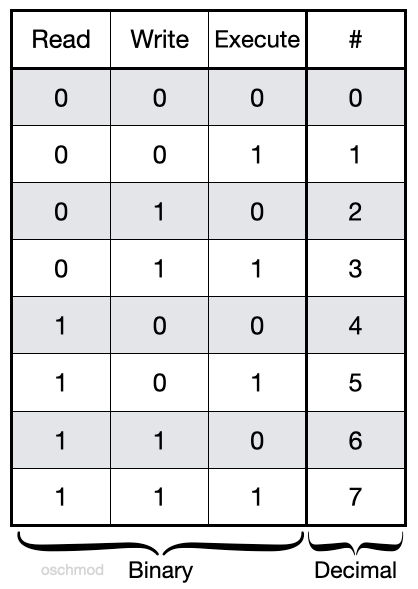
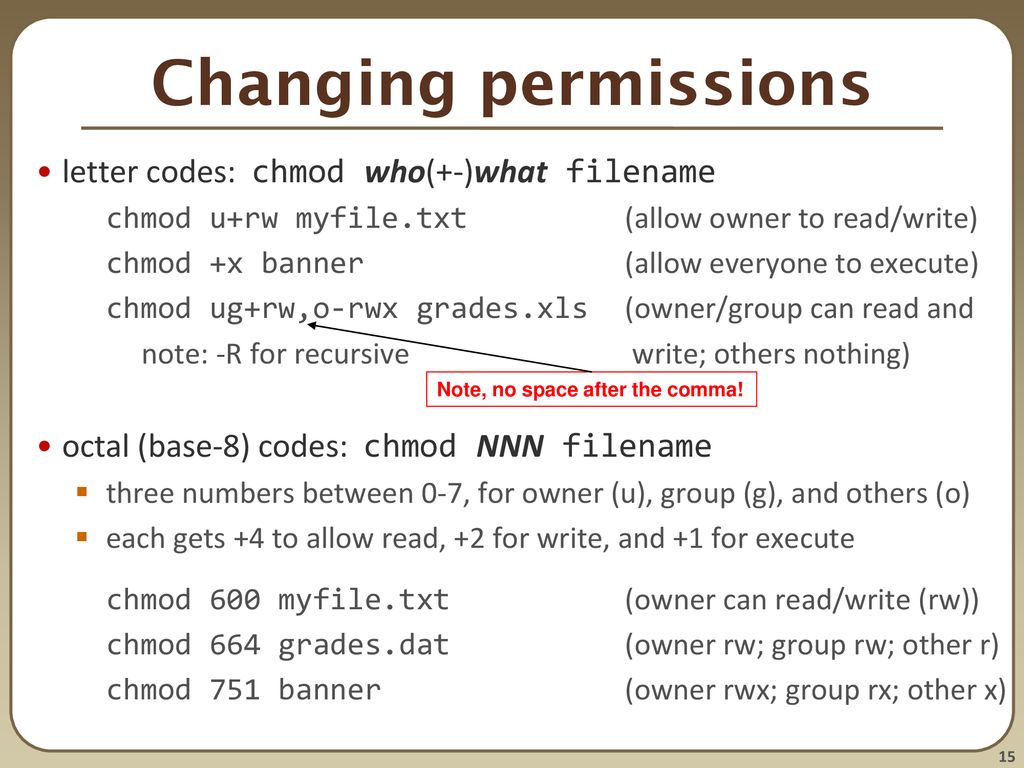
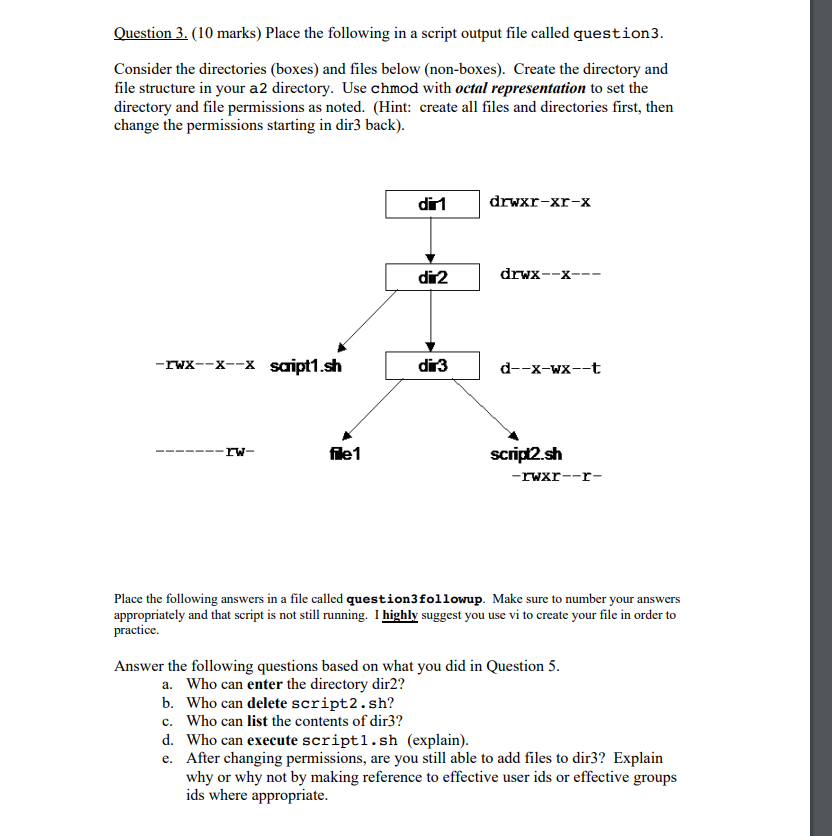
Chmod Octal Codes
The first digit contains the permissions for file owner, 7 is the octal code in which the permissions are set for the owner:.

Chmod octal codes. Chmod Calculator Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in Linux servers. The second digit contains the permissions for group members, 0 is the octal code that is set is to no permissions amongst the members. In this case, ---x--x--x converted to it's Octal or Number value is.
Note – If you use the chmod command to change the file group permissions on a file with ACL entries, both the file group. Absolute Mode Absolute mode lets you use octal notation to set each bit in the permission code. See Table 15–5 for the list of valid octal values.
It is a string, Buffer or URL that denotes the path of the file of which the permission has to be changed. Any omitted digits are assumed to be leading zeros. Obtaining a specified "Octal Value" usually starts with a file's "Symbolic Value", and transmuting it to it's corresponding number value.
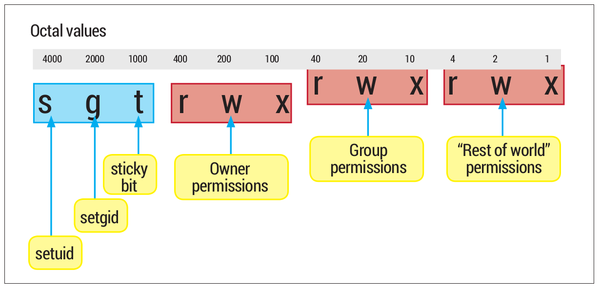
The other, symbolic notation, which uses letters and symbols to define which permissions are set. When the octal is 4 digits long, the first digit is a setuid, setguid or sticky flag. You can use the chmod command to set permissions in either of two modes:.
Select the permissions you require below. The chmod system call cannot change their permissions. We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article.
Even the man page for chmod says this. This code is formed as described under Absolute Mode in the DESCRIPTION section. An absolute form using octal to denote which permissions bits are set e.g:.
The symbolic notation using letters and allocation of data rights through digit-based octal codes. (O)thers can read, can't write and can execute. The command chmod changes the file mode bits of each given file according to mode, which can be either a symbolic representation of changes to make, or an octal number representing the bit pattern for the new mode bits.
The command can accept one or more files and/or directories separated by space as arguments. Chmod ugo+rwx file_name chmod 777 file_name Both of them provides full read write and execute permission (code=7) to all the group. Actually, in this context, specifying 8 is best.
These octal values, can be used to change or manage a file or directory's permissions, using a well known command-line-utility called chmod. Define File Permission in Octal/Numeric Mode. 777) or symbolic notation (e.g.
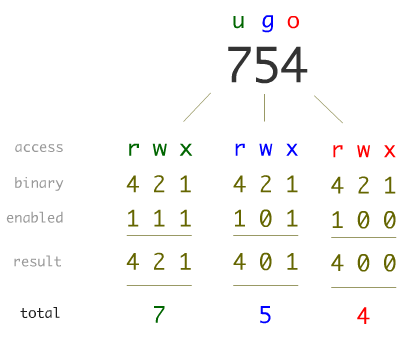
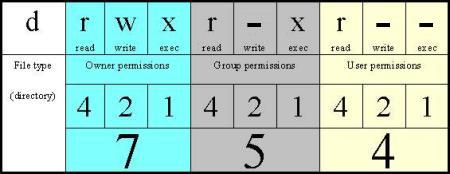
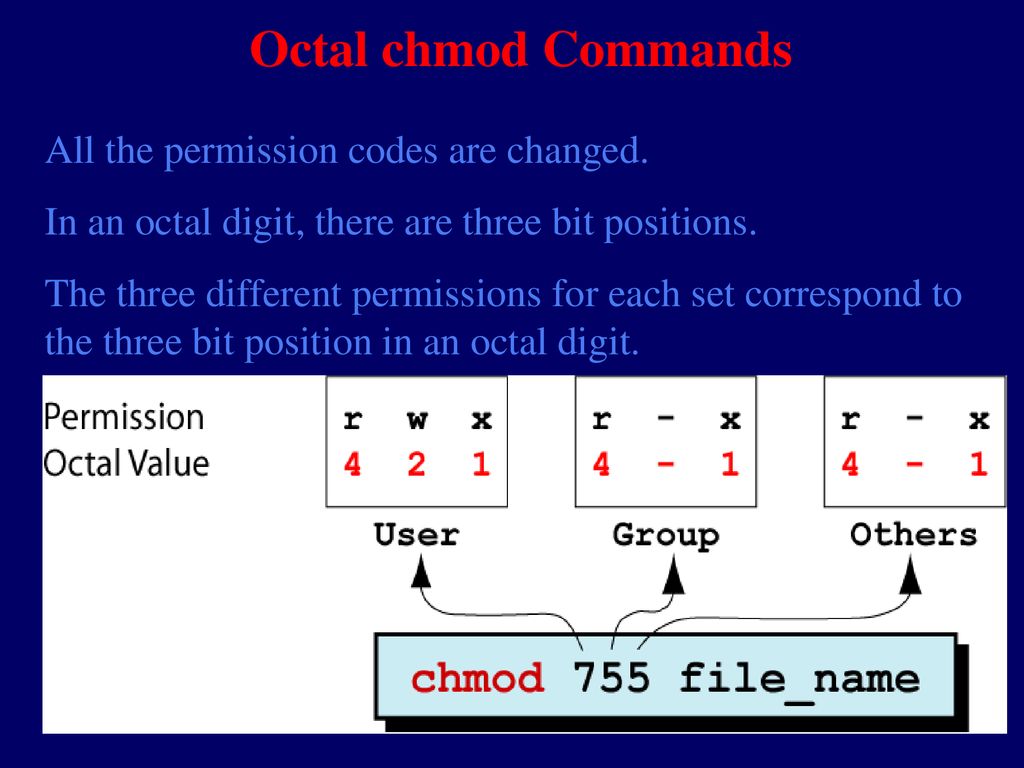
Fs.chmod( path, mode, callback ) Parameters:. Chmod special modes Setuid and setgid. The octal (0-7) value is calculated by adding up the values for each digit User (rwx) = 4+2+1 = 7 Group(rx) = 4+1 = 5 World (rx) = 4+1 = 5 chmode mode = 0755.
As previously mentioned, changes to access rights can only be made by the file owner or root user. You must be superuser or the owner of a file or directory to change its permissions. How do I get octal file permissions on Linux/Unix?.
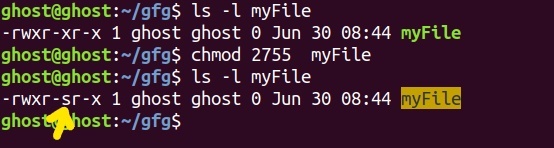
Setuid and setgid (short for 'set user ID upon execution' and 'set group ID upon execution', respectively) are Unix access rights flags that allow users to run an executable with the permissions of the executable's owner or group respectively and to change behaviour in directories. Use --no-preserve-root to override this failsafe. Chmodprovides two types of syntax that can be used for changing permissions.
How to set permissions with chmod in octal mode. Owner (you) Group (a group of other users that you set up) World (anyone else browsing around on the file system) Each digit of this code sets permissions for one of these groups as follows. If you need a more in-depth guide on how to use Chmod In Linux to change file permissions recursively, read our Chmod Recursive guide.
U G W rwx rwx rwx chmod 777 filename rwx rwx r-x chmod 775 filename rwx r-x r-x chmod 755 filename rw- rw- r-- chmod 664 filename rw- r-- r-- chmod 644 filename U = User G = Group W = World r = Read w = write x = execute - = no. In general, the system for Unix data rights relies on user classes and individual access rights. Who Specifies whether permissions are being defined for a user,.
The first digit selects the set user ID (4) and set group ID (2) and restricted deletion or sticky (1) attributes. So, the following work the same. Because the PDP-11 used octal notation, the original permission codes for Unix, which first appeared on the PDP-11, also used octal.
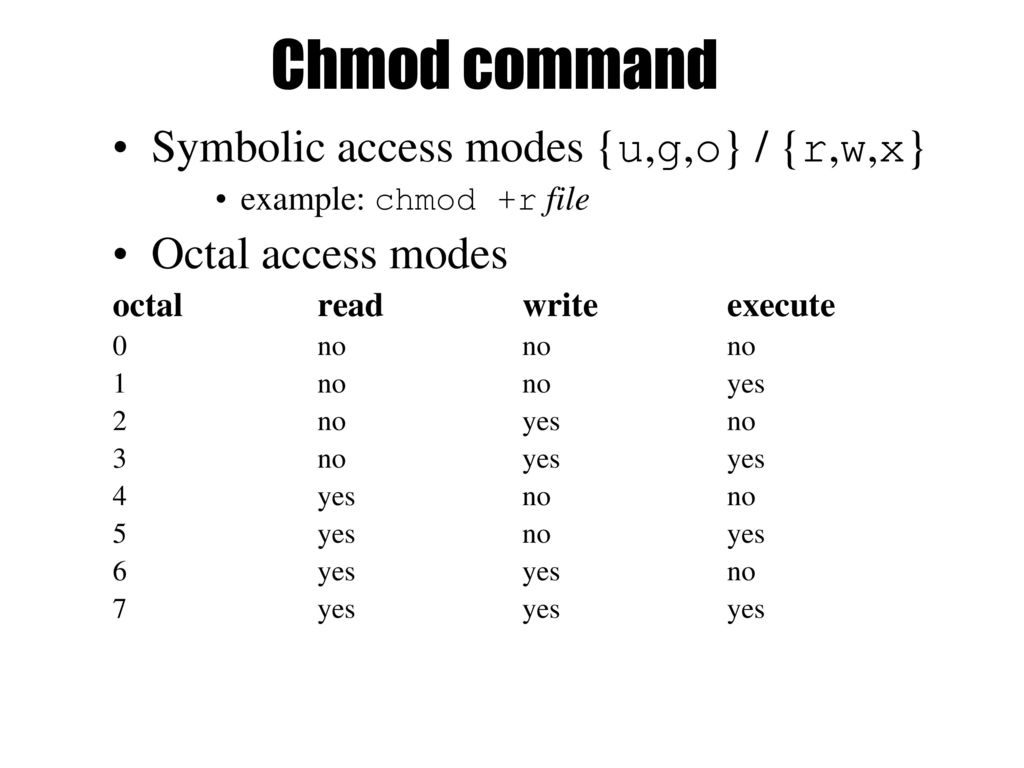
A numeric mode is from one to four octal digits (0-7), derived by adding up the bits with values 4, 2, and 1. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file. $ chmod u+x filename 2.
The octal values have the following meaning:. My most recent contribution (not yet approved) has been to add --exclude-filed and --exclude-directories to chown, chmod, chgrp to make setting filesystem permissions recursively much simpler, needing to depend less on find and +X. Chmod -R o-r *.page Numerical Shorthand.
The leftmost digit represents the permissions for the owner. Each digit octal notiation can be used of either of the group ‘u’,’g’,’o’. For octal conversion, use strtol () (or, as Chris Jester-Young points out, strtoul () - though the valid sizes of file permission modes for Unix all fit within 16 bits, and so will never produce a negative long anyway) with either 0 or 8 as the base.
I have created a directory /tmp/marketing on which I will apply linux sticky bit special permission # mkdir /tmp/marketing. The permission_code is constructed by combining (logical OR) the following values:. I’ll also explain some the popular terms like chmod 777 or chmod 755 or chmod -r.
Chmod 775 Chmod 775 (chmod a+rwx,o-w) sets permissions so that, (U)ser / owner can read, can write and can execute. You need to use the stat command to view or get octal file permissions for given filename. If you need to list a file's permissions, use the ls command.
One thing I have to remember when using rwx for chmod is that 'o' does not stand for owner. A numeric mode is from one to four octal digits (0 - 7), derived by adding up the bits with values 4, 2, and 1. So that’s how permissions are displayed in Linux using symbols.
It can be applied recursively using the "-R" option. The same permission settings can be defined using the octal format with the command:. Omitted digits are assumed to be leading zeros.
Specifies the file or directory. This tech-recipe describes the more complex octal chmod syntax. This is done with the chmod command.
The three digits of the chmod code set permissions for these groups in this order:. Specifies the octal values that represent the permissions for the file owner, file group, and others, in that order. Chmod 707 myfile chmod – is the command to change permissions 7:.
The chmod command can be used with either a text-based argument or 3 octal digits (see note 1) to change the permissions on a file. Remove permission from a file/directory. It's easy to do.
Chmod(1) NAME chmod - Changes permission codes SYNOPSIS. Sets user ID on execution. The chmod command enables you to change the permissions on a file.
So if you take the octal digit that expresses the permissions in each category, and you line them up in order, you get a three-digit octal number. Absolute_mode Octal permission_code for setting the file permissions. The chmod numerical format accepts up to four octal digits.
Unix or any *nix uses octal for permissions – it’s pretty simple once you get the chart into your brain 😉. Any omitted digits are assumed to be leading zeros. For example, to add execute permissions for the owner of a file you would run:.
It is string or octal integer constant that denotes the permission to be granted. The permission in octal form is useful for many commands such as chmod command and other sysadmin tasks. This method accepts three parameters as mentioned above and described below:.
Another way to use chmod is to provide the permissions you wish to give to the owner, group, and others as a three-digit number. In this article, I’ll share with you some of the practical examples of chmod command. The mode parameter consists of three octal number components specifying access restrictions for the owner, the user group in which the owner is in, and to everybody else in this order.
Now if we use chmod, it does not allow to modify root permission # chmod -c --recursive 755 / chmod:. The first digit selects the set user ID (4) and set group ID (2) and sticky (1) attributes. Absolute Mode - Use numbers to represent file permissions (the method most commonly used to set permissions).
$ chmod u+r,g+x filename 3. Rwxrwxrwx) to see its value in other formats. Using chmod command will.
The chmod command changes the access permissions of files and folders. One component can be computed by adding up the needed permissions for that target user base. The chmod command, like other commands, can be executed from the command line or through a script file.
Read, write, execute 0:. The logical OR operator. The second way to represent the same permissions is by using octal numbers.
The third digit contains the. Or, to add read and write permissions for the group that owns the file, you would run:. (G)roup can read, can write and can execute.
Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (e.g. The optional leading digit, when 4 digits are given, specifies the special setuid, setgid, and sticky flags. Rwxrwxrwx) to see its value in other formats.
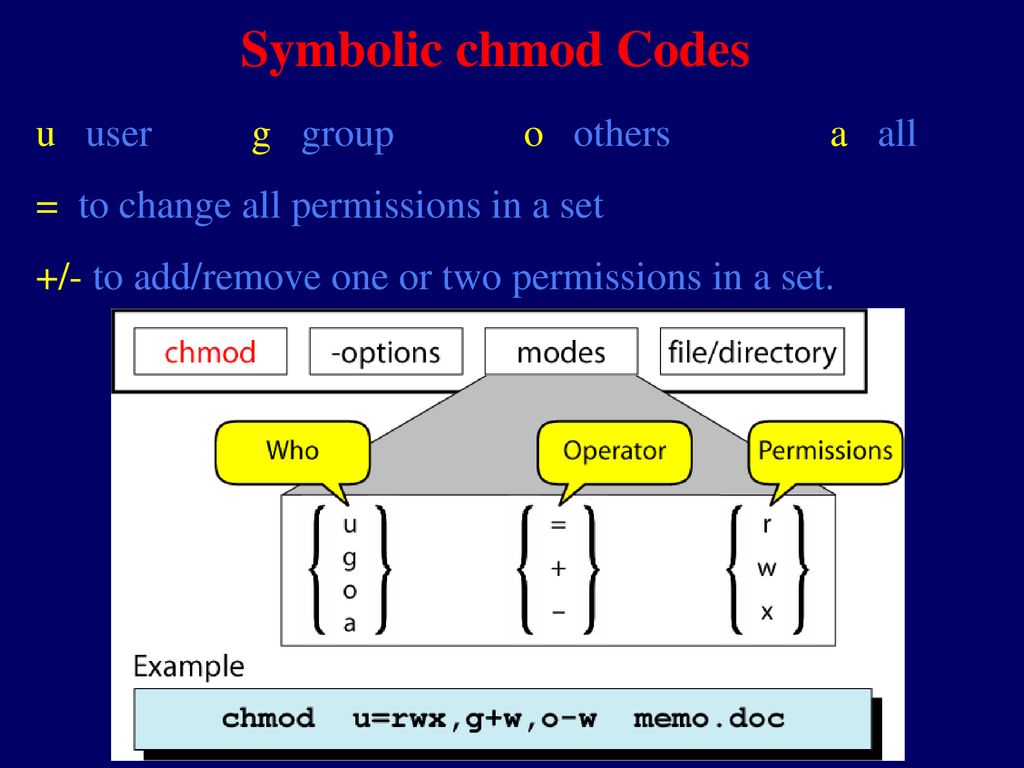
Using the octal notations table instead of ‘r’, ‘w’ and ‘x’. It may be used to add or remove permissions symbolically. Chmod¶ The chmod ("change mode") command is used to change the permission flags on existing files.
See the tech-recipe Set UNIX file access permissions with chmod for the basics of file permissions and chmod. It stands for other. The three rightmost digits define permissions for the file user, the group, and others.
Change permission for all roles on a file/directory. The chmod command sets the permissions to the permission_code you provide. Each digit of the three rightmost digits represents a binary value, which controls the "read", "write" and "execute" permissions respectively.
Chmod Calculator is a free utility to calculate the numeric (octal) or symbolic value for a set of file or folder permissions in unix or unix-like systems such as linux or ubuntu. U = user g = group o = other (not user or group) a = all + = add permissions - = remove permissions r = read w = write x = execute t = sticky bit so to add read permissiones for people in the files group I would do chmod g+r file. A numeric mode is from one to four octal digits (0-7), derived by adding up the bits with values 4, 2, and 1.
The tool will provide you with an octal code that corresponds to these permissions which can then be applied to relevant directories and files with chmod. It can be invoked with either octal values representing the permission flags, or with symbolic representations of the flags. By default the ls command will not display the permissions on a file in octal form.
Set sticky bit using Octal method (1) Below are some examples to apply linux sticky bit using the Octal method with chmod in Linux and Unix. The chmod command uses a three-digit code as an argument. When we use the chmod command later on, you’ll see that you can change the permissions using either symbols or octal numbers.
How to use Check the desired boxes or directly enter a valid numeric value (e.g. Examples chmod 400 file - Read by owner chmod 040 file - Read by group chmod 004 file - Read by world chmod 0 file - Write by owner chmod 0 file - Write by group chmod 002 file. And there you have it:.
Chmod - Unix, Linux Command - chmod - To change access permissions, change mode. I am aware, but I like using octal numbers, maybe because I'm a computer nerd plus it's shorter to write. $ chmod u-rx filename 4.
To apply sticky bit with 755 permission # chmod 1 755 marketing/. You can use this table to understand the different symbolic or octal value to use with chmod. I've often made that mistake.
777) or symbolic notation (e.g. This legacy persists in Linux, where the chmod command still uses octal to specify each of the three bit 'rwx' fields. Add multiple permission to a file/directory.
I am assuming you don't want the binary codes, though I quite like them, so here are the text codes:. There are no relative assignments of permissions using octal. The chmod command is used to alter the permissions of a file.
Use comma to separate the multiple permission sets as shown below. The above functions do NOT deal with four digit chmod octals. Chmod supports two different systems:.
An example of the text-based command to add "read" permission for group members and others to a file named foo is:. Following example removes read and write permission for the user. These are the GNU core utilities (commands such as ls, cp, chmod, chown, etc.) used on operating systems such as Linux, BSD, Mac OSX, etc.
$ chmod u+x file_name. Instead of “u=rwx,go=rx”, you would have “755”. Number 1 means that you grant execute rights, number 2 means that you make the file writeable, number 4 means that you.
Chmod never changes the permissions of symbolic links;.

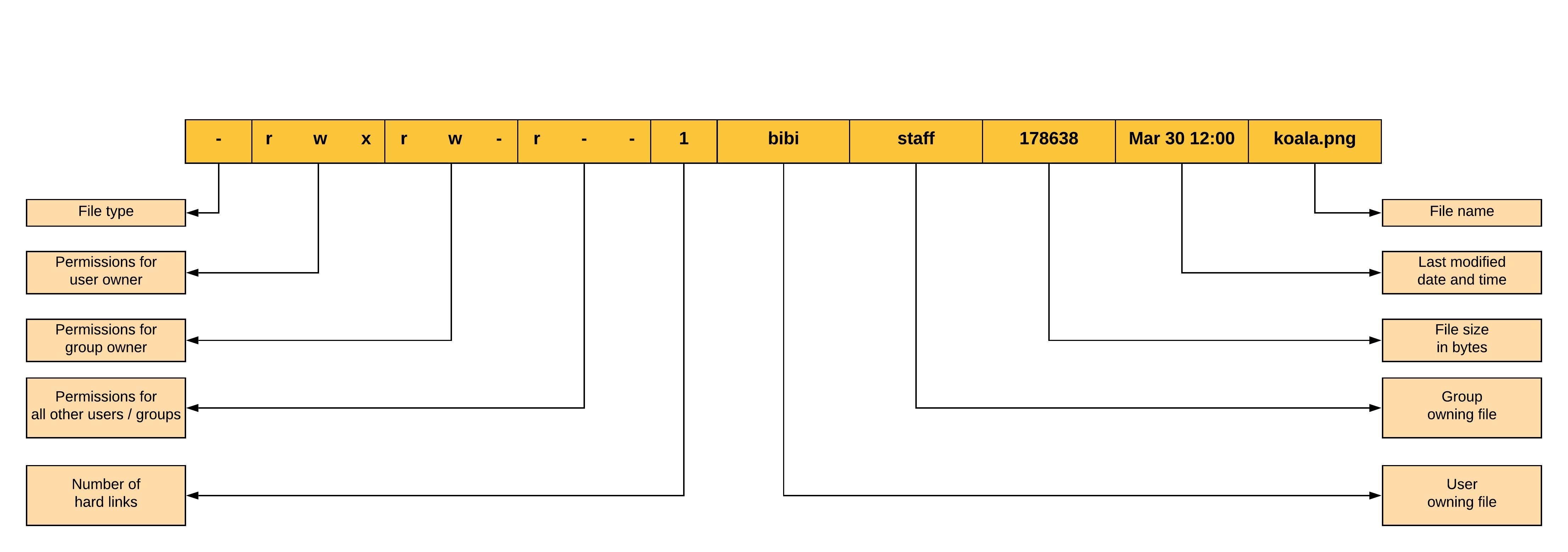
Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
Securing Files On Windows Macos And Linux By Dirk Avery Faun Medium

File Security And Access Control Ppt Download
Chmod Octal Codes のギャラリー
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsqtj7hmhwhqltb Dg3vru7pifk7qn5xlkqq4c3n1r24dp3rp4d Usqp Cau

I Made This Chmod Cheat Sheet And Thought It Might Be Useful Linux4noobs
Chmod Chown Wsl Improvements Windows Command Line

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux
Security And File Permission Ppt Download

Explained How To Use Chmod Command Complete Guide Youtube

Linux Chmod Command Clearly Explained Codedodle

Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command

Advance File Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

I Made This Chmod Cheat Sheet And Thought It Might Be Useful Linux4noobs
2

Solved 6 For Each Of The Following Commands Enumerate T Chegg Com

Quick Answer How To Use Chmod In Linux Os Today

Linux File Permissions Tutorial How To View And Change Permission

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Linux Users And Groups Linode

Linux Chmod Command Clearly Explained Codedodle

Os Mkdir And Os Mkdirall Permission Value Stack Overflow

Solved File Permissions In Unix Command And Python I Hav Chegg Com
Advance File Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Frequently Use Linux Command Line

What Does Chmod 775 Mean Quora
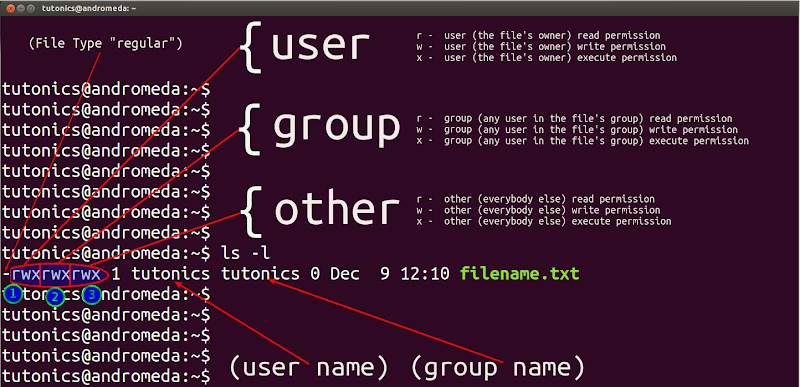
Linux File Permissions Chmod Umask Tutonics
Freechmodcalculator

Chmod Example Why Chmod Calculator Is The Best
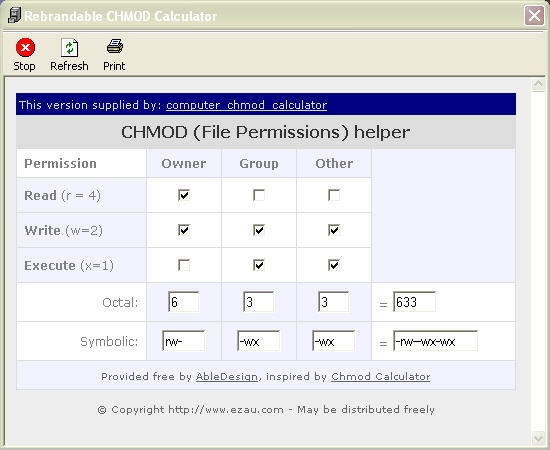
Computer Chmod Calculator Standaloneinstaller Com

Unix Permissions

A Complete Guide To Chmod Recursive Force And More

Solved Part 3 Permissions For Files Follow The Instructi Chegg Com

Chmod Help Examples How To Use Chmod In Linux Ionos

Foundation Topics Exploiting Local Host Vulnerabilities Exploiting Local Host And Physical Security Vulnerabilities Pearson It Certification

19b Permissions

Solved 1 Using The Touch Mkdir Chmod Command Create T Chegg Com

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World
Q Tbn 3aand9gcr2lfpzbutqythmvbwafnxvyggqfj7hnw6fhh Kcozkk8m5 V7o Usqp Cau
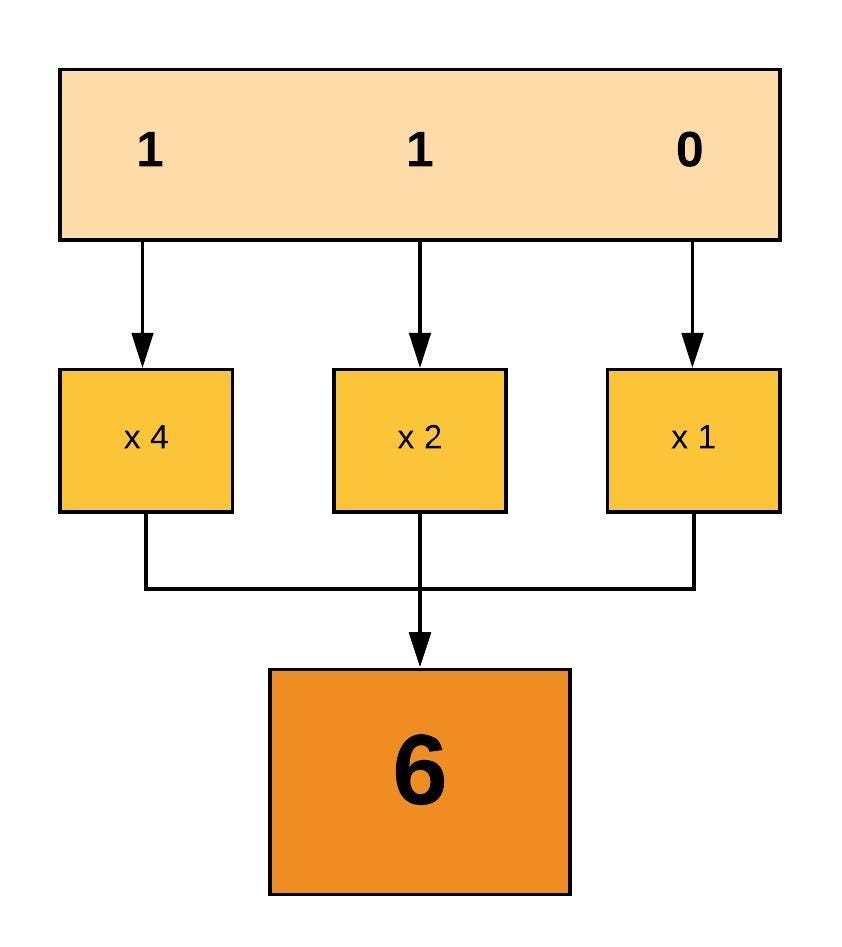
Linux File Permissions And Ownership By Udara Bibile Level Up Coding
Persistent Shell Settings Users Groups Permissions Ppt Download

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

Change File Permissions Easily With Online Chmod Calculator Convert

Is There A Web Based Converter Between Rwx And The Octal Version Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Understanding Unix Permissions And File Types Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Changing File Permissions In Linux The Chmod Command By Saswat Subhajyoti Mallick Medium

Codepen Chmod Numeric To Symbolic Calculator

Rwx2octal C Include Include Int Main Void C Chegg Com
Online Chmod Calculator Free Easy To Use Converter What Is Chmod Calculator Convertforfree Wattpad

Linux Chmod Calculator Chmodcalculator

Online Calculator In Chmod Calculator Scoop It

Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do By Claudio Sabato Medium

Online Chmod Calculator Free Easy To Use Converter What Is Chmod Calculator Convertforfree Wattpad

I Made This Chmod Cheat Sheet And Thought It Might Be Useful Linux4noobs
Linux File Permissions And Ownership By Udara Bibile Level Up Coding

How To Get Octal File Permissions From Command Line In Mac Os Osxdaily

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

Linux Users And Groups Linode

Unit 2 Resource Management In Linux Ppt Download
Nix Question With Incorrect Answer Daily Challenge Beta
Chmod Command In Unix Unix File Permissions Chmod With Examples Chwn Command Chgrp Command Unmask

Basic Linux Commands Ubuntu

Chmod 755 Command What Does It Do Codefather
Chmod 0400 Means

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

Changing File Permissions In Linux The Chmod Command By Saswat Subhajyoti Mallick Medium

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

Linux Commands Chmod Cloudaffaire
9g2kbl3fl68hem

Setting File And Directory Permissions Computational And Information Systems Laboratory
Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Linux File Permissions And Chmod Doug Vitale Tech Blog

Linux Free Course Module 3 Chapter 1 File Management File Attributes Permissions
Why Does Doing Chmod 777 Not Make A File Executable But Chmod 755 Does Isn T 777 Greater Than 755 Quora
Linuxvoice Still Using Octal With Chmod Here S Our Guide To File Permissions And Access Controls T Co Dhfcsds54a T Co Cwwekypyr9

Chmod Command In Linux With Examples Geeksforgeeks

Chmod Wikipedia

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions

Introduction To Unix Family File Permissions Learning Tree Blog

Umask Wikipedia

Change File Permissions Easily With Online Chmod Calculator By Chmodcalcu Issuu
Solved Options For Process A File1 File2 File3 Options Chegg Com

What Is Chmod And Chmod Calculator Convert For Free

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

Is There A Web Based Converter Between Rwx And The Octal Version Unix Linux Stack Exchange
Online Chmod Calculator Free Easy To Use Converter What Is Chmod Calculator Convertforfree Wattpad

Command Line Understanding Chmod Symbolic Notation And Use Of Octal Ask Ubuntu

Chmod Wiki Ask Ubuntu
Linux File Permissions Octal Mode

I Made This Chmod Cheat Sheet And Thought It Might Be Useful Linux4noobs
Q Tbn 3aand9gcsuqrd7yr237u Am8msiqf70j96klzxefjagdqqwjyc32uhwnrw Usqp Cau

Solved 1 2 Which Command Can Create A New File Without Chegg Com
Github Jhuesser Chmod Calculator A Small Chmod Calculator For Windows

How To Get Octal File Permissions On Linux Unix Command Line Nixcraft

104 5 Manage File Permissions And Ownership Lpic1 Exam Guide

Linux File Permissions Octal Mode
Media Management Permissions Error Must Contain A Valid Unix Permissions Octal Issue 3869 Sonarr Sonarr Github

Linux Chmod Command Clearly Explained Codedodle

Pin By Dr Stefan Gruenwald On Cheatsheets Computer Science Programming Learn Javascript Linux Operating System

Solved File Permissions In Linux Can Be Set Using A 3 Dig Chegg Com

File Permission In Linux Chmod Command Armantutorial

Chmod Helper Is A Simple Online Tool For Calculating File Permissions Adafruit Industries Makers Hackers Artists Designers And Engineers
Q Tbn 3aand9gct7wt7gzhduflbfyn8phh8frjezj69hwxbeqqg4p T9 V8epo92 Usqp Cau

Unix Permissions The Easy Way Index Of All Chmod Permutations By Semi Koen Sep Towards Data Science
Security And File Permission Ppt Download



