Linux Chmod Permissions Table
The request is filtered by the umask.The name is an abbreviation of change mode.

Linux chmod permissions table. Set permission in Linux using chmod:. Chmod -R 755 myfiles. It’s usually used when installing and configuring various services and features in a Linux system.
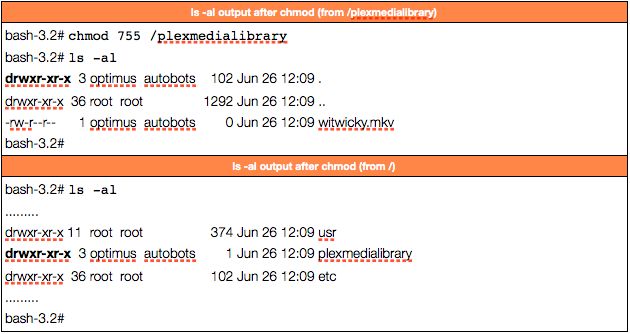
Changing permissions using “chmod”. It allows the permissions to be changed in either Symbolic form or in numerical form. Running chmod 770 on project-a gives us the permission set we want:.
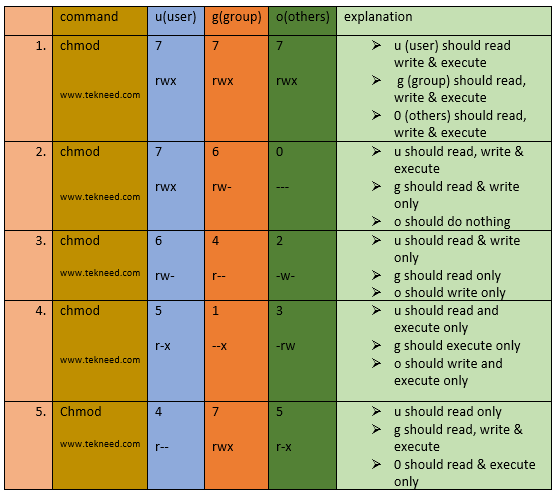
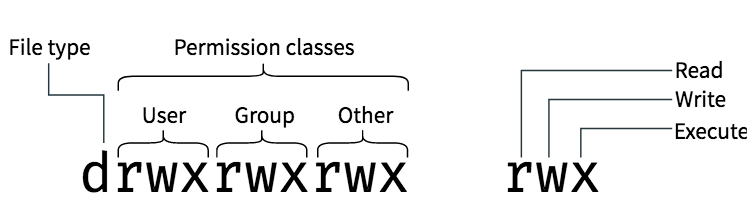
777 = rwxrwxrwx 755 = rwxr-xr-x 644 = rw-r--r-- 700 = rwx----- 750 = rwxr-x---. Unlike files, a directory has files in it. Others have read permissions represented by the last bits:.
Mykyta Dolmatov / Getty Images. In Linux, you may face permission problems while installing software packages, exploring directories, reading/writing files. You must be superuser or the owner of a file or directory to change its permissions.
To meet our goal, we will run:. The Linux command chmod allows you to control exactly who is able to read, edit, or run your files. View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 700 (chmod a+rwx,g-rwx,o-rwx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily.
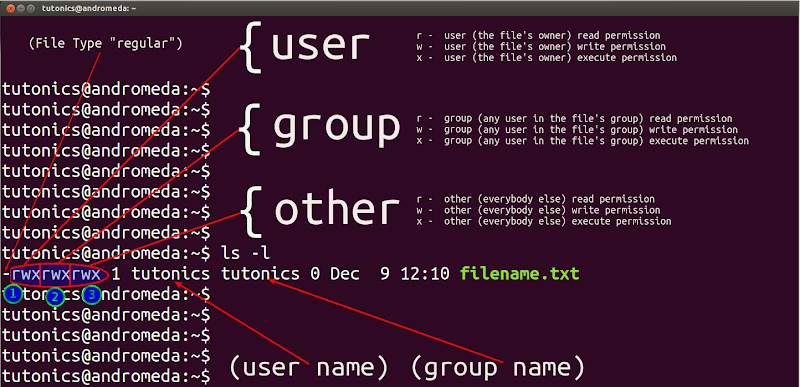
Sudo chmod XXX -R directory-location. Chmod is a command in Linux and other Unix-like operating systems that allows to change the permissions (or access mode) of a file or directory. One set for the owner of the file, another set for the members of the file’s group, and a final set for everyone else.
Linux Permissions Syntax You can use this table to understand the different symbolic or octal value to use with chmod Perform chmod recursive with -R or --recursive If all your files and directories are under one parent directory then you can directly use chmod -R <dir_name> to assign the permission recursively. A compiled list of 30 exercises about linux permissions, the binary system, chmod, chgrp and chown. Fileforchmod = file name.
Using chmod with Absolute Permissions The second way to modify permissions with the chmod command is to use a number to specify each set of permissions for the file. The highly productive Linux system offers various levels of permission to ensure that the user has enough ways to interact with files and directories. The chmod command enables you to change the permissions on a file.
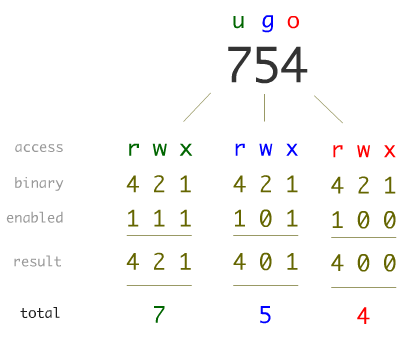
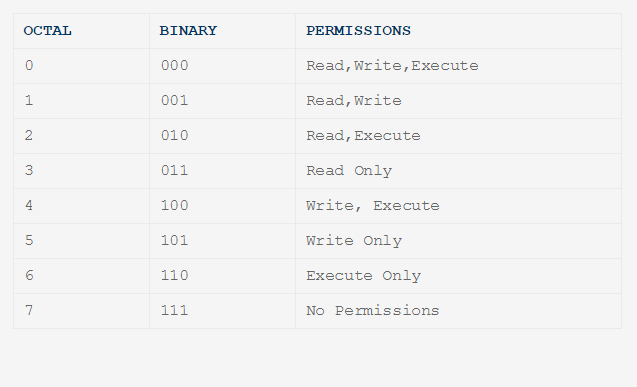
I have to change the permissions of the htdocs directory in apache to a certain group and with certain read/write/execute. In this article, I will take you through 11 Popular Unix/Linux chmod command examples to Change File Permissions. User Group Other Read 4 4 4 Write 2 2 2 Execute 1 1 1 U G O X X X Chmods:.
Examples chmod 644 file.htm. CHMOD Permissions Reference Chart. Chmod options mode filename filename1… chmod options mode directory_name.
Others can read only". Absolute Mode – Use numbers to represent file permissions (the method most commonly used to set permissions). The “mode” consists of three parts:.
The following table shows some commonly used settings. While trying to debug a mail server, I typed:. Let's say the directory chmod_directory was created with the default permissions of 755.
This is how I remember permissions and most likely, it will help you remember it as well. The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders. Here is a short note/cheat sheet for Linux directory and file permissions.
To copy the permissions of one file to another, you can use the reference option of the chmod command. You can use the chmod command to set permissions in either of two modes:. Recursively (-R) Change the permissions of the directory myfiles, and all folders and files it contains, to mode 755:.
Rwxrwx--- How does 770 correspond to rwxrwx---?. Say you do not want your colleague to see your personal images. Linux chmod command is one of the most commonly used commands especially by system administrators when assigning modifying file and folder permissions.
The name speaks for itself. Each of the three digits in our chmod statement — 7, 7, 0 — corresponds to Owner, Group, and Others rights. Both forms can be interchangeably used.
Group – The Group permissions apply only to the group that has been assigned to the file or directory, they will not effect the actions of other users. In Linux systems, the chmod command is used to change the permissions and access mode of files or directories. You must be superuser or the owner of a file or directory to change its permissions.
Select the permissions you require below. How to Set File Permissions Using `chmod' Files and directories in Unix may have three types of permissions:. Chmod -R 777.
Below is the command's general structure:. You can also simply navigate to the folder (Using cd command) where you want to apply the permissions to all of the folder contents and run the following command. In Unix and Unix-like operating systems, chmod is the command and system call which is used to change the access permissions of file system objects (files and directories).It is also used to change special mode flags.
Chmod = calls the program to change permissions. Rwxrwxrwx ) to see its value in other formats. The file’s group creator (group) has read permissions:.
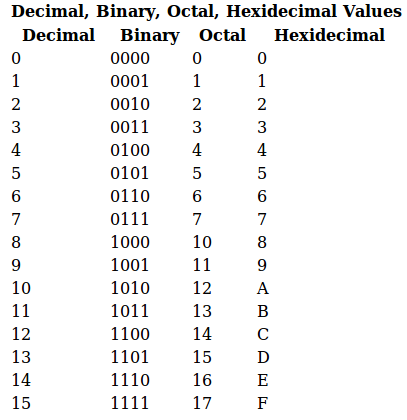
The table below gives numbers for all permission types of a File/Directory. When running chmod we need first to define over who the permission or restriction is applied, if we want to add or rest a permission, what permission and what file for. In this lesson we will focus on one of these, called the octal notation method.
If you need a more in-depth guide on how to use Chmod In Linux to change file permissions recursively, read our Chmod Recursive guide. Chmod.(change mode) is a widely used command to change the permissions of files and directories.It allows the setting of user, group and other bits which each define what rights each classification of user has over the files. Who is specified as.
Exercises about the sticky bit included. Below is the table of file permissions and options which effects on file:. I don't want to change the directories manually.
Group members and other users can read and execute, but cannot write. Chmod is an abbreviation for change mode;. If you want an easy way to know the Linux file permission in numeric or symbolic mode, you can use this chmod calculator.
Linux Permissions are a great set of rules which. When using chmod, you need to be aware that there are three types of Linux users that you are setting permissions for. The permissions control the actions that can be performed on the file or directory.
How to change file permissions using chmod and chown. Here's an example using the testfile. There are three sets of permissions.
Just select the appropriate permissions and it will tell you the permissions in both absolute and symbolic mode. The chmod command is used to alter the permissions of a file. Conclusion # The chmod command changes the file’s permissions.
$ sudo chmod <specify the file permissions> <specify the file/directory name>. This article explains how to use chmod command to change the access permissions of files or directories. We can use chmod and chown to manipulate the file permission.
Group can read only;. I believe a script could fix it if it restored the permissions of the filesystem based on data from the package manager, but i do not know how I would go about doing this. There are three different possible user levels, each with three different possible settings.
If I do a recursive 664 to the htdocs, then all files and directories will change to 664. Learn about access modes such as suid, sgid, and the sticky bit and how to use them to enhance security. View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 600 (chmod a+rwx,u-x,g-rwx,o-rwx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily.
It may be used to add or remove permissions symbolically. The tool will provide you with an octal code that corresponds to these permissions which can then be applied to relevant directories and files with chmod. In Linux, files and directories are treated similarly.
To change the permissions — or access mode — of a file, use the chmod command in a terminal. Each permission is assigned a value, as the following table shows, and the total of each set of permissions provides a number for that set. How To Change File Permissions In Linux Using ‘chmod’ Command.
The directories need to have 775 permissions and the files need to have 664. The permissions can be set using either the symbolic or numeric mode. Read-It is not.
The main difference between access rights for files and directories is that the x permission on a file grants permission to execute it, where on a directory, it grants permission to enter it. Set the permissions of file.htm to "owner can read and write;. Therefore, when setting permissions, you are assigning them for "yourself", "your group" and "everyone else" in the world.
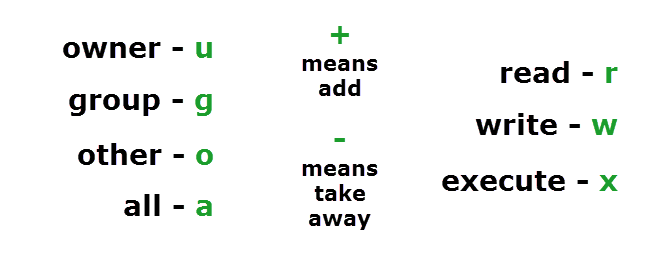
Using the command, we can set permissions (read, write, execute) on a file/directory for the owner, group and the world. The file or directory owner;. Chmod -R XXX.
The chmod command is used to change the permissions of a file or directory. You can add it to the make file or a script depending on what kind of scripting you know , to chmod it how you see fit when needed – pyCthon Feb 15 '12 at 2:22 1 Just so I get this straight:. There are two ways to specify the permissions.
This can be achieved by changing file permissions. It is a confusing topic until you learn it, but it is needed if you plan to work with UNIX or Linux web servers. Other people in the same group as the owner;.
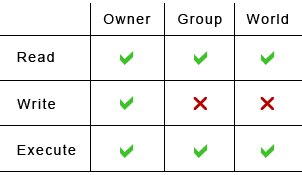
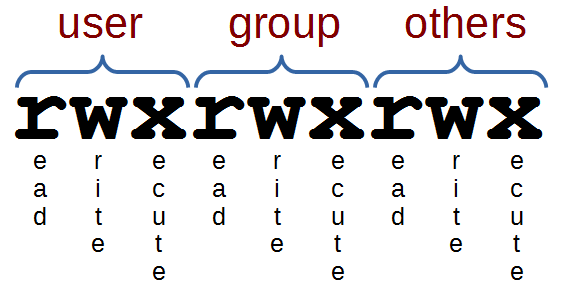
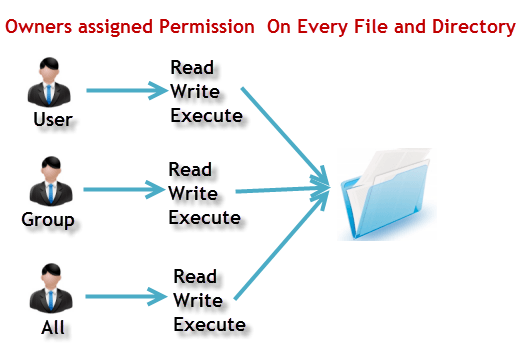
There may also a concern about security that permissions specify what a particular user may or may not do changes to a particular file and directory. Owner – The Owner permissions apply only the owner of the file or directory, they will not impact the actions of other users.;. Each file and directory has three user based permission groups:.
The chmod command enables you to change the permissions on a file. We can use the ' chmod' command which stands for 'change mode'. Chmod -R 777 / instead of:.
Linux SMB file share setup issues. Chmod is a UNIX and Linux command for setting file or directory permissions. In Linux, who can do what to a file or directory is controlled through sets of permissions.
How to use Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (e.g. In this quick tutorial, we will see how we can use chmod command in an Ubuntu machine to find, modify and remove user permissions from specific files which exist on the user’s file system. Changing User File and Group Ownership Aside from changing file permissions, you may come across a situation that requires changing the user file ownership or even group ownership.
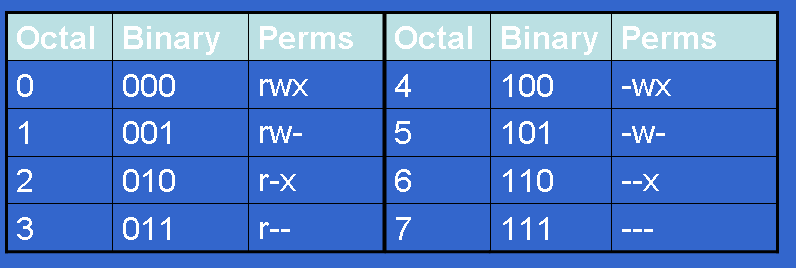
Each permission (nine total) is given a numeric value as shown in Table A. 777 ) or symbolic notation (e.g. This method can be memorized easily using the following table.
By using this command, we can set the read, write, and execute permissions for all three of the permission groups (Owner, Group and Other) in Linux. Chmod is used to make changes:. The chmod command only allows you to change the permission of files and directories that you own.
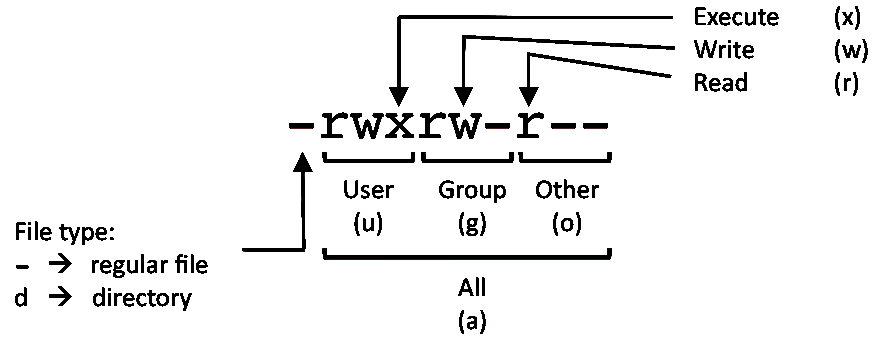
Therefore, full permissions for everyone on the system would look like:-rwxrwxrwx. The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file. Chmod stands for “ Change Mode ” and is used to modify the permissions of files and directories in a Linux based system.
User can read, write, and execute;. Chmod command is used to change the permissions of files and directories in Linux. Read (`r'), write (`w'), and execute (`x').
Let’s play through various conditions so that we can master basic chmod commands which can make our everyday life easier with Ubuntu. The find command will search for files and directories under /var/www/my_website and pass each found file and directory to the chmod command to set the permissions. Change permission on all the files in a directory recursively.
You can use the chmod command to set permissions in either of two modes:. To use it, we specify the desired permission settings and the file or files that we wish to modify. Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers.
Chmod Modifies File Permissions. You can use the material in this tutorial to study for the LPI 101 exam for Linux system administrator certification, or just to learn about file ownership, permissions, and security. You're copying an executable image elsewhere, looking for a certain pattern, modifying the binary image in place, and then plan on executing it again?.
Learn to manage file ownership and permissions on your Linux filesystems. In Linux, you will often need to make use of the chmod command. As an example, let’s clone the permissions of file1 to file2 using the following command:.
You can also use numbers (octal values) instead of letters to set the permissions. The three user levels are Owner, Group, and Other. Absolute Mode - Use numbers to represent file permissions (the method most commonly used to set permissions).
Rw = reading and writing rights. I hope this article has helped you in applying the chmod command to a folder and all of its contents. In case you need to change the permission of files and directories that you don’t own, you will need to use sudo.
Each permission may be `on' or `off' for each of three categories of users:. Additionally server-side languages provide functions that are roughly analogous to chmod in terms of operation using absolute notation. A = means “All” –= means minus, we are removing rights,not adding.
Users can simply modify file permissions using the chmod (change mode) command. If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command.

Execute Vs Read Bit How Do Directory Permissions In Linux Work Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Linux Chmod Command Linuxfordevices
Chmod Command In Unix Unix File Permissions Chmod With Examples Chwn Command Chgrp Command Unmask
Linux Chmod Permissions Table のギャラリー
How To Set And Manage File Permission In Linux Part 1

Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin
How Do I Set File Permissions For Files Scripts Or Directories Linux Accounts Only
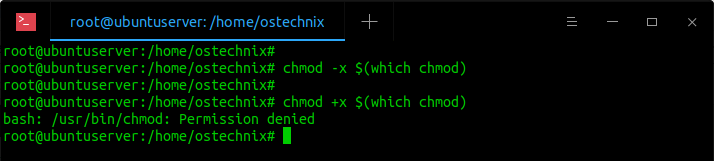
Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct

Linux Users And Groups Linode

How To Modify The File S And Directories Permission In Linux Vasanth Blog
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Use Of Chmod Command In Linux Devopsdex
Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Understanding Unix Permissions And File Types Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Unix Linux Os X File Permissions

File Security
Linux Chmod Tips
Linux Commands Cheat Sheet Linux Training Academy

Chmod Wikipedia
Solved This Is In Linux While Logged In As A Regular Use Chegg Com
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr9rnnth31jdnr94db Zmbdt5bh907clokeeor9me5yqbuufaiw Usqp Cau

Beginner S Guide To File Permission In Linux Sharing Is Caring

Managing Linux Permissions

Protect Your Data With Super Easy File Security Tricks

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage
Controlling File Permissions With Umask
Learn Oracle Database Administration Unix Permissions Table

Restore Executable Permission To Chmod Command In Linux Ostechnix

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

I Made This Chmod Cheat Sheet And Thought It Might Be Useful Linux4noobs

File Permissions Linuxhowto Net

How To Change Permissions And Owners Via Linux Command Line

Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

Permissions Why Am I Not Able To Use Chmod 000 For A Folder Ask Ubuntu

Understanding File Permissions

Linux Users And Groups Linode

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Linux File Permission Javatpoint
Read Just Enough Linux Leanpub

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint
Linux File Permissions Chmod Umask Tutonics

An Introduction To Linux Permissions Digitalocean

I Made This Chmod Cheat Sheet And Thought It Might Be Useful Linux4noobs

Linux Unix Permissions And Attributes Linuxsecrets

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples

File Permissions In Linux Unix Vk9 Security
Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
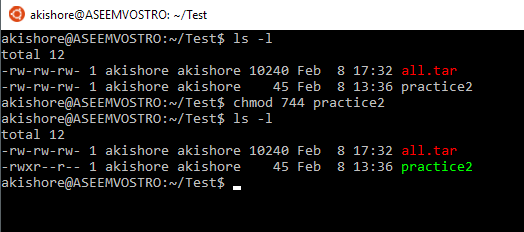
Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Understanding Basic File Permissions And Ownership In Linux The Geek Diary
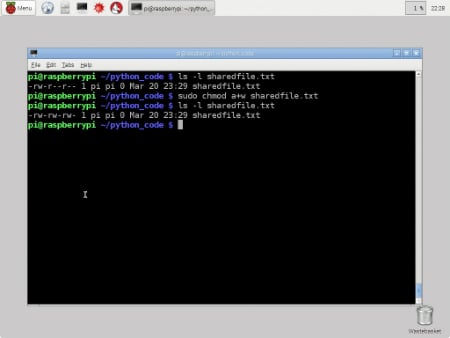
Working With File Permissions On Your Raspberry Pi Dummies

File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Chmod Change Permissions To A Specific User In Ubuntu 12 04 Ask Ubuntu

Csc128 Permissions And Links Chmod And Ls Linux Permissions Custom Sheds Lotus Elite

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs Trmaopb41lzfo2wl Mi6olorurkywaddbudhnw Ne1mor3ct Usqp Cau
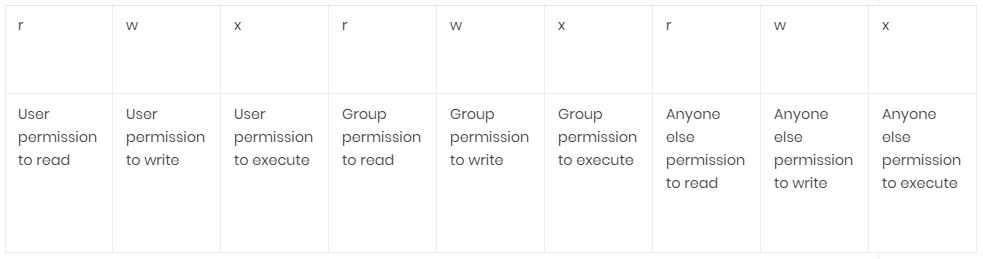
Linux Permissions Explained Linux Hint

Modifying File Permissions With Chmod Command In Gnu Linux Openforums

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

File Permission In Linux Chmod Command Armantutorial
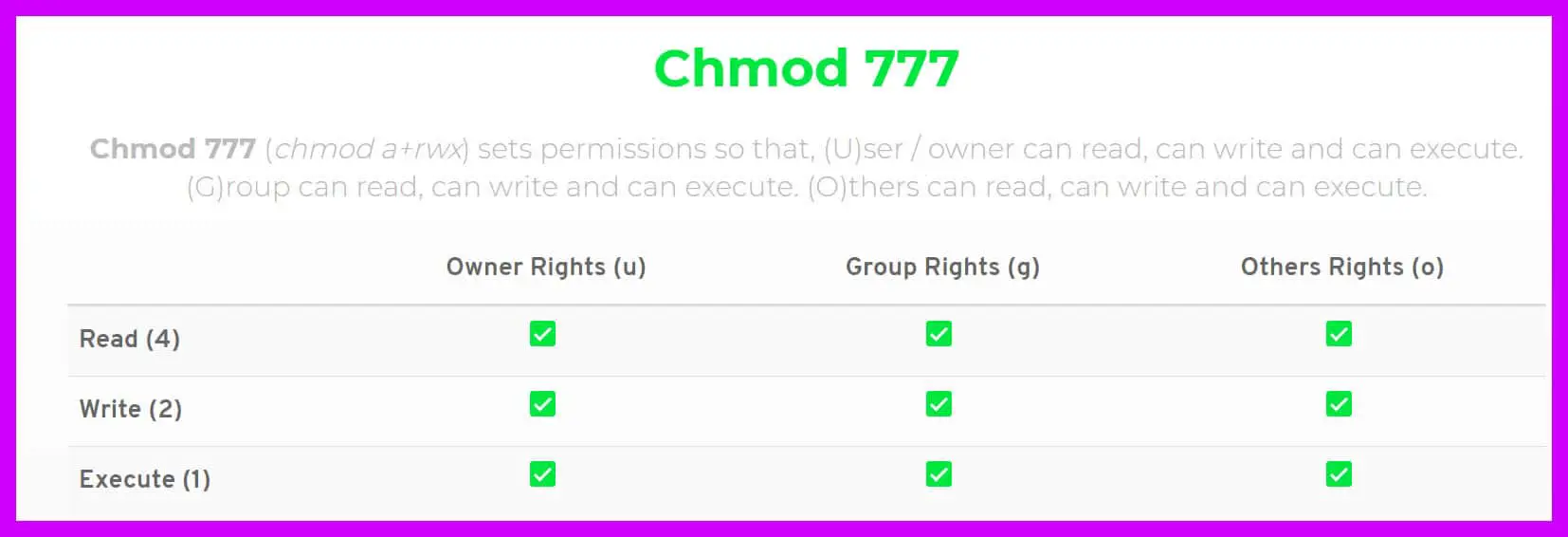
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

Understanding Linux Permissions And Chmod Usage

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support

Understand Linux File Permissions Using Chmod And Chown Commands Programming Tips For Versatile Coders

19b Permissions

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions
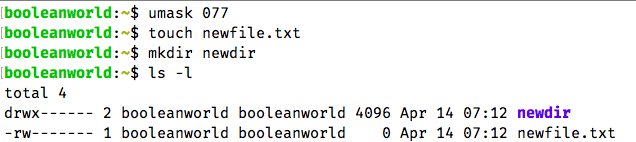
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example
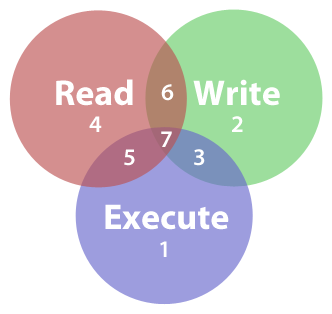
How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct
Verizon Droid Turbo Has Been Rooted Page 2 Droidforums Net Android Forums News
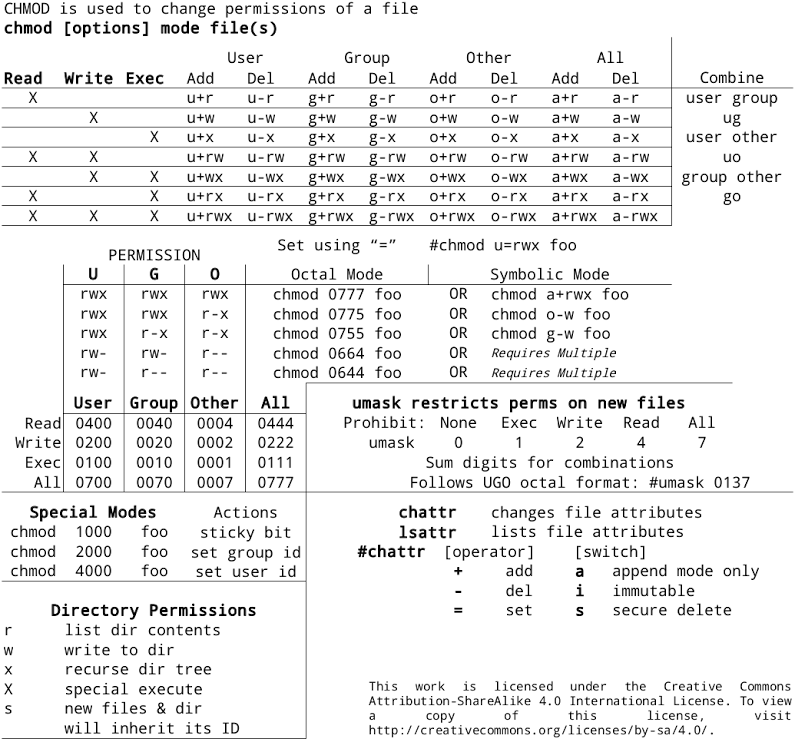
Linux Permissions Tables Reffffference

Linux Permissions Pluralsight
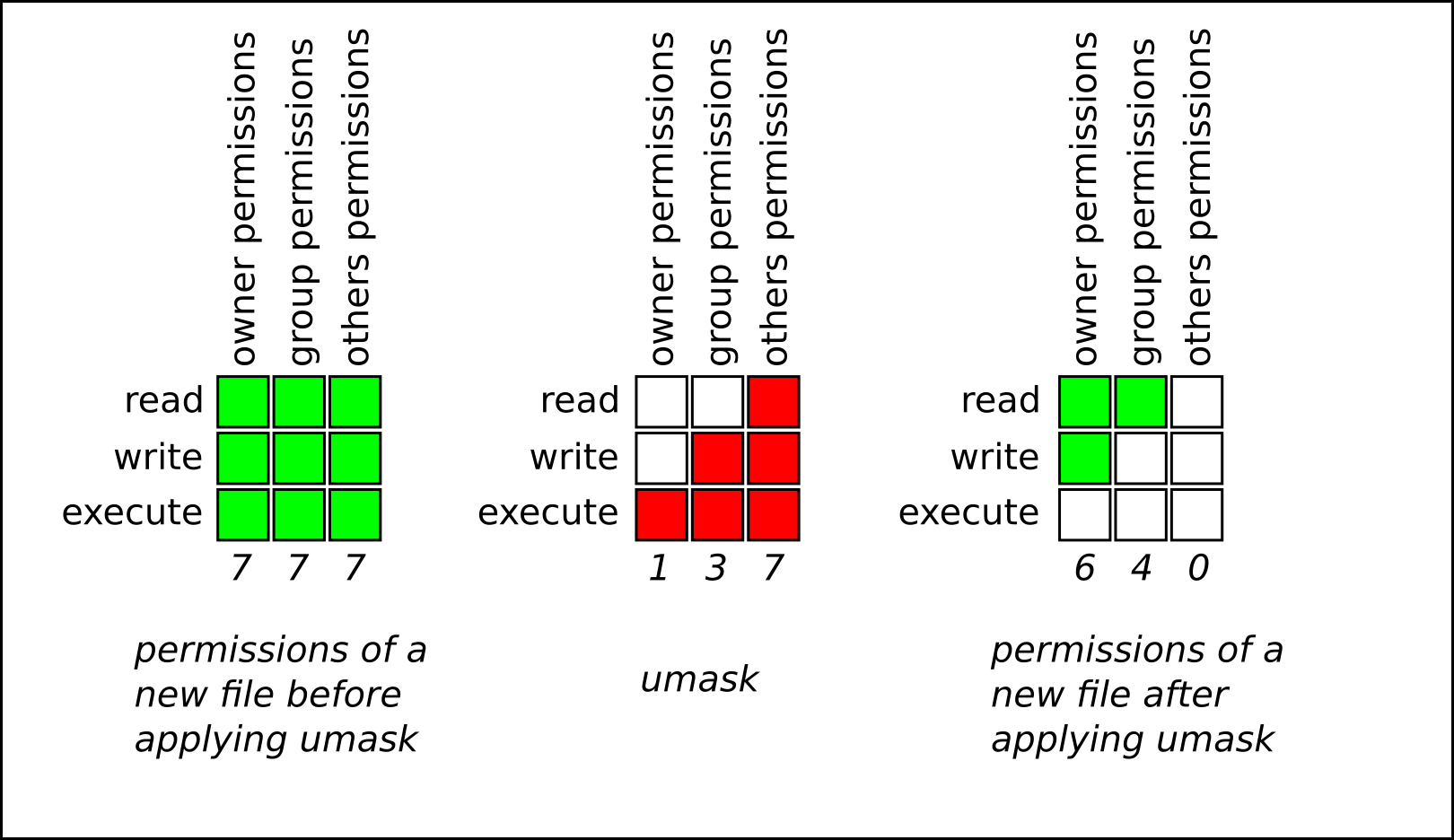
Chapter 5 Managing File Permissions Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 Red Hat Customer Portal
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World
Umask User Mask Or User File Creations Mask In Linux And How To Set Umask Looklinux
Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs9h1s9aymhgxuiwaruv5svj Iw49oju6dx0zyl3syy0y4ft3ya Usqp Cau

Ownership And Permissions

Workbook 4 File Ownerships And Permissions Ppt Video Online Download
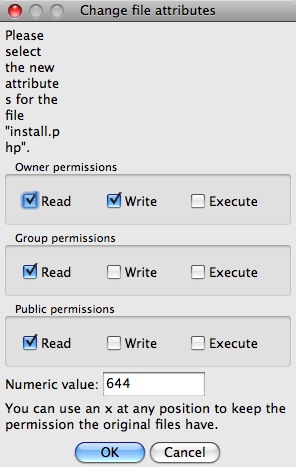
Linux Chmod How To Make A Perl Script Executable Alvinalexander Com

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

System Integrity Using Files Permissions Processes Root And Sudo Teklimbu S Weblog

Linux Chmod Command Clearly Explained Codedodle
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq1nsq3kxri7ryrifobs2rfobawbv4hezfw9 Ldf4feblahyn09 Usqp Cau
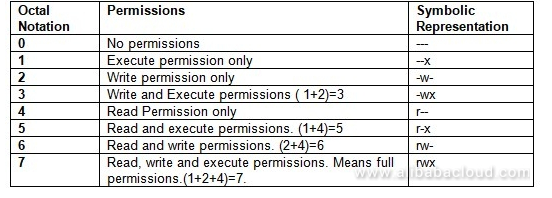
How To Use Linux File Permissions And Ownership On Alibaba Cloud Ecs Dzone Open Source

Linux File Permissions Chmod Umask Tutonics

File Permissions Suid Sgid Sticky Bit Acl Nmcli Ssh And Nmtui Tools For Rhcsa Unixmen

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected

14 Permission And Modification Times

Unix Permissions

Beginner S Guide To File Permission In Linux Sharing Is Caring

Unix Chmod Cheat Sheet Computer Science Programming Learn Javascript Linux Operating System

Linux Permissions Pluralsight
.png)
File Permissions In Linux Unix With Example

Linux Users And Groups Linode

Linux Permissions Guide Plex Support
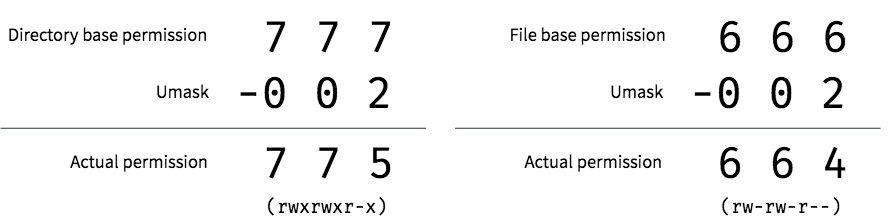
An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

How To Use Chmod Command In Linux Explained With Examples



