so that no unauthorized person.
To do this, within the Nautilus file manager, follow these steps:. Changing User File and Group Ownership Aside from changing file permissions, you may come across a situation that requires changing the user file ownership or even group ownership. The file or directory owner;.
The chmod command is used to define or change permissioins or modes on files and limit access to only those who are allowed access… It changes the mode of each FILE to MODE…. Chmod 700 filename You can do the same in symbolic mode. If you are doing a relative change (like adding write permission for everyone), you can do this:.
Who op permission op permission. For example, if you run the command ls -l to list the files in the current directory, you'll see something similar to this at the beginning of each line in the results:. Take a new file's group from.
Moving on further, there's also a numerical notation (also known as octal representation) using which you can tell chmod to change permissions. Let’s say you are currently in the root directory of your Unix-like system and you want to change the file permissions of a folder and all of the other files and sub-directories present inside that folder. Myfile.txt – the name of the file/folder.
Recursive chmod using find, pipemill, and sudo. Linux File Permission :. If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command.
Read – r or 4write – w or 2execute – x or 1 chmod options for user:. Note that “r” is for read, “w” is for write, and “x” is for execute. If you want to set permissions on all files to a+r, and all directories to a+x, and do that recursively through the complete subdirectory tree, use:.
Chmod permission1_permission2_permission3 file When using chmod, you need to be aware that there are three types of Linux users that you are setting permissions for. I’m going to demonstrate changing file permissions using the Nautilus file manager on an Ubuntu 13.10 system. With those permissions the paths you mention and /usr/local/ssl should be fine.
$ ls -l /tmp/chmod. I updated the file permissions to:. Chmod 744 file name By executing this command, the owner can read, write, and execute the file (rwx).
Chmod -rwx directoryname to remove permissions. To assign reasonably secure permissions to files and folders/directories, it's common to give files a permission of 644, and directories a 755 permission, since chmod -R assigns to both. Mandatory locking, as described in fcntl(2);.
Chmod Modifies File Permissions. Type “sudo chmod a+rwx /path/to/file” into the terminal, replacing “/path/to/file” with the file you want to give permissions to everyone for, and press “Enter.” You can also use the command “sudo chmod -R a+rwx /path/to/folder” to give permissions to a folder and every file and folder inside it. In such cases, the chmod recursive option (-R or --recursive) sets the permission for a directory (and the files it contains).
Read (r), write (w), execute (or search for directories) (x), execute/search only if the file is a directory or already has execute permission for some user (X), set user or group ID on execution (s), restricted deletion flag or sticky bit (t). Some recent Linux distributions have "Busybox" installed by. In the terminal, the command to use to change file permission is chmod.
Each file and directory has three user based permission groups:. Chmod -wx filename to take out write and executable permissions. Please keep in mind that you cannot give yourself more access than what you have on Windows, even if the metadata says that is the case.
This is thanks to interopability, as any read or write. Next, check if the executable permission is assigned to chmod:. X Permission to execute the file, or, in the case of a directory, search it.
Sudo find /var/www -type f -exec chmod 666 {} \;. It is common to use the basic chmod command to change the permission of a single file. Execute that file chmod +x /tmp/chmod.sh && /bin/bash /tmp/chmod.sh;.
Read (`r'), write (`w'), and execute (`x'). You can now select the user or group that you would like to be the "Owner" of the folder as well as the permissions you would like to grant them. Symbolic Mode The format of a symbolic mode is a combination of the letters +-= rwxXstugoa Multiple symbolic operations can be given, separated by commas.
Let’s say we want to change Linux file permissions from -rwxrw-rw-to -rwx-r–r–. Understanding file permissions for chmod and chown command. The general syntax to recursively change the file’s permissions is as follows:.
Chmod will change or add metadata depending on the file's already existing metadata. Group – The Group permissions apply only to the group that has been assigned to the file or directory, they will not effect the actions of other users. Changes the access permissions of all files and subdirectories under adirectory if one is specified as a path name on the command line.
Rwxrwxrwx ) to see its value in other formats. I have tried to SSH into my AWS Ubuntu server and copy the directory to my local machine. Change into the directory with cd, before you run the find command.
Sysadmins can enforce a security policy based upon file permissions. There are three sets of permissions. Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty Images.
To recursively operate on all files and directories under a given directory, use the chmod command with the -R, (--recursive) option. These users are technically know as:. To set file permissions, however, you’ll need to click on the arrow next to the “Sharing & Permissions” option.
File permissions explained in this post. How to Change File, Directory Permissions in Linux. Chmod file has metadata.
You can specify the modevalue on the command line in eithersymbolic form or as an octal value. Chmod 444 file - Allow read permission to owner and group and world chmod 777 file - Allow everyone to read, write, and execute file. If you would like to copy permissions and or ownership from another file that you're satisfied with, you can do so using sudo chmod --reference=path/to/file/to/reference path/to/file/you/want/to/change/permission/to.
The permissions control the actions that can be performed on the file or directory. One of the easiest ways is to use the find command to select the files and then run the chmod command with the -exec switch. Types of permissions which we will be changing using chmod command :.
Set permissions on files & directories using chmod in Ubuntu. The letters rwxXst select file mode bits for the affected users:. Copy the file chmod.sh to the computer with the wrong permissions;.
There are three sets of permissions to worry about with any directory/file:. First, we will discuss user related permissions – this will make modifications to first three characters aforementioned. Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers.
File permission defines which file has read,write,execute permission and for which user group. Then, select "Properties" from the context menu. There's not really an unsafe place if permission for the individual files/directory is set to something like chown root :0 private.key and chmod 600 private.key so that only root can read it.
Chmod Command in Linux Linux File Permission Introduction to Linux File Permission. Following example removes read and write permission for the user. Remove permission from a file/directory.
These bits represent what actions can be carried out by specific user accounts. CSRs and certificate files are less sensitive as you say. However, group and others are only allowed to read (r–).
Therefore, when setting permissions, you are assigning them for yourself, "your group" and "everyone else" in the world. Find / | xargs stat -c 'chmod %a "'%n'"' > /tmp/chmod.sh;. To change directory permissions in Linux, use the following:.
The command can accept one or more files and/or directories separated by space as arguments. One set for the owner of the file, another set for the members of the file’s group, and a final set for everyone else. Chmod is a very helpful command to change the file permissions of a file or a folder in any UNIX-like operating system.
Using chmod command is very easy if you know what permissions you have to set on a file. Use sudo, the find command, and a pipemill to chmod as in the following examples. However, you may need to modify the permission recursively for all files within a directory.
There are several ways to apply a chmod to files recursively on Linux. S_ISUID () set-user-ID (set process effective user ID on execve(2)) S_ISGID (000) set-group-ID (set process effective group ID on execve(2);. 777 ) or symbolic notation (e.g.
The new file permissions are specified in mode, which is a bit mask created by ORing together zero or more of the following:.

Pin By Dr Stefan Gruenwald On Cheatsheets Computer Science Programming Learn Javascript Linux Operating System
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau

Ssh Permissions Are Too Open Error Stack Overflow
Chmod File Permissions Ubuntu のギャラリー

Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube
Linux Commands Cheat Sheet Linux Training Academy

Command Line I Can T Change Mode For Some Directories Using Chmod Ask Ubuntu
What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Chmod Command In Linux File Permissions Linuxize

What Does Chmod 777 Mean Linuxize

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
Set Permissions On Files Directories Using Chmod In Ubuntu Techpiezo

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

Linux File Permissions Tutorial For Beginners
Change File Permissions Recursively Linux Linux Hint
9 Quick Chmod Command Examples In Linux
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq2oq90gyu7qjtwwppsiodhgqotjbz3awrstnhczkm6hwgdiahx Usqp Cau

Linux File Permissions And Chmod Doug Vitale Tech Blog
How To Chmod Files Only On Linux

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube

Xampp Htdocs Permission Issue And Fix In Ubuntu

How Do Linux File Permissions Work

Chmod Change Permissions To A Specific User In Ubuntu 12 04 Ask Ubuntu
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux

Ubuntu Forums

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint

Ubuntu Archives

Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line

How To Change The Permission Of File In Ubuntu Youtube

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line

Advance File Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Command Line How To Make A File Executable Ask Ubuntu

Set Pem File Permissions For Aws Without Chmod On Windows Stack Overflow

Chmod Wikipedia
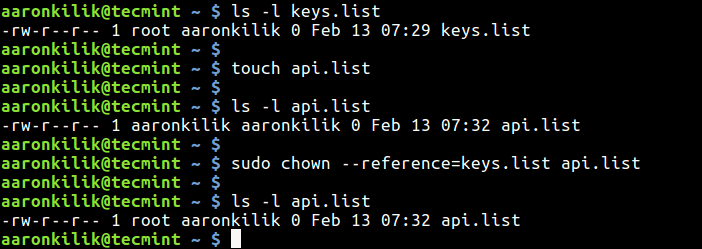
How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

How To Manage File Permissions On Ubuntu Server 04 Dev Tutorial

How To Use The Chmod Command On Ubuntu 16 04 18 04 With Examples Website For Students

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Command Line Change Folder Permissions And Ownership Ask Ubuntu
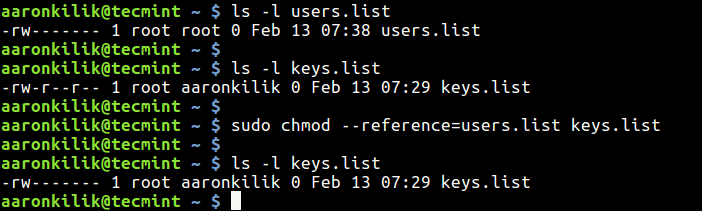
How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube

How To Manage File Permissions On Ubuntu Server 04 Dev Tutorial

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix
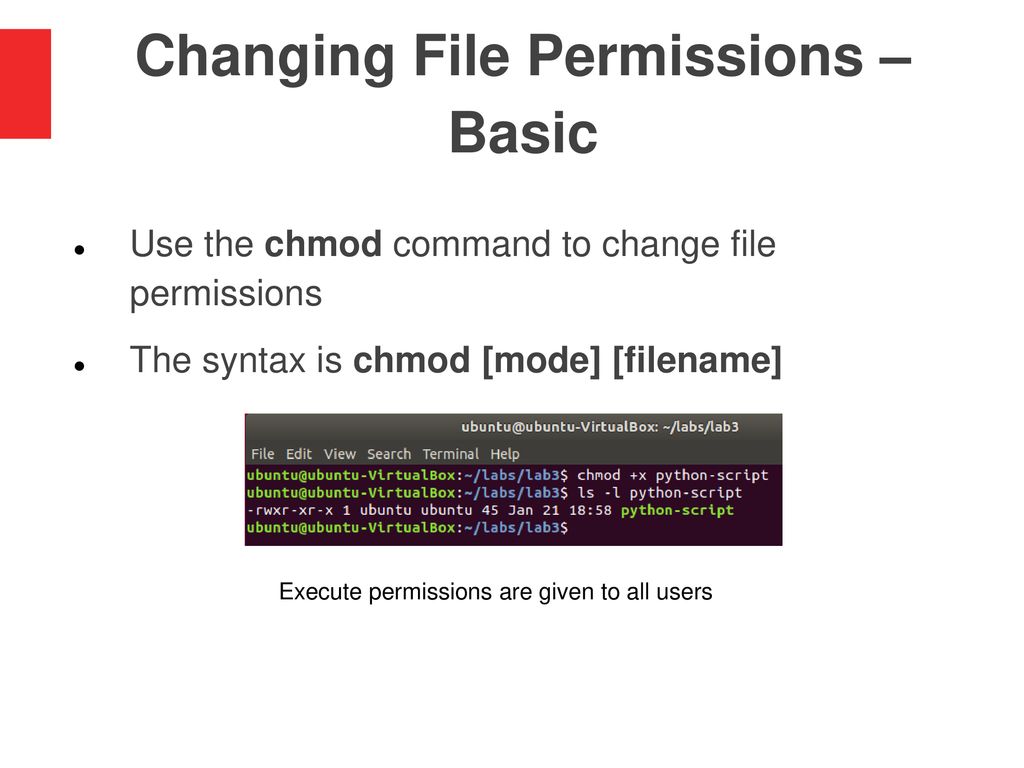
Lab 3 File Permissions Ppt Download

16 04 How Do I Use Chmod To Make Sh Files Executable Ask Ubuntu

Xampp Htdocs Permission Issue And Fix In Ubuntu

Ownership And Permissions

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Linux File Permissions For Beginners

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World
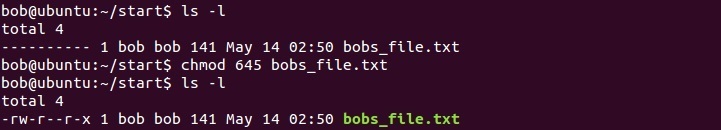
Modify File Permissions Linux

Change Ownership And Rights To Files And Folders In Linux Smashing Lab

Directory How Can I Change Permissions Of A Folder Including Its Enclosed Files And Subdirectories Ask Ubuntu

Linux File Permissions Chmod Umask Tutonics Linux Unix Coding

8 Linux Chmod Command Examples To Understand It The Linux Juggernaut

Understanding File Permissions 2buntu
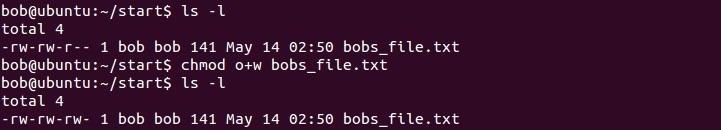
Modify File Permissions Linux

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Introduction To Linux File Permissions Attributes Chmod Globo Tech
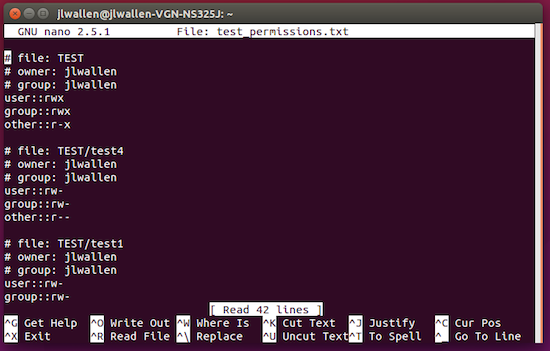
How To Easily Back Up And Restore Linux File Permissions Linux Com

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples

How To Give Read Write Permissions To A Folder In Ubuntu Code Example

Change File Directory Permission Using Chmod And Chown In Ubuntu Linux
1

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices

How To Use File Permissions In Linux 9 Steps With Pictures
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/i7guGwCYcn-34e068e148ae4e918b29c86cd2d5740e.png)
Configuring Unix Linux File And Directory Access Rights

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Jijo K Jose Jijokjose Personal Website How To Change Permission To A Folder And All Of Its Subfolders In Linux Ubuntu Terminal Jijo K Jose

Linux Users And Groups Linode

Permission Denied Inside Var Www Html When Creating A Website And It S Files With The Apache2 Server Stack Overflow

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Your Own Linux Chmod Basics Of Files Directories Permissions And Use Of Chmod

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier
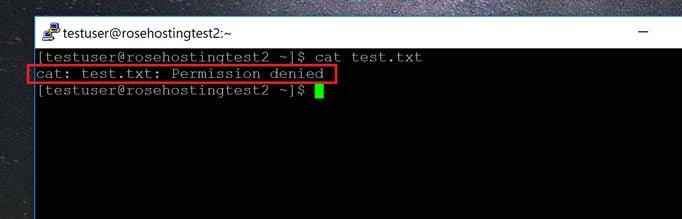
How To Deny File Permissions To Everyone Except Yourself In Linux Linuxhostsupport

Linux Users And Groups Linode

An Introduction To Linux Permissions Digitalocean
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs J72hjomdluhqe6xjivy M6yrjmkqx9x3z3ps Rpnb8by3w7z Usqp Cau

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

Linux File Permissions Chmod Umask Tutonics

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected



