Chmod 777 File Permissions Example
This adds/appends permissions to a specified user.
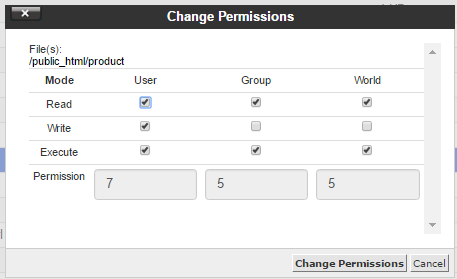
Chmod 777 file permissions example. View (u)ser, (g)roup and (o)thers permissions for chmod 644 (chmod a+rwx,u-x,g-wx,o-wx) or use free online chmod calculator to modify permissions easily. The flag removes the file permissions from a specified user. Make permission for a file same as another file (using reference) If you want to change a file permission same as another file, use the reference option as shown below.
9 Comments Originally posted October 13, 14. Sooner or later in the Linux world, you will have to change the permission on a file or directory. ---means no permissions have been granted at all.
Chmod -R permission directory Therefore, to set the 755 permission for all files in the Example directory, you would type:. Sudo chmod -R 755 Example. For example, if we wanted to add the execute permission to both our Owner and Group permission groups for a file called usergroup then we can use the following.
Chmod -R 755 myfiles. There's no way to set the permissions for files automatically in only this directory that are created after you set the permissions, but you could change your system-wide default file permissions with by setting umask 022. Chmod u=rx file (Give the owner rx permissions, not w) chmod go-rwx file (Deny rwx permission for group, others) chmod g+w file (Give write permission to the group) chmod a+x file1 file2 (Give execute permission to everybody) chmod g+rx,o+x file (OK to combine like this with a comma).
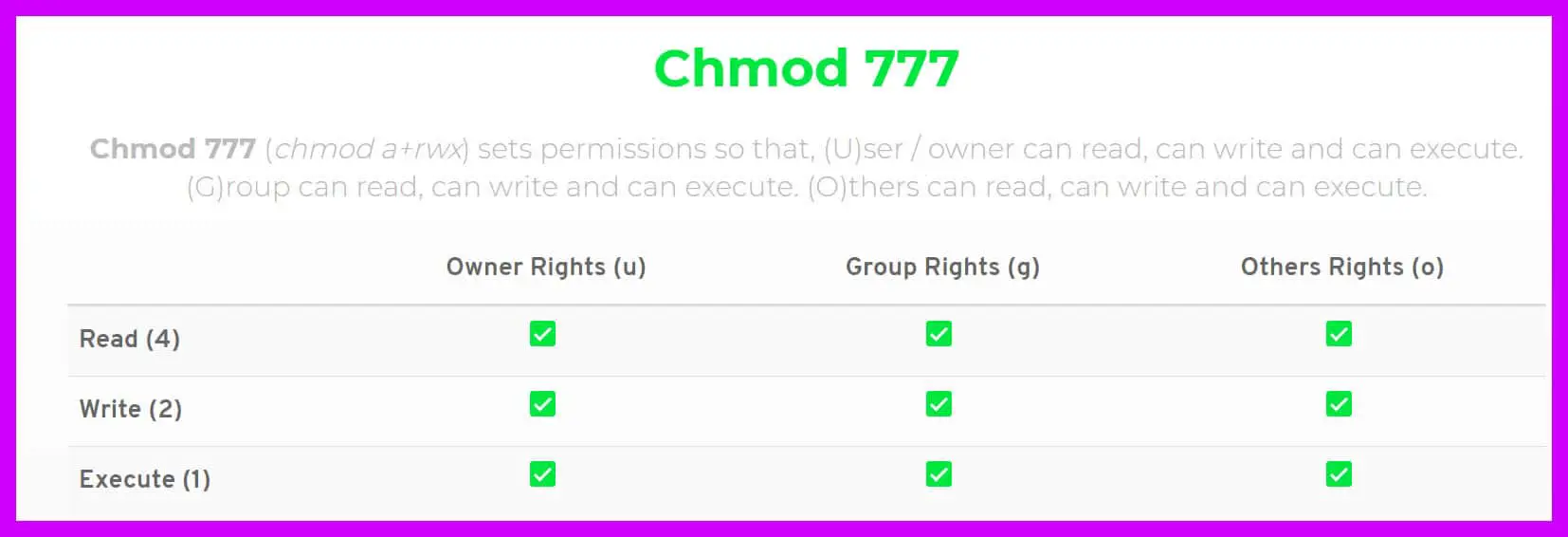
To assign reasonably secure permissions to files and folders/directories, it's common to give files a permission of 644, and directories a 755 permission, since chmod -R assigns to both. Using the command, we can set permissions (read, write, execute) on a file/directory for the owner, group and. If you use chmod 777 that means you assigned all the permissions i.e.
Group members and other users can read and execute, but cannot write. We can also change permissions for file contained in a specific directory with a single command. Chmod can be used only by the file owner or a superuser.
Chmod 755 -R /opt/lampp/htdocs will recursively set the permissions. 3 chmod Examples Give read, write and execute to everybody (user, group, and others) read, write and execute = 4 + 2 + 1 = 7. Chmod a-x file Allow read permission to everyone:.
The file can be opened, and its content viewed. So if you want to recursively change the permission of all the files of example directory to 777 then you need to use chmod -R 777 example command as shown below. The “mode” consists of three parts:.
More of a permission mechanism though. To change the permissions of the file participants so that everybody has full access to it, enter:. Set the permissions for a file or directory by using the chmod command.
Octal Representation Sometimes, you'll see permissions referred to numerically in base 8 octal (i.e. Chmod is a command to change permission of a file. Basically, it allows or disallows modifications of the file.
How to use chmod?. The chmod numerical format accepts up to four octal digits. Or similarly, we can take away write access for the group by calling:.
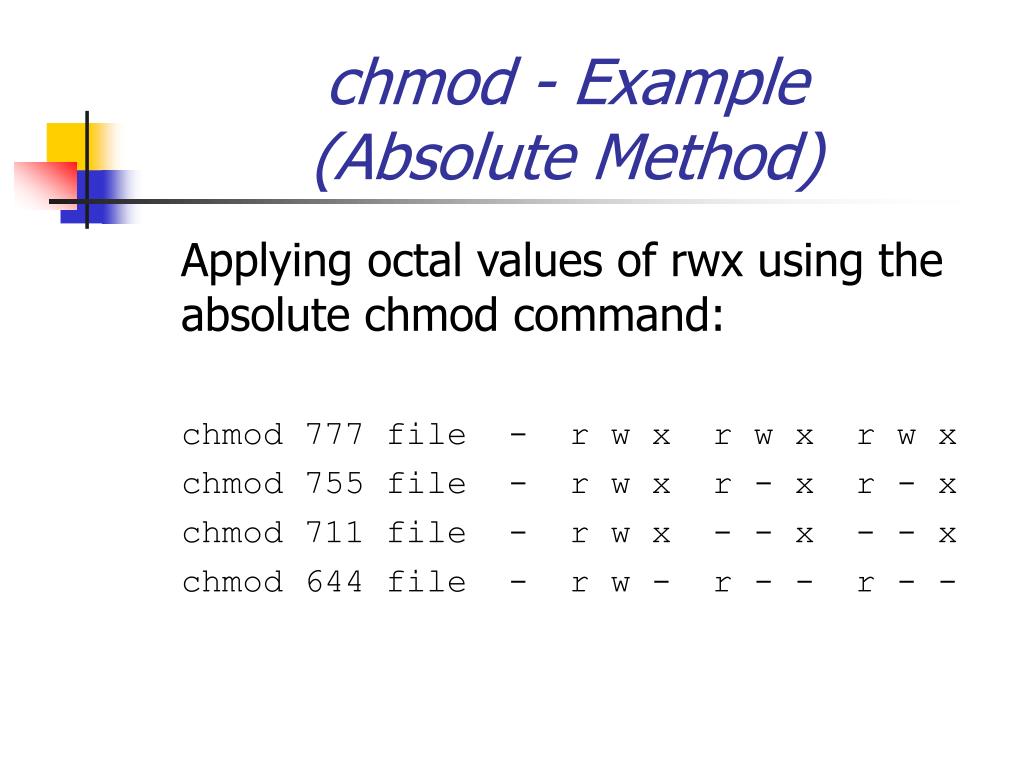
It’s also possible to add permissions incrementally. I.e Three permissions (read, write and execute) available for three types of users (owner, groups and others). Changes the permission of the file to octal value 777, which is the same as.
Here’s a chmod example using for setting permissions so that:. $ chmod --reference=file1 file2 6. Chmod 775 /path/to/file chmod command uses & Explanation.
7 — no permissions. Chmod ug+x usergroup You can see that all we needed to do to add the permissions to two different groups was to combine the letter for each permission group. The three rightmost digits define permissions for the file user, the group, and others.
Chmod options mode filename filename1… chmod options mode directory_name. For example, for read and write permission, it is 4+2 = 6. I want to detail it as the most common way of changing file permissions.
Bash, Shell, Terminal, Command Line cheat sheets linux Ubuntu. This is done with the chmod command. In the terminal, the command to use to change file permission is chmod.
To change permission of only files under a specified directory. It stands for change mode. Chmod 777 access to a file Posted 08-02-17 12:15 PM (9361 views) | In reply to Tal The surest way is to set it after the file has been written, either with the x statement, or the filename pipe method.
In the output of ls -l command, the 9 characters from 2nd to 10th position represents the permissions for the 3 types of users. We can use the 'chmod' command which stands for 'change mode'. Examples Deny execute permission to everyone:.
For example, we can add write permissions for others:. Say you do not want your colleague to see your personal images. Example 4) Assign read permissions to a file $ chmod o=r filename.
Following are some examples:. U – user , g – group, o – others , a – all + to add permission , – to remove permission , = to assign permission r w x is used for read , write,execute , s is used to set the sticky bit;. Rwx means full permissions have been granted.
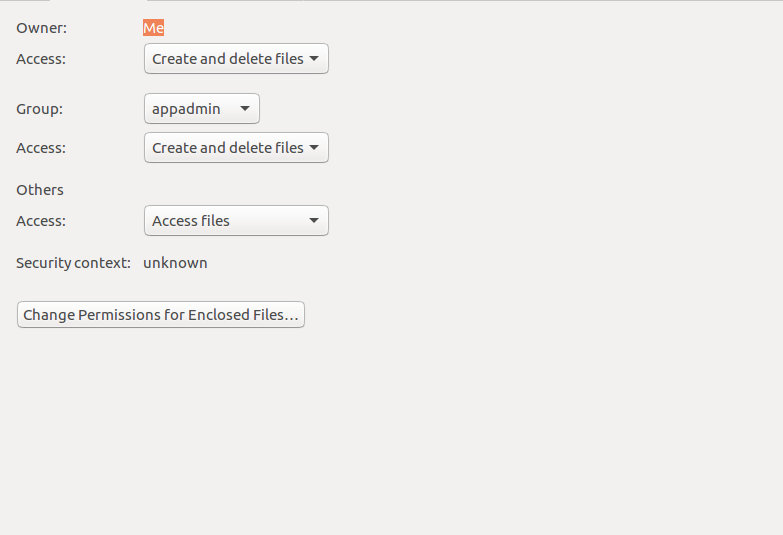
Recursively (-R) Change the permissions of the directory myfiles, and all folders and files it contains, to mode 755:. There will be a Permission tab where you can change the file permissions. Assign execute permission to user and group in file.
Chmod examples using symbolic mode :. You can then execute it like this:. We can copy given file permissions to the specified file.
Who the permissions apply to, how the permissions are set and which permissions to set. Chmod options mode file_name You can change permissions using alphanumeric characters (a+rwx) or with octal numbers (777). The syntax for changing the file permission recursively is:.
In this article, I’ll share with you some of the practical examples of chmod command. This can be achieved by changing file permissions. If the file is a script or a program, it can be run (executed).
In this example, users who are not the owner of the file and who are not members of the Group (and, thus, are in the Others class) have no permission to access the file. File ownership can be changed using the chown command and permissions with the chmod command. The chmod command allows you to change the permissions on a file using either a symbolic or numeric mode or a reference file.
We will use --reference option and the reference file name. This assigns specified users distinct permissions and removes the previous permissions of the user segment. (Modes determine who can read, write, or search a directory or file.) Users with read access to SUPERUSER.FILESYS.CHANGEPERMS (a UNIXPRIV class profile), can use the chmod command to change the permission bits of any file.
Here, the write permission was being assigned to the user group of the owner of the file. In short, “chmod 777” means making the file readable, writable and executable by everyone. Root@localhost ~# chmod -v -R 777 example mode of ‘example’ retained as 0777 (rwxrwxrwx) mode of ‘example/hello.rs’ changed from 0644 (rw-r--r--) to 0777 (rwxrwxrwx) mode of.
You can change file permissions in this format:. Chmod changes the access permissions, or modes, of the specified file or directory. $ chmod -v 777 file.txt mode of 'file.txt' changed from 0664 (rw-rw-r--) to 0777 (rwxrwxrwx) Assign permission with output (This command will give output only if there is any changes) chmod command with argument -c also do’s the same thing as Verbose output (i.e.
The X flag is ignored if the File parameter is specified and none of the execute bits are set in the current mode bits. To have combination of permissions, add required numbers. Symbol are used to assign the permissions :.
If you move your files to a new computer using an external drive, you may find that when you pull the files off the external drive and onto the destination computer, they all have permissions 777.For example, this happened to me when I used an exFAT-formatted external hard drive. We can set these same permissions with the symbolic notation:. Understanding the Linux systems helps make your system secure by restricting access to your files.
How to change file permissions using chmod and chown. In Linux, you can easily change the file permissions by right-clicking the file or folder and select “Properties”. User can read, write, and execute;.
Search permission for directories. I am writing a document that details that users need to change the file permissions of a certain file. Execute permission for files if the current (unmodified) mode bits have at least one of the user, group, or other execute bits set.
Examples chmod 644 file.htm. In this example, file2’s permission will be set exactly same as file1’s permission. The first set three letters after the file type tell what the Owner of the file, have permissions to do.
Owner can read, write and execute;. If we have already set some file permissions we can use this file as a reference point for permission. I’ll also explain some the popular terms like chmod 777 or chmod 755 or chmod -r.
This is thanks to interopability, as any read or write commands to Windows files are routed through your Windows user permissions. Chmod ug+x file ;. Take for example confidential.txt which has the following permissions:-rw-r--r--The same as octal value 644.
There's no way to set the permissions for files automatically in only this directory that are created after you set the permissions, but you could change your system-wide default file permissions with by setting umask 022. The command gives read, write, and execute privileges to the owner (7) and read and execute access to everyone else (55). In this example we remove users execute permission from file ping.txt $ chmod u-x ping.txt Copy Permissions From Other File.
For example, you could set the metadata to display that you have write permissions to a file using chmod 777, but if you tried to access that file you would still not be able to write to it. The file can be edited, modified, and deleted. Chmod a+r file Make a file readable and writable by the group and others:.
Let’s have a look at a few examples:. With the octals knowledge from my previous post it only takes one command to change the permissions on an object. Chmod command used to change the permission of files and directories.
$ chmod 777 file.txt (or) $ chmod ugo+rwx file.txt Give execute privilege to user. If you experience permission issues with your web server, instead of recursively setting the permission to 777, change the file’s ownership to the user running the application and set the file’s permissions to 644 and directory’s permissions to 755. The first 7 sets the permissions for the user, the second 7 sets the permissions for the group, and the third 7 sets the permissions for everybody else.
We can use chmod and chown to manipulate the file permission. Use sudo, the find command, and a pipemill to chmod as in the following examples. For example, if you want to provide read only permission to a file you can set it, there is three permission in Linux read, write and execute and three classes user, group, and others.
Group can read only;. We will explain the modes in more detail later in this article. So for example, using the table above, we can see that the file permissions -rwxrwxrwx can be represented in octal as 777 (because each rwx translates to an octal digit 7).
Chmod 755 -R /opt/lampp/htdocs will recursively set the permissions. Make a shell script executable by the user/owner $ chmod u+x myscript.sh. Changing file/directory permissions with 'chmod' command.
To modify the permissions of each and every file and folder in a provided directory at once, use sudo chmod with -R:. - Set permissions on file.txt as per the example below:. Execute permission for files;.
Group can read, write and execute. Set the permissions of file.htm to "owner can read and write;. Chmod 777 is one of those file control mechanisms.
Others can read only". Chmod is a command used to change those file permissions and controls in terminals. Unix file and directory permission is in the form of a 3×3 structure.
The command can accept one or more files and/or directories separated by space as arguments. The file's permissions becomes the default permission. Each row has 2 examples, one for setting that permission for a file, and one for a directory named ‘dir’.
In assgn1_client.c, has owner’s permission as rw-, which means the owner mik can only read(r) and write(w) the file but cannot execute(x).
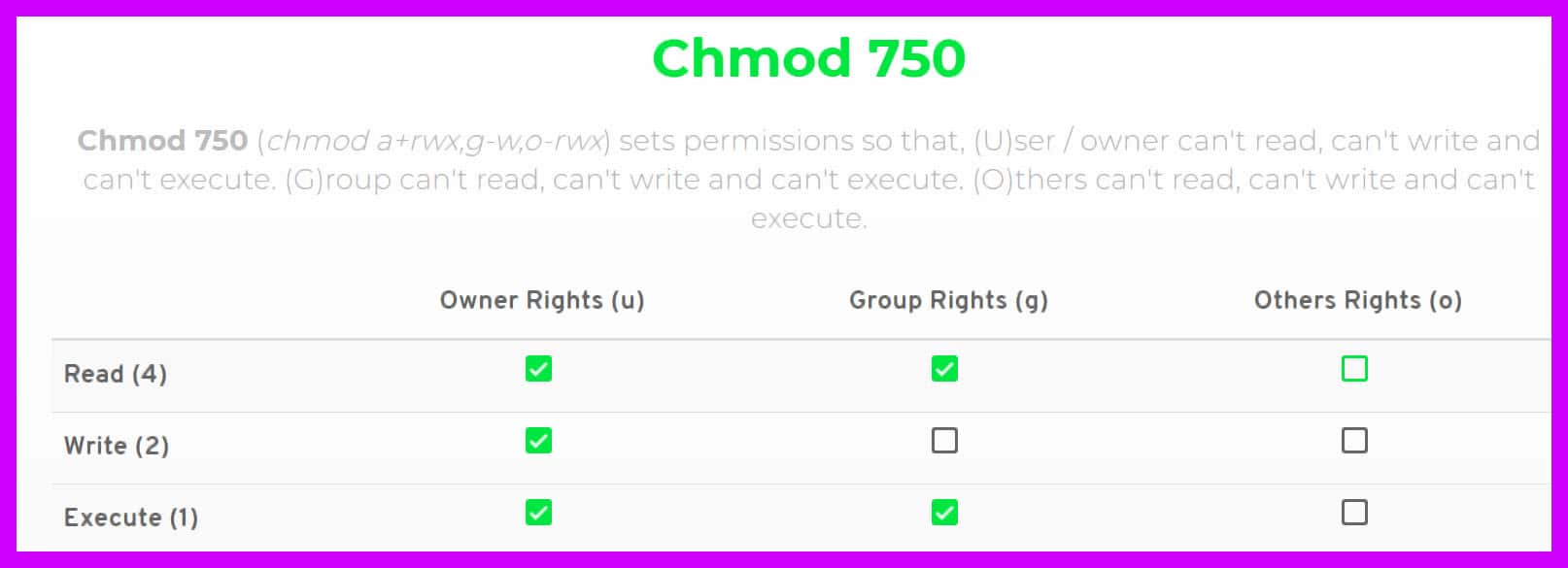
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

Illustrated Why Setting 777 File Permission Is A Bad Idea On Your Linux System Linuxmasterrace

Chmod 777 Codeigniter Configuration Error Stack Overflow
Chmod 777 File Permissions Example のギャラリー
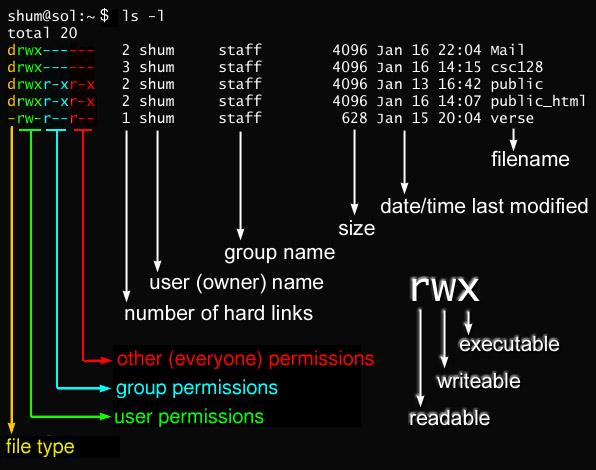
Javarevisited 10 Example Of Chmod Command In Unix Linux

Chmod Calculator Chmod Generator Chmod Command
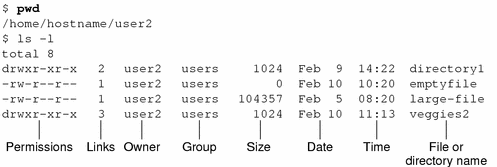
File And Directory Security Solaris Advanced User S Guide

Understanding File Permissions And Using Them To Secure Your Site
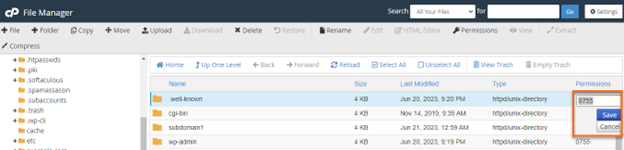
How To Change Permissions Chmod Of A File Hostgator Support

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples
Q Tbn 3aand9gct I9jvgnhaxowmpzpaajfkfizchmnvqt Bi Nz3ljrxwqpkb8l Usqp Cau

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Understanding Unix Permissions And File Types Unix Linux Stack Exchange

Linux File Permissions Complete Guide Devconnected
Q Tbn 3aand9gcq6mtqrr2tbkvj8mt7j61itbsugnnfl3ltc9cdgqfgdswx0kkor Usqp Cau

Posted Withrepost Terminalworld It Is The First Column In The Output Of Ls L Command Which Tells All About The Linux Linux Permissions Software Engineer
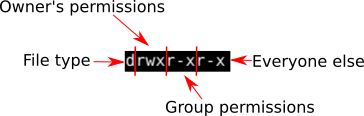
Chmod 777 Or 755 Learn To Use Chmod Command With Examples

Change File And Folder Permission On Ubuntu Chmod Chown Command In Linux Youtube
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command Nixcraft
What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Learning The Shell Lesson 9 Permissions

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro
Chmod 777 What Does This Mean Learn Linux Permissions Easy Way

What Does Chmod 777 Mean Ms Tv Life Com
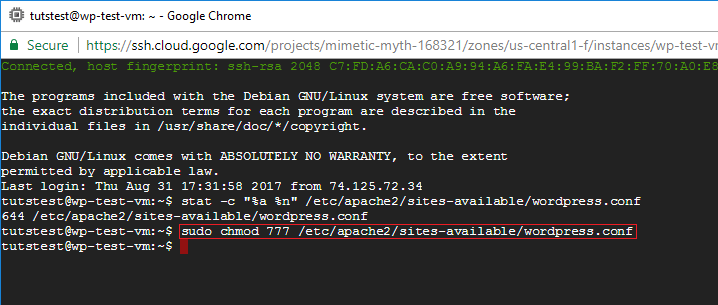
How To Fix Ftp Permission Errors On Google Cloud One Page Zen
Q Tbn 3aand9gcs J72hjomdluhqe6xjivy M6yrjmkqx9x3z3ps Rpnb8by3w7z Usqp Cau

Pin By Dr Stefan Gruenwald On Cheatsheets Computer Science Programming Learn Javascript Linux Operating System

Linux Terminal File Permissions Chmod Chown And Chgrp Youtube
Linux Cheat Sheet

Bif703 File Permissions Ppt Download
Chmod 777 Unix Linux Chmod Command Examples 01 12

Linux Permissions An Introduction To Chmod Enable Sysadmin
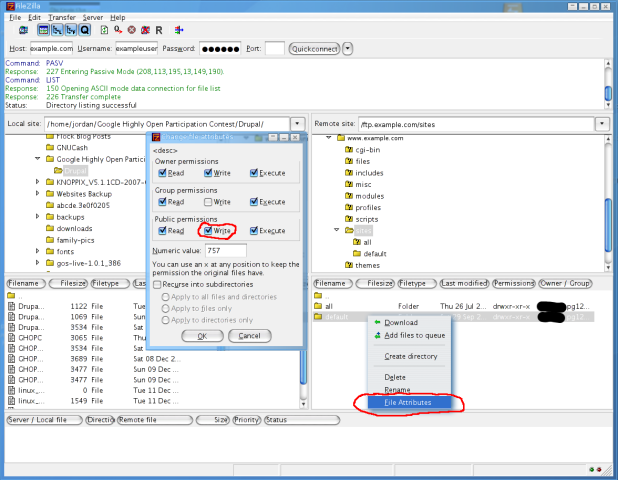
Modifying Linux Unix And Mac File Permissions Drupal Org

Chmod 777 In Terminal The Command To Make All Changes Affect Every File And Folder Ask Ubuntu

Android Uses Chmod To Change The Permissions Of File Read And Write Execution Under Android Project Programmer Sought
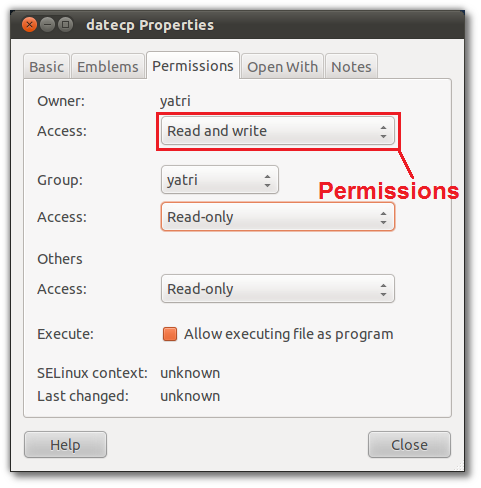
What Is Chmod 777

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks

Linux Chmod Chown Syntax And Chmod Chown Examples

Linux Chmod Example Linux Hint

How To Use Chmod And Chown Command In Linux

How To Change Directory Permissions In Linux Pluralsight
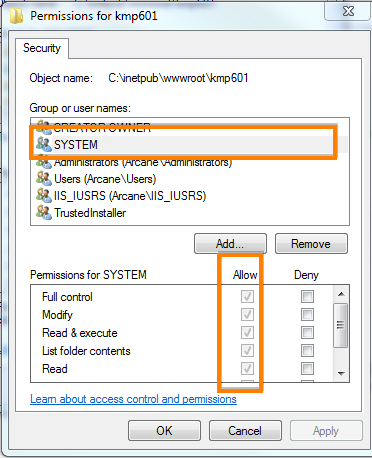
Changing File Permissions During And After Update Web Site Scripts Com
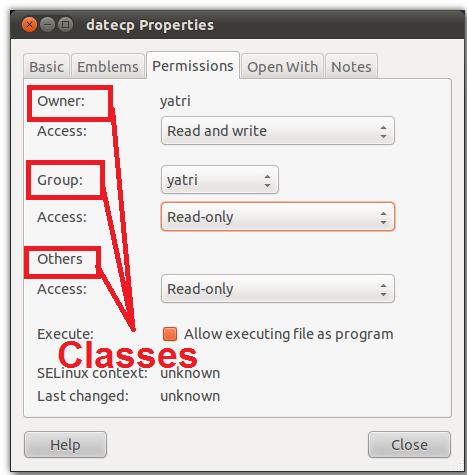
What Is Chmod 777

Chmod 777 Comic Dzone Security

What Does Chmod 777 Mean Linuxize

An Introduction To Linux File Permissions Boolean World

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Linux File Permissions Know The Reason Behind That Chmod 777 By Abhishek Chandra Medium

How To Copy File Permissions And Ownership To Another File In Linux

Linux Chmod 777 Archives Ms Tv Life Com

Changing File Permissions Wordpress Org

Chmod Wikipedia

How To Change Permission Of Cache Directory To 777 Vamtam Help Desk

Recover From Chmod 777 Permission On A Root Filesystem

Solved 11 Which Unix Command Is Used To Change The Permi Chegg Com
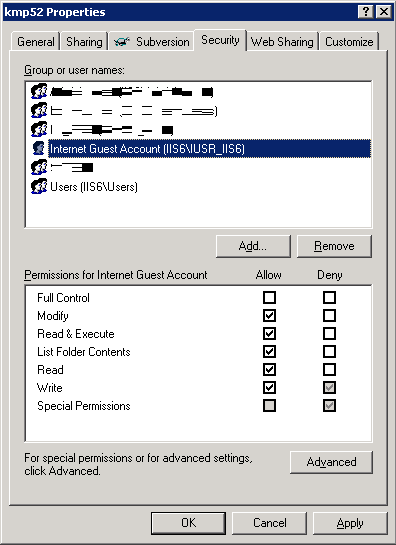
Changing File Permissions During And After Update Web Site Scripts Com

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

How To Give Read Write Permissions To A Folder In Ubuntu Code Example

Ownership And Permissions

Linux Chmod Command Tutorial With Examples To Change Permission Of Files And Folders Poftut

Chmod 777 Tutorial The Electric Toolbox Blog

How To Set A File To This Drwxrwsrwx Permission On Ubuntu Stack Overflow
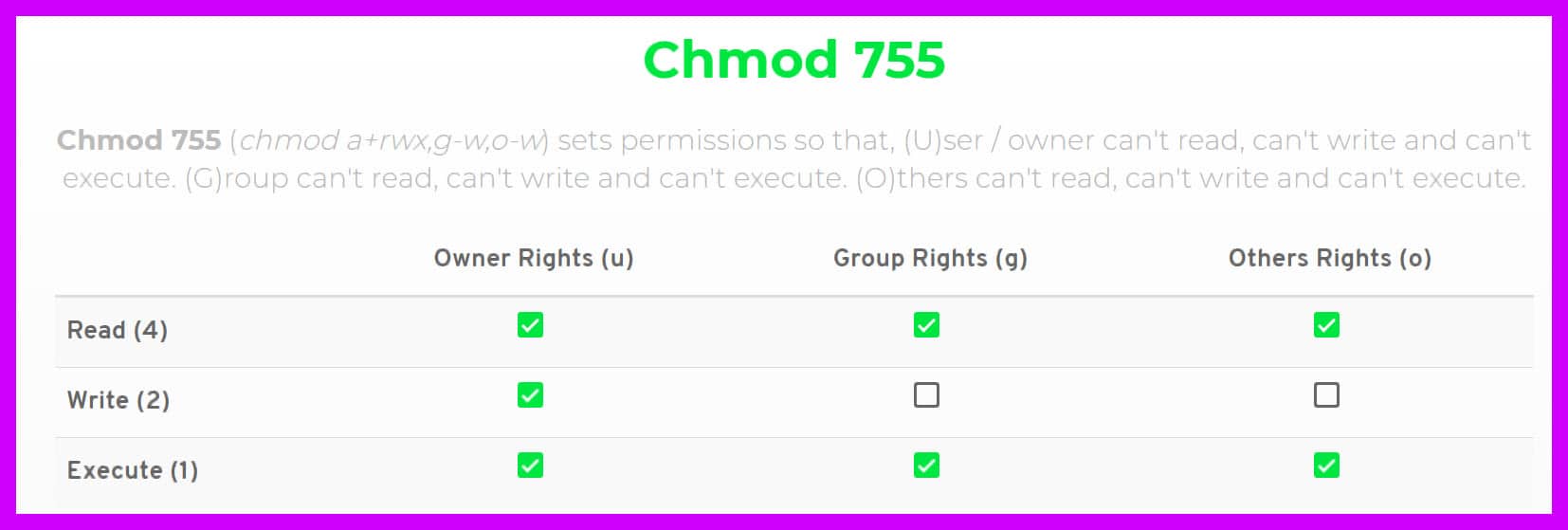
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

What Is Chmod 777

Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

Using Terminal To Set File Permissions Amsys

How To Recursively Change The File S Permissions In Linux Linuxize

How To Set File Permissions In Mac Os X Macinstruct
/GettyImages-1021092796-ea8c63ee76f84bd5bf98c4222337fbb4.jpg)
How To Use The Chmod Command In Linux

Modify File Permissions With Chmod Linode

Course 102 Lecture 14 Users And Permissions

Zencart C Tester For Mt4

How Did The Number 777 In Chmod 777 Come Out Under Linux Laptrinhx

What Did We Do When We Were Chmod 777 Develop Paper

What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

Linux File Permission Javatpoint
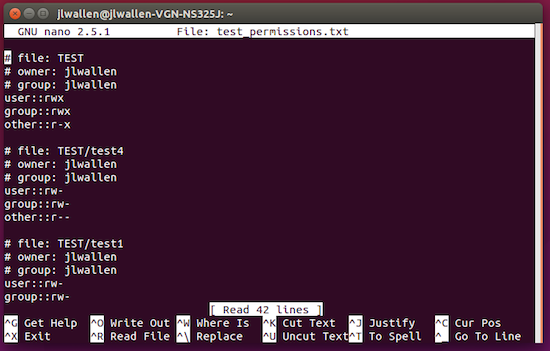
How To Easily Back Up And Restore Linux File Permissions Linux Com

Devrant A Fun Community For Developers To Connect Over Code Tech Life As A Programmer

Chmod 777 Allocating The Least By Amith Jayasekara Medium

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials
Why Would Using Chmod 777 Recursively From The Root Cause A Linux Box To Not Boot I Could Understand This If I Were Limiting Permissions But Why Would Adding Permissions Cause This

Chmod Umask Stat Fileperms And File Permissions

What Is Chmod 777
Linux Chmod Tips

Permissions In Linux Geeksforgeeks
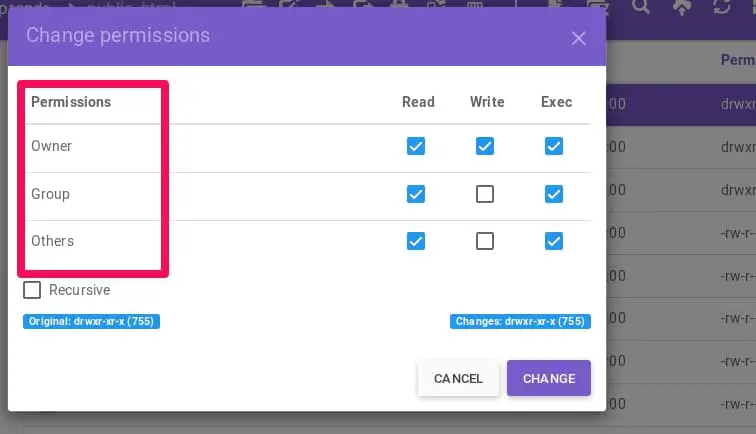
Chmod 777 A Definitive Guide To File Permissions

How To Use The Chmod Command On Linux

Chmod Ftp File Permissions Stadtaus Com

Linux Commands 5 File Permission Chmod Youtube

How To Fix Folder And File Permissions In Wordpress

Chmod Ftp File Permissions Stadtaus Com

Chmod Command In Unix Learn Unix Online Fresh2refresh Com

Chmod 777 What Does It Really Mean Make Tech Easier
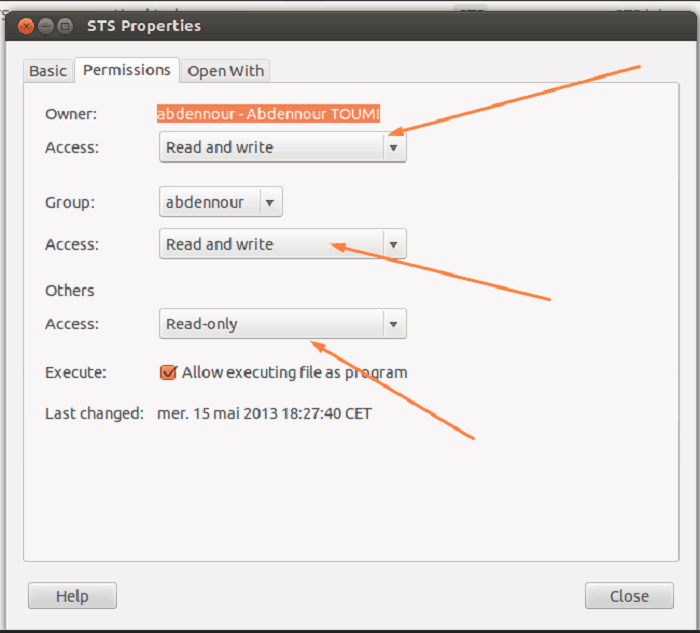
What Is Chmod 777 How To Change File Permissions For Linux Tech Ninja Pro

Chmod Cheatsheet Linux
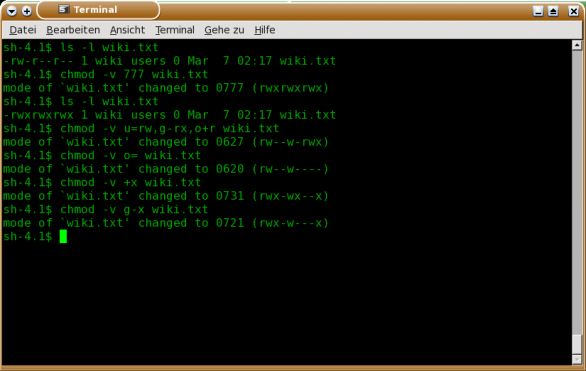
Chmod Shortcuts For Linux
Q Tbn 3aand9gcqylo Axq4l Wudkigbim4eyyuri1sgeprxwkotr9pe74bpl6ic Usqp Cau
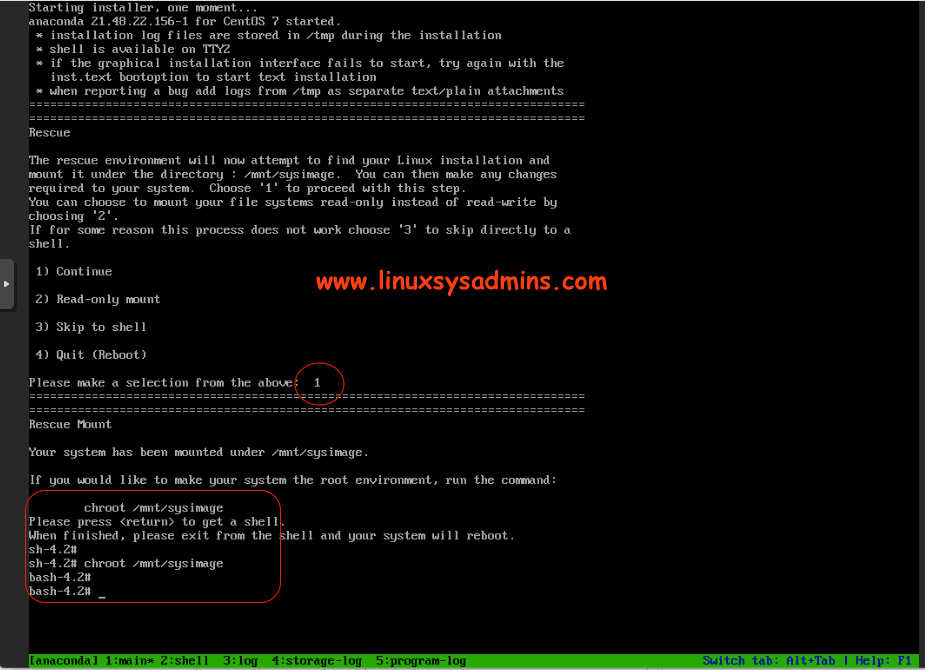
Recover From Chmod 777 Permission On A Root Filesystem

Chmod Ftp File Permissions Stadtaus Com

Chmod 777 755 655 644 And More Permissions Linux Files Tutorials

Understanding File Permissions What Does Chmod 777 Means Linux Technology Theory Report

How Can I Recursively Change The Permissions Of Files And Directories Ask Ubuntu



